- refresh_interval 설정은 얼마나 자주 Lucene flush가 발생하는지에 대해 정의한다. 말인즉, 얼마나 자주 각각의 샤드가 in-memory buffer로 부터 document를 제거하는지 그리고 그것들을 포함하는 segment를 만드는지를 의미한다. search의 관점에서, document가 index operation후에 검색이 불가능한 최대 시간을 의미한다.
정답
PUT my_refresh_test
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 0,
"refresh_interval": "1h"
}
}- 다음의 경로로 들어가보자
cd /var/lib/elasticsearch/nodes/0/indices
ls
# uuid로 나열된 index가 보인다.정답
GET _cat/indices/my_refresh_test?v
# output
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open my_refresh_test FxzYyrITThitG8CdR-Pirg 3 0 0 0 783b 783b- 첫번째 노드에서 uuid확인하여 my_refresh_test index의 경로로 들어가보자
# example
cd FxzYyrITThitG8CdR-Pirg/
ls
# output
2 _state-
위의 output은 shard 2가 해당 노드에 위치해 있다는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
-
kibana console에서 cat command를 사용해서 확인할 수 있다.
GET _cat/shards/my_refresh_test?v&s=node
# response
index shard prirep state docs store ip node
my_refresh_test 2 p STARTED 0 261b 10.142.0.4 itmare-hot01
my_refresh_test 0 p STARTED 0 261b 10.142.0.5 itmare-hot02
my_refresh_test 1 p STARTED 0 261b 10.142.0.6 itmare-hot03정답
PUT my_refresh_test/_settings
{
"number_of_replicas": 1
}cd /var/lib/elasticsearch/nodes/0/indices
ls
- 각 노드별로 shard의 갯수가 늘어난 걸 확인 할 수 있다.
정답
# node, shard 이름 순으로 정렬
GET _cat/shards/my_refresh_test?v&s=node,shardcd 0
ls
_state index translogcd index
ls
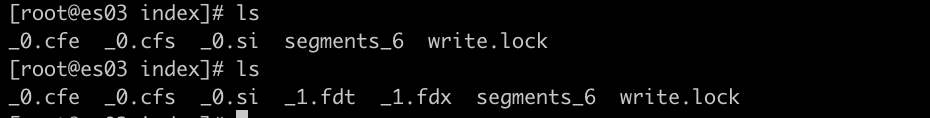
segments_4 write.lock- 해당 shard 경로에서 segment_x와 write.lock 파일을 볼 수 있다.
PUT my_refresh_test/_doc/_bulk
{ "index" : { "_id" : "1"}}
{ "level" : "test"}
{ "index" : { "_id" : "2"}}
{ "level" : "test"}
{ "index" : { "_id" : "8"}}
{ "level" : "test"}
GET my_refresh_test/_search정답
{
"took" : 4,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 3,
"successful" : 3,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 0,
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}- 0개가 리턴된다. (hits.total => 0), 현재 refresh_interval이 1시간으로 설정되어 있다. 그래서 Lucene flush가 발생하고 document가 저장될 segment가 생성 될때까지 최대 1시간이 걸린다.
GET my_refresh_test/_doc/1정답
docuemnt 1은 리턴된다. 기본적으로 GET API는 실시간이다. index의 refresh rate에 영향을 받지 않는다.POST my_refresh_test/_refresh정답
{
"took" : 13,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 3,
"successful" : 3,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 3,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "my_refresh_test",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"level" : "test"
}
},
{
"_index" : "my_refresh_test",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "8",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"level" : "test"
}
},
{
"_index" : "my_refresh_test",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"level" : "test"
}
}
]
}
}- 3개의 hit를 확인할 수 있다.
_refresh는 in-memory buffer를 비우기 위해, 그리고 새로운 segment를 만들기 위한 lucene flush를 작동시킨다.
PUT my_refresh_test/_doc/_bulk
{ "index" : { "_id" : "3"}}
{ "level" : "test"}
{ "index" : { "_id" : "4"}}
{ "level" : "test"}
{ "index" : { "_id" : "14"}}
{ "level" : "test"}
- shard 경로 확인
_1.fdt와_1.fdx가 추가 되었다.
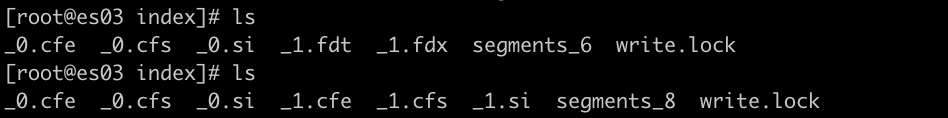
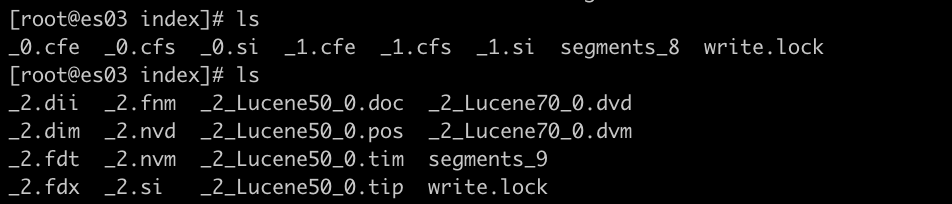
POST my_refresh_test/_refreshPOST my_refresh_test/_forcemerge- 아무런 옵션없는 forcemerge는 Lucene이 상황에 따라서 merge를 결정한다. 현재 2개의 아주 작은 segment를 가지고 있어서 Lucene은 merge하지 않기로 결정한 것으로 보인다.
POST my_refresh_test/_forcemerge?max_num_segments=1_0과_1로 시작하는 파일은 사라지고,_2로 시작하는 많은 파일들이 생긴다.
현재 refresh_interval은 1시간으로 설정되어 있다. 때로는 즉각 refresh 필요한 문서가 있을지도 모른다. 이럴 경우, document를 추가할때 refresh option을 true로 설정하고 document를 추가해보자
PUT my_refresh_test/_doc/5?refresh=true
{
"level":"test"
}
GET my_refresh_test/_search- refresh_interval이 1시간이지만 document가 바로 추가되는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
때로는 사용자가 response를 받고 싶을 수도 있다. refresh의 wait_for option을 사용해서, refresh_interval을 10초로 변경해보고, document를 추가해서 기다림을 확인해보자.
정답
PUT my_refresh_test/_settings
{
"refresh_interval": "10s"
}
PUT my_refresh_test/_doc/6?refresh=wait_for
{
"level":"waiting test"
}DELETE my_refresh_test정답
- data type이 `date`인 `publish_date` field를 제외하고 모든 field의 data type은 `text`이다.- "너의 직업은 무엇인가?"
- 1-10중에 training course rate은?
- 추가 커멘트는?
- 트레이닝을 참가하기 위해 얼마나 멀리서 왔는가?
{
"job_title": "Elasticsearch Engineer",
"course_rating": 9,
"comments": "Great class. I want to get certified now!",
"miles_travelled": "0-25"
}정답
text,keyword: 유저가 원하는 아무것이나 넣을 수 있을 떄. (만약, UI에 고정된 숫자와 함께 drop-down 바가 있다면,keyword가 적절할 것이다.)
정답
text: free-form text는 text
정답
integer_range: 범위처럼 보이는 것은 range
-
- mapping type은 "_doc"
-
- job_title field는 text 와 keyword 로 매핑해라.
-
- miles_travelled field는 integer_range 로 매핑해라.
-
- field name 끝에 _rating 으로 끝나는 field는 integer 로 dynamic하게 매핑해라.
-
- 마지막으로, 아직 매핑되지 않은 string field들은 dynamic하게 keyword 로 매핑해라. (the field is not indexed.)
정답
PUT surveys
{
"mappings": {
"_doc":{ # 1)
"properties":{
"job_title":{ # 2)
"type":"text",
"fields":{
"keyword":{
"type":"keyword"
}
}
},
"miles_travelled":{ # 3)
"type":"integer_range"
}
},
"dynamic_templates":[
{
"rating_fields":{ # 4)
"match": "*_rating",
"mapping":{
"type":"integer"
}
}
},
{
"undefined_string_fields":{ # 5)
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping":{
"type":"keyword",
"index":false
}
}
}
]
}
}
}{
"job_title": "Elasticsearch Engineer",
"course_rating": 9,
"comments": "Great class. I want to get certified now!",
"miles_travelled": "0-25"
}정답
PUT surveys/_doc/1
{
"job_title": "Elasticsearch Engineer",
"course_rating":9,
"comments": "Great class. I want to get certified now!",
"miles_travelled":{
"gte":0,
"lte": 25
}
}PUT surveys/_doc/2
{
"job_title": "Software Engineer",
"labs_rating": 10,
"city": "Berlin",
"miles_travelled": {
"gt": 50,
"lte": 100
}
}정답
- "labs_rating"은 integer로 매핑
- "city"는 "index" set -> false와 함께 keyword로 매핑
- "miles_travelled"는 integer_range로 매핑
GET surveys/_mapping정답
GET surveys/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"filter": {
"range": {
"miles_travelled": {
"gte": 30,
"lte": 60
}
}
}
}
}
}surveys2 라는 이름으로 새로운 index를 만들어보자. surveys2 index는 다음 4가지의 field만 mapping한다. (copy_to 와 default값을 null로 정의하는 것에 대한 리뷰)
-
- field명이 "all_feedback", type이 "text"
-
- field명이 "instructor_feedback", "all_feedback" field로 부터 copy된 "text" type
-
- field명이 "labs_feedback", "all_feedback" field로 부터 copy된 "text" type
-
- field명이 "course_rating", null값이 1이고 coercion이 disabled인 "integer" type
-
- 추가적으로, mapping이 upexpected field로써 변하지 않고, unexpected field와 함께하는 document는 indexing이 실패할 것이다.
정답
PUT surveys2
{
"mappings": {
"_doc":{
"dynamic": "strict", # 5)
"properties":{
"all_feedback":{ # 1)
"type": "text"
},
"instructor_feedback":{ # 2)
"type": "text",
"copy_to": "all_feedback"
},
"labs_feedback":{ # 3)
"type": "text",
"copy_to": "all_feedback"
},
"course_rating":{ # 4)
"type": "integer",
"null_value":1,
"coerce": false
}
}
}
}
}- corece: false 지정일 경우 숫자가 아니면 오류, true일 경우 문자열은 숫자로 변환, 정수필드에 실수가 들어오면 정수로 변환, 참고
정답
GET surveys2/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"all_feedback": "great"
}
}
}정답
GET surveys2/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"course_rating": {
"gte": 1
}
}
}
}
}
}# 1.
PUT surveys2/_doc/2
{
"course_rating": null
}
# 2.
PUT surveys2/_doc/3
{
"course_rating": "8"
}
# 3.
PUT surveys2/_doc/4
{
"food_rating": 10
}정답
- course_rating field 값 null 과 함께 id가 2인 document가 추가된다.
- course_rating field 값 "8" 은 integer로 coerce될 수 없다. (coerce는 false로 설정되어 있다.)
- surveys2 index의 "dynamic" setting은 "strict"으로 되어 있으므로, food_rating field는 추가 될 수 없다. 참고
- doc_values: Sorting, aggregations, and access to field values in scripts requires a different data access pattern.
이름이 test 인 새로운 index를 만들기 위해 다음의 PUT command 실행하자. (type이 text인 message field와 type이 keyword이고 doc_values disable인 level field)
정답
GET test/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"match": {
"level": "INFO"
}
}
}
}
}GET test/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"top_levels": {
"terms": {
"field": "level",
"size": 5
}
}
}
}정답
- search 에러: keyword field는 fielddata 를 사용 할 수 없고, 대신 doc_values 를 사용해야 한다. keyword field에서 aggregation은 항상 doc_values 를 사용해야 하지만, 현재 doc_values 는 disable되어있다. 그래서 level field에서 aggregate할 수 없다. 만약 doc_values 를 enable하길 원한다면, 현재 data를 새로운 index로 reindex해야 한다.
GET test/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"top_message_words": {
"terms": {
"field": "message",
"size": 5
}
}
}
}정답
- search 에러: fielddata 는 text field에서 disable되어 있다.
때때로 data를 분석하거나, 디버깅 할때, analyzed field에서 aggregation을 실행이 이루어져야 한다. 하지만 조심해야하는 이유가 이것은 중요한 heap resource를 소비한다. message field를 위해 fielddata 를 enable하고, aggreation을 다시 사용해보자. 이번엔 terms aggregation이 성공할 것이다.
정답
PUT test/_mapping/_doc
{
"properties":{
"message":{
"type": "text",
"fielddata": true
}
}
}
GET test/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"top_message_words": {
"terms": {
"field": "message",
"size": 5
}
}
}
}DELETE testPUT blogs_fixed
{
"mappings": {
"_doc": {
"properties": {
"author": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
"category": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"content": {
"type": "text"
},
"locales": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"publish_date": {
"type": "date"
},
"seo_title": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"url": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
"number_of_views": {
"type": "integer"
},
"reindexBatch": {
"type": "byte"
}
}
}
}
}- "script" 안에, 각 document에 number_of_views field를 추가하고 0으로 설정
- "script" 안에, field name이 reindexBatch 인 index를 추가하고, 1로 설정
정답
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "blogs"
},
"dest":{
"index": "blogs_fixed"
},
"script":{
"source": """
ctx._source.number_of_views= 0;
ctx._source.reindexBatch = 1;
"""
}
}
# 추가된 두개의 field값이 제대로 할당되었는지 확인
GET blogs_fixed/_search- script는 id add_to_number_of_views 와 함께 cluster state에 저장된다.
- script는 new_views parameter에 있는 value를 number_of_views 에 추가 & 증가시킨다.
정답
POST _scripts/add_to_number_of_views
{
"script":{
"lang": "painless",
"source":"""
ctx._source.number_of_views += params.new_views"
"""
}
}
GET blogs_fixed/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"match": {
"url.keyword": "/blog/elasticsearch-storage-the-true-story"
}
}
}
}
}- 1 hit: title이 "The true story behind Elasticsearch storage requirements"인 blog가 리턴된다.
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "2017-05-12",
"lt": "2017-05-13"
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"originalUrl.keyword": "/blog/elasticsearch-storage-the-true-story"
}
}
]
}
}
}- 상위 blog에 5월 12일의 모든 log entry가 hit된다. (41 hits)
_update 와 add_to_number_of_views script를 사용해서, 41을 blog의 number_of_views field에 더하자. blog의 _id 가 필요할 것이다.
정답
POST blogs_fixed/_doc/NXXVW2kBn3Lh_w-wuCGq/_update
{
"script": {
"id":"add_to_number_of_views",
"params": {
"new_views": 41
}
}
}정답
GET blogs_fixed/_doc/NXXVW2kBn3Lh_w-wuCGq- 해당 blog의 _id 를 사용
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "2017-05-13",
"lt": "2017-05-14"
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"originalUrl.keyword": "/blog/elasticsearch-storage-the-true-story"
}
}
]
}
}
}정답
POST blogs_fixed/_doc/NXXVW2kBn3Lh_w-wuCGq/_update
{
"script":{
"id":"add_to_number_of_views",
"params":{
"new_views": 11
}
}
}
# 확인
GET blogs_fixed/_doc/NXXVW2kBn3Lh_w-wuCGq다음 query를 실행해서, seo_title field empty인 것을 찾아보자. 1,220개의 blog post의 seo_title field가 비워져 있을 것이다. (전체 blog의 75% 이상)
GET blogs_fixed/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"match": {
"seo_title.keyword": ""
}
}
}
}
}- pipeline name은 fix_seo_title
- "script" processor 추가, 만약 seo_title 이 emtpy string ""와 같으면, seo_title 을 title field의 값으로 설정
정답
PUT _ingest/pipeline/fix_seo_title
{
"processors": [
{
"script":{
"source": """
if ("".equals(ctx._source.seo_title))
{
ctx.seo_title = ctx.title;
}
ctx.reindexBatch = 2;
"""
}
}
]
}생성한 pipeline은 전체 index에 적용하기 전에 샘플 document로 항상 테스트 해야한다. fix_seo_title pipeline을 다음 두개의 document를 가지고 테스트 해보자.
{
"title": "Where in the World is Elastic? - Elastic{ON}Tour London & Paris",
"seo_title": ""
}
{
"title": "This week in Elasticsearch and Apache Lucene",
"seo_title": "What's new in Elasticsearch and Apache Lucene"
}정답
POST _ingest/pipeline/fix_seo_title/_simulate
{
"docs": [
{
"_source":{
"title": "Where in the World is Elastic? - Elastic{ON}Tour London & Paris",
"seo_title": ""
}
},
{
"_source":{
"title": "This week in Elasticsearch and Apache Lucene",
"seo_title": "What's new in Elasticsearch and Apache Lucene"
}
}
]
}각각의 document를 fix_seo_title pipeline을 통해 보내기 위해, blogs_fixed index에서 _update_by_query 를 실행해 보자. Update by query는 reindexBatch value가 1인 document만 업데이트 해야 한다. (1594 document)
정답
POST blogs_fixed/_update_by_query?pipeline=fix_seo_title
{
"query":{
"match":{
"reindexBatch": 1
}
}
}- 첫 _update_by_query 는 시간이 조금 걸린다.
- _update_by_query API: source의 변경없이 index에 있는 모든 document의 업데이트를 수행한다. Update By Query API
위의 update by query를 한번 더 실행해보자. 모든 document들은 첫 _update_by_query 에 의해 업데이트 되었기 때문에, 이번엔 아주 짧은 시간이 걸리고 0 document의 update를 볼 수 있다.
GET blogs_fixed/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"match": {
"seo_title.keyword": ""
}
}
}
}
}GET blogs_fixed/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"locale_terms": {
"terms": {
"field": "locales",
"size": 10
}
}
}
}총 1495 document의 locales field값이 비워져있는 것을 확인했다. 현재 locales field는 정리가 잘 안되어 있다. locales field를 다음 조건을 바탕으로 pipeline 을 만들어서 수정해보자.
- pipeline의 이름은 fix_locales 로 정의
- 첫번째 processor는 locales field가 empty string임을 확인하는 script processor이다. 이런 경우에, "en-en" 값을 할당해라. empty가 아니라면 그냥 놔두자.
- 위에서 설정한 script processor는 모든 document의 reindexBatch 값을 3으로 설정 해야 한다.
- 두번째 processor는 separator로써 comma(,)를 사용하여 locales field값을 array로 나누는 split processor이다.
정답
PUT _ingest/pipeline/fix_locales
{
"processors": [
{
"script": {
"source": """
if("".equals(ctx.locales))
{
ctx.locales = "en-en";
}
ctx.reindexBatch = 3;
"""
}
},
{
"split": {
"field": "locales",
"separator": ","
}
}
]
}{
"locales": "de-de,fr-fr,ja-jp,ko-kr"
}
{
"locales": ""
}정답
POST _ingest/pipeline/fix_locales/_simulate
{
"docs": [
{
"_source":{
"locales": "de-de,fr-fr,ja-jp,ko-kr"
}
},
{
"_source":{
"locales": ""
}
}
]
}
# result
{
"docs" : [
{
"doc" : {
"_index" : "_index",
"_type" : "_type",
"_id" : "_id",
"_source" : {
"locales" : [
"de-de",
"fr-fr",
"ja-jp",
"ko-kr"
],
"reindexBatch" : 3
},
"_ingest" : {
"timestamp" : "2019-04-03T07:21:43.162Z"
}
}
},
{
"doc" : {
"_index" : "_index",
"_type" : "_type",
"_id" : "_id",
"_source" : {
"locales" : [
"en-en"
],
"reindexBatch" : 3
},
"_ingest" : {
"timestamp" : "2019-04-03T07:21:43.162Z"
}
}
}
]
}정답
POST blogs_fixed/_update_by_query?pipeline=fix_locales
{
"query":{
"match":{
"reindexBatch": 2
}
}
}# query
GET blogs_fixed/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"new_locales": {
"terms": {
"field": "locales",
"size": 10
}
}
}
}
# response
{
"took" : 29,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1595,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"new_locales" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "en-en",
"doc_count" : 1495
},
{
"key" : "ja-jp",
"doc_count" : 67
},
{
"key" : "fr-fr",
"doc_count" : 61
},
{
"key" : "de-de",
"doc_count" : 59
},
{
"key" : "ko-kr",
"doc_count" : 54
},
{
"key" : "zh-chs",
"doc_count" : 10
}
]
}
}
}GET blogs_fixed/_search
{
"size": 100,
"_source": "locales"
}- 저장된 script list 확인하기
GET _cluster/state/metadata?pretty&filter_path=**.stored_scriptslog_server* document는 runtime_ms field를 가지고 있다. script_fields 를 사용해서, runtime_ms 의 값을 second로 리턴하는 query를 작성해보자.
정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"script_fields": {
"response_sec": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": """
doc['runtime_ms'].value /1000.0
"""
}
}
}
}-
- script_fields 를 사용해서, geoip.city_name 값과 geoip.region_name 값이 comma(,)로 분리된 single field를 리턴
-
- geoip.city_name field와 geoip.region_name field 둘다 존재하고, null값이 아닌 document를 리턴
-
- 각 hit의 모든 _source 를 리턴
정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"_source": [], ### 3)
"script_fields": { ### 1)
"city_region": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": """
doc['geoip.city_name.keyword'].value + "," + doc['geoip.region_name.keyword'].value
"""
}
}
},
"query":{ ### 2)
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"exists":{
"field": "geoip.city_name"
}
},
{
"exists":{
"field": "geoip.region_name"
}
}
]
}
}
}GET logs_server*/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "2017-05-12",
"lt": "2017-05-13"
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"originalUrl.keyword": "/blog/elasticsearch-storage-the-true-story"
}
}
]
}
}
}정답
POST _scripts/daily_hits
{
"script":{
"lang": "mustache",
"source": {
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":{
"match":{
"originalUrl.keyword": "{{url}}"
}
},
"filter":{
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "{{start_date}}",
"lt": "{{end_date}}"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}- url: "/blog/brewing-in-beats-postgresql-module-in-filebeat"
- start_date: "2017-08-11"
- end_date: "2017-08-12"
정답
GET logs_server*/_search/template
{
"id": "daily_hits",
"params": {
"url": "/blog/brewing-in-beats-postgresql-module-in-filebeat",
"start_date": "2017-08-11",
"end_date": "2017-08-12"
}
}정답
POST _scripts/daily_hits
{
"script": {
"lang": "mustache",
"source": """
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match": {
"originalUrl.keyword": "{{url}}"
}
},
"filter": {
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "{{start_date}}"
{{#end_date}}
,
"lt": "{{end_date}}"
{{/end_date}}
}
}
}
}
}
}
"""
}
}date_historgram aggregation을 사용해서 월별 visitor의 수를 분석해보자. aggregation 이름은 number_of_visitors_by_month" 로 정하고, 월별 웹사이트의 visitor수를 계산하자.
정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"number_of_visitors_by_month": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "@timestamp",
"interval": "month"
}
}
}
}정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"number_of_visitors_by_month": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "@timestamp",
"interval": "month"
}
},
"max_monthly_visitors":{
"max_bucket": {
"buckets_path": "number_of_visitors_by_month._count"
}
}
}
}각 월마다 top 5 visited URL을 찾는 top_visited_urls nested aggregation을 number_of_visitors_by_month 에 추가하자. (originalUrl.keyword field를 사용)
정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"number_of_visitors_by_month": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "@timestamp",
"interval": "month"
},
"aggs": {
"top_visited_urls": {
"terms": {
"field": "originalUrl.keyword",
"size": 5
}
}
}
},
"max_monthly_visitors":{
"max_bucket": {
"buckets_path": "number_of_visitors_by_month._count"
}
}
}
}number_of_visitors_by_month 에 most_visited_url_of_month pipeline aggregation을 추가하자. most_visited_urL_month pipeline aggregation은 달마다 가장 많은 방문객 수를 계산한다. 위에 term agg에서 이미 해당 값을 return 했지만, pipeline agg에서 max value만을 찾아보자.
정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"number_of_visitors_by_month": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "@timestamp",
"interval": "month"
},
"aggs": {
"top_visited_urls": {
"terms": {
"field": "originalUrl.keyword",
"size": 5
}
},
"most_visited_url_of_month": {
"max_bucket": {
"buckets_path": "top_visited_urls._count"
}
}
}
},
"max_monthly_visitors": {
"max_bucket": {
"buckets_path": "number_of_visitors_by_month._count"
}
}
}
}most_visited_url_of_month most_visited_url_of_month 의 가장 큰 값을 찾는 month_with_most_visited_url_by_month pipe aggregation을 추가해 보자.
정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"number_of_visitors_by_month": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "@timestamp",
"interval": "month"
},
"aggs": {
"top_visited_urls": {
"terms": {
"field": "originalUrl.keyword",
"size": 5
}
},
"most_visited_url_of_month": {
"max_bucket": {
"buckets_path": "top_visited_urls._count"
}
}
}
},
"max_monthly_visitors": {
"max_bucket": {
"buckets_path": "number_of_visitors_by_month._count"
}
},
"month_with_most_visited_url_by_month": {
"max_bucket": {
"buckets_path": "number_of_visitors_by_month>most_visited_url_of_month"
}
}
}
}정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"missing_log_events": {
"missing": {
"field": "originalUrl.keyword"
}
}
}
}정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"top_20_cities": {
"terms": {
"field": "geoip.city_name.keyword",
"size": 20
},
"aggs":{
"top_urls": {
"terms":{
"field": "originalUrl.keyword",
"size": 3
}
}
}
}
}
}top 3 URL의 terms aggregation을 significant_terms aggregation으로 바꾸고, 두개의 query를 비교해 보. (Notice how the URLs have changed to be less generic and more specific topics.)
정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"top_cities": {
"terms": {
"field": "geoip.city_name.keyword",
"size": 20
},
"aggs": {
"top_urls": {
"significant_terms": {
"field": "originalUrl.keyword",
"size": 3
}
}
}
}
}
}- term으로써, geoip.region_name 과 originalUrl 의 combination을 사용해라. script에서 두개의 field는 semi-colon(:)으로 구분된다.
- 100의 term을 리턴해라.
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "2017-08-01",
"lte": "2017-08-07"
}
}
}
}
}
}정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "2017-08-01",
"lte": "2017-08-07"
}
}
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"status_plus_url_terms": {
"terms": {
"script": {
"source": """
doc['geoip.region_name.keyword'].value + ':' + doc['originalUrl.keyword'].value
"""
},
"size": 100
}
}
}
}위의 결과에 region_name 이 null 값인 log event가 많다. 우의 query를 변경해서 region_name 이 null이 아닌 document의 terms agg만을 결과값으로 리턴하도록 수정해보자.
정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "2017-08-01",
"lte": "2017-08-07"
}
}
},
{
"exists":{
"field": "geoip.region_name"
}
}
]
}
},
"aggs": {
"status_plus_url_terms": {
"terms": {
"script": {
"source": """
doc['geoip.region_name.keyword'].value + ':' + doc['originalUrl.keyword'].value
"""
},
"size": 100
}
}
}
}정답
GET logs_server*/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"range": {
"@timestamp": {
"gte": "2017-08-01",
"lte": "2017-08-07"
}
}
},
{
"exists":{
"field": "geoip.region_name"
}
}
]
}
},
"aggs": {
"status_plus_url_terms": {
"terms": {
"script": {
"source": "doc['geoip.region_name.keyword'].value + ':' + doc['originalUrl.keyword'].value"
},
"size": 100,
"order": {
"_key": "asc"
}
},
"aggs": {
"top_hits_of_status_plus_url_terms": {
"top_hits": {
"size": 3
}
}
}
}
}
}- "my_temp", "my_rack" tag names 설정
- "my_cluster" cluster name으로 설정
- minimum_master_nodes 값을 1로 설정
- 각 노드의 network.host 값을 "_site_" 로 설정
| Node | Server | Type | box_type | rack_type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| node1 | server1 | dedicated master-eligible | none | none |
| node2 | server2 | data and ingest | hot | rack1 |
| node3 | server3 | dedicated data | warm | rack1 |
| node4 | server4 | data and ingest | hot | rack2 |
| node5 | server5 | dedicated data | warm | rack2 |
정답
#node1 config
cluster.name: my_cluster
node.name: ${NODENAME}
network.host: _site_
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 1
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["server1","server2","server3"]
xpack.security.enabled: true
node.master: true
node.data: false
node.ingest: false
#node2 config
cluster.name: my_cluster
node.name: ${NODENAME}
network.host: _site_
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["server1","server2","server3"]
xpack.security.enabled: true
node.master: false
node.data: true
node.ingest: true
node.attr.my_temp: hot
node.attr.my_rack: rack1
#node3 config
cluster.name: my_cluster
node.name: ${NODENAME}
network.host: _site_
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["server1","server2","server3"]
xpack.security.enabled: true
node.master: false
node.data: true
node.ingest: false
node.attr.my_temp: warm
node.attr.my_rack: rack1
#node4 config
cluster.name: my_cluster
node.name: ${NODENAME}
network.host: _site_
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["server1","server2","server3"]
xpack.security.enabled: true
node.master: false
node.data: true
node.ingest: true
node.attr.my_temp: hot
node.attr.my_rack: rack2
#node5 config
cluster.name: my_cluster
node.name: ${NODENAME}
network.host: _site_
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["server1","server2","server3"]
xpack.security.enabled: true
node.master: false
node.data: true
node.ingest: false
node.attr.my_temp: warm
node.attr.my_rack: rack2my config settings
# node1
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
path.repo: /shared_folder/my_repo
network.host: _site_
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["es01:9300", "es02:9300", "es03:9300"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 1
network.bind_host: 0.0.0.0
network.publish_host: es01
http.port: 9200
transport.tcp.port: 9300
cluster.name: my_cluster
node.name: node1
node.master: true
node.data: false
node.ingest: false
xpack.security.enabled: false
# node2
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
path.repo: /shared_folder/my_repo
network.host: _site_
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["es01:9300", "es02:9300", "es03:9300"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 1
network.bind_host: 0.0.0.0
network.publish_host: es02
http.port: 9200
transport.tcp.port: 9300
cluster.name: my_cluster
node.name: node2
node.master: false
node.data: true
node.ingest: true
node.attr.box_type: hot
node.attr.rack_type: rack1
xpack.security.enabled: false
# node3
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
path.repo: /shared_folder/my_repo
network.host: _site_
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["es01:9300", "es02:9300", "es03:9300"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 1
network.bind_host: 0.0.0.0
network.publish_host: es03
http.port: 9200
transport.tcp.port: 9300
cluster.name: my_cluster
node.name: node3
node.master: false
node.data: true
node.ingest: false
node.attr.box_type: warm
node.attr.rack_type: rack1
xpack.security.enabled: false
# node4
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
path.repo: /shared_folder/my_repo
network.host: _site_
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["es01:9300", "es02:9300", "es03:9300"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 1
network.bind_host: 0.0.0.0
network.publish_host: es04
http.port: 9200
transport.tcp.port: 9300
cluster.name: my_cluster
node.name: node4
node.master: false
node.data: true
node.ingest: true
node.attr.box_type: hot
node.attr.rack_type: rack2
xpack.security.enabled: false
# node5
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch
path.repo: /shared_folder/my_repo
network.host: _site_
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["es01:9300", "es02:9300", "es03:9300"]
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 1
network.bind_host: 0.0.0.0
network.publish_host: es05
http.port: 9200
transport.tcp.port: 9300
cluster.name: my_cluster
node.name: node5
node.master: false
node.data: true
node.ingest: false
node.attr.box_type: warm
node.attr.rack_type: rack2
xpack.security.enabled: false정답
GET _cat/nodes?v
GET _cat/nodeattrs?v정답
PUT logs_server1/_settings
{
"index.routing.allocation.require.box_type": "warm"
}
PUT logs_server2/_settings
{
"index.routing.allocation.require.box_type": "warm"
}
PUT logs_server3/_settings
{
"index.routing.allocation.require.box_type": "hot"
}정답
GET _cat/shards/logs_server*?v&h=index,shard,node&s=index,shard,node강제로 shard allocation awareness를 실행하기 위한 rack_type attribute를 사용하는 cluster를 transient setting을 사용하여 설정해보자.
정답
PUT _cluster/settings
{
"transient": {
"cluster":{
"routing":{
"allocation.awareness.attributes": "rack_type",
"allocation.awareness.force.rack_type.values": "rack1,rack2"
}
}
}
}GET _cat/shards/logs_server*?v&h=index,shard,prirep,state,node&s=index,shard- 각각의 primary와 replica shard는 다른 rack에 위치하게 된다. 다음과 비슷한 결과 확인 가능
index shard prirep state node
logs_server1 0 r STARTED node5
logs_server1 0 p STARTED node3
logs_server1 1 p STARTED node5
logs_server1 1 r STARTED node3
logs_server1 2 r STARTED node5
logs_server1 2 p STARTED node3
logs_server1 3 r STARTED node5
logs_server1 3 p STARTED node3
logs_server1 4 r STARTED node5
logs_server1 4 p STARTED node3
logs_server2 0 p STARTED node5
logs_server2 0 r STARTED node3
logs_server2 1 p STARTED node5
logs_server2 1 r STARTED node3
logs_server2 2 r STARTED node5
logs_server2 2 p STARTED node3
logs_server2 3 r STARTED node5
logs_server2 3 p STARTED node3
logs_server2 4 r STARTED node5
logs_server2 4 p STARTED node3
logs_server3 0 p STARTED node2
logs_server3 0 r STARTED node4
logs_server3 1 p STARTED node2
logs_server3 1 r STARTED node4
logs_server3 2 r STARTED node2
logs_server3 2 p STARTED node4
logs_server3 3 p STARTED node2
logs_server3 3 r STARTED node4
logs_server3 4 r STARTED node2
logs_server3 4 p STARTED node4정답
PUT logs-2018-07-04
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 1
}
}정답
POST _aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "logs-2018-07-04",
"alias": "logs-write"
}
}
]
}정답
POST _aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "logs-2018-07-04",
"alias": "logs-read"
}
}
]
}PUT logs-write/_doc/_bulk
{ "index" : { "_id" : "1"}}
{ "level" : "INFO", "message" : "recovered [20] indices into cluster_state", "date" : "2018-07-04"}
{ "index" : { "_id" : "2"}}
{ "level" : "WARN", "message" : "received shard failed for shard id 0", "date" : "2018-07-04"}
{ "index" : { "_id" : "3"}}
{ "level" : "INFO", "message" : "Cluster health status changed from [YELLOW] to [GREEN]", "date" : "2018-07-04"}
GET logs-read/_search날짜가 7월4일에서 7월5일로 변경되었다고 가정하고, primary shard가 1, replica shard가 1인 새로운 logs-2018-07-05 index를 생성 해보자.
정답
PUT logs-2018-07-05
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 1
}
}정답
POST _aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "logs-2018-07-05",
"alias": "logs-write"
}
},
{
"remove": {
"index": "logs-2018-07-04",
"alias": "logs-write"
}
}
]
}PUT logs-write/_doc/_bulk
{ "index" : { "_id" : "4"}}
{ "level" : "INFO", "message" : "[node2] started", "date" : "2018-07-05"}
{ "index" : { "_id" : "5"}}
{ "level" : "WARN", "message" : "not enough master nodes discovered during pinging", "date" : "2018-07-05"}
GET logs-2018-07-05/_search정답
POST _aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "logs-2018-07-05",
"alias": "logs-read"
}
}
]
}GET logs-read/_searchDELETE logs-read정답
- 에러 발생, alias를 삭제할 수 없다. 6.0이하 버전에서는 alias에 해당하는 모든 index를 삭제 했지만, index삭제를 위해선 정확한 index 명을 입력해야한다. 위의 command는 잘못된 command이다.PUT vehicles_temp/_doc/1
{
"cars" : [
{ "model" : "Corvette", "color" : "red", "horsepower" : 455},
{ "model" : "Volt", "color" : "yellow", "horsepower" : 149}
]
}
정답
GET vehicles_temp/_mapping정답
GET vehicles_temp/_search
{
"query":{
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"cars.color": "yellow"
}
},
{
"match": {
"cars.model": "Corvette"
}
}
]
}
}
}정답
- document에서 반드시 yellow의 Corvette인 차는 존재하지 않으므로 0 hit을 기대했지만, 위의 결과는 1 hit이다. 원하는 결과값이 아니다vehicles_temp index의 mapping 정보를 활용해서, vehicles index를 새롭게 mapping하자. 단 cars의 inner object는 nested type으로 설정하자.
정답
PUT vehicles
{
"mappings" : {
"_doc" : {
"properties" : {
"cars" : {
"type": "nested", # cars를 nested type으로~
"properties" : {
"color" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"horsepower" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"model" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}정답
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "vehicles_temp"
},
"dest": {
"index": "vehicles"
}
}정답
GET vehicles/_search
{
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "cars",
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"match": {
"cars.color": "yellow"
}
},
{
"match": {
"cars.model": "corvette"
}
}
]
}
},
"inner_hits": {}
}
}
}
정답
GET vehicles/_search
{
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "cars",
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": [
{
"match": {
"cars.color": "red"
}
},
{
"match": {
"cars.model": "corvette"
}
}
]
}
},
"inner_hits": {}
}
}
}car의 parent로써 "owner"를 나타내는 relation field를 추가해서 vehicles index에 parent/child relationship을 적용해보자. relationship field가 정의되면, name이 "John Doe"인 owner_name으로 indexing하고, Toyota Prius의 owner로 만들자. 그리고 적용이 잘 되었는지 테스트하기 위해, has_child 와 has_parent query를 실행해보자.
정답
PUT vehicles/_doc/_mapping
{
"properties":{
"owner_car_relation":{
"type": "Join",
"relations":{
"owner": "car"
}
}
}
}
PUT vehicles/_doc/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"owner_car_relation": {
"type": "join",
"relations": {
"owner": "car"
}
}
}
}
PUT vehicles/_doc/10
{
"owner_name": "John Doe",
"owner_car_relation": {
"name": "owner"
}
}
PUT vehicles/_doc/2?routing=10
{
"cars": [
{
"model": "Prius",
"color": "grey",
"horsepower": 121
}
],
"owner_car_relation":{
"name": "car",
"parent": 10
}
}
GET vehicles/_search
{
"query": {
"has_child": {
"type": "car",
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "cars",
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"match": {
"cars.model": "Prius"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
GET vehicles/_search
{
"query": {
"has_parent": {
"parent_type": "owner",
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"match": {
"owner_name": "John"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}정답
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
To be fully prepared for the Elastic Certified Engineer exam, candidates should be able to complete all of the following exam objectives with only the assistance of the Elastic documentation:
- Deploy and start an Elasticsearch cluster that satisfies a given set of requirements
- Configure the nodes of a cluster to satisfy a given set of requirements
- Secure a cluster using Elasticsearch Security (doc)
- Define role-based access control using Elasticsearch Security (doc)
-
Define an index that satisfies a given set of requirements
-
Perform index, create, read, update, and delete operations on the documents of an index
-
Define and use index aliases
-
Define and use an index template for a given pattern that satisfies a given set of requirements
-
Define and use a dynamic template that satisfies a given set of requirements
-
Use the Reindex API and Update By Query API to reindex and/or update documents
-
Define and use an ingest pipeline that satisfies a given set of requirements, including the use of Painless to modify documents
-
Write and execute a search query for terms and/or phrases in one or more fields of an index
-
Write and execute a search query that is a Boolean combination of multiple queries and filters
-
Highlight the search terms in the response of a query
-
Sort the results of a query by a given set of requirements
-
Implement pagination of the results of a search query
-
Use the scroll API to retrieve large numbers of results
-
Apply fuzzy matching to a query
-
Define and use a search template
-
Write and execute a query that searches across multiple clusters
-
Write and execute metric and bucket aggregations
-
Write and execute aggregations that contain sub-aggregations
-
Write and execute pipeline aggregations
-
Define a mapping that satisfies a given set of requirements
-
Define and use a custom analyzer that satisfies a given set of requirements
-
Define and use multi-fields with different data types and/or analyzers
-
Configure an index so that it properly maintains the relationships of nested arrays of objects
-
Configure an index that implements a parent/child relationship
-
Allocate the shards of an index to specific nodes based on a given set of requirements
-
Configure shard allocation awareness and forced awareness for an index
-
Diagnose shard issues and repair a cluster’s health
-
Backup and restore a cluster and/or specific indices
-
Configure a cluster for use with a hot/warm architecture
-
Configure a cluster for cross cluster search