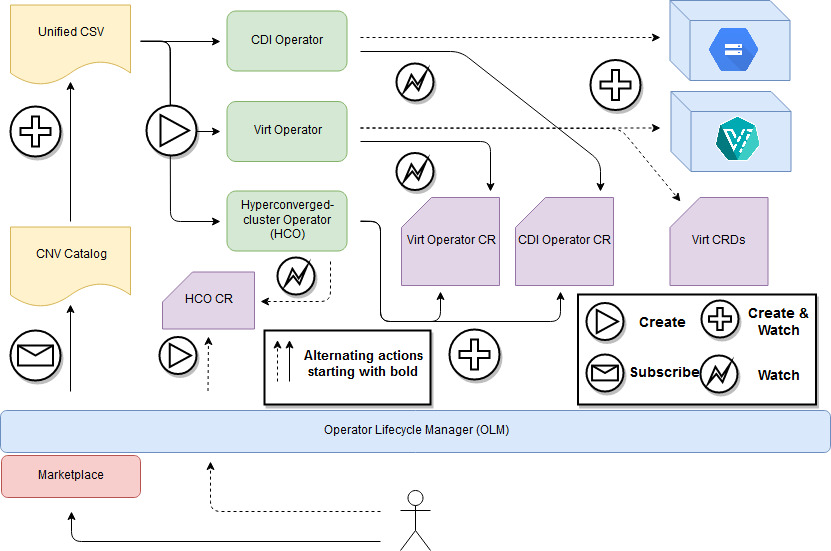
Hyperconverged Cluster Operator
A unified operator deploying and controlling KubeVirt and several adjacent operators:
- Containerized Data Importer
- Scheduling, Scale and Performance
- Cluster Network Addons
- Node Maintenance
This operator is typically installed from the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM), and creates operator CustomResources (CRs) for its underlying operators as can be seen in the diagram below. Use it to obtain an opinionated deployment of KubeVirt and its helper operators.
Installing HCO using kustomize (Openshift OLM Only)
To install the default community HyperConverged Cluster Operator, along with its underlying components, run:
$ curl -L https://api.github.com/repos/kubevirt/hyperconverged-cluster-operator/tarball/main | \
tar --strip-components=1 -xvzf - kubevirt-hyperconverged-cluster-operator-*/deploy/kustomize
$ ./deploy/kustomize/deploy_kustomize.shThe deployment is completed when HCO custom resource reports its condition as Available.
For more explanation and advanced options for HCO deployment using kustomize, refer to kustomize deployment documentation.
Installing Unreleased Bundle Using A Custom Catalog Source
Hyperconverged Cluster Operator is publishing the latest bundle to quay.io/kubevirt
before publishing tagged, stable releases to OperatorHub.io.
The latest bundle is quay.io/kubevirt/hyperconverged-cluster-bundle:1.6.0-unstable. It is built and pushed on every merge to
main branch, and contains the most up-to-date manifests, which are pointing to the most recent application images: hyperconverged-cluster-operator
and hyperconverged-cluster-webhook, which are built together with the bundle from the current code at the main branch.
The unreleased bundle can be consumed on a cluster by creating a CatalogSource pointing to the index image that contains
that bundle: quay.io/kubevirt/hyperconverged-cluster-index:1.6.0-unstable.
Make the bundle available in the cluster's packagemanifest by adding the following CatalogSource:
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: CatalogSource
metadata:
name: hco-unstable-catalog-source
namespace: openshift-marketplace
spec:
sourceType: grpc
image: quay.io/kubevirt/hyperconverged-cluster-index:1.6.0-unstable
displayName: Kubevirt Hyperconverged Cluster Operator
publisher: Kubevirt Project
EOFThen, create a namespace, subscription and an OperatorGroup to deploy HCO via OLM:
cat <<EOF | oc apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: kubevirt-hyperconverged
---
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1
kind: OperatorGroup
metadata:
name: kubevirt-hyperconverged-group
namespace: kubevirt-hyperconverged
---
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: hco-operatorhub
namespace: kubevirt-hyperconverged
spec:
source: hco-unstable-catalog-source
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
name: community-kubevirt-hyperconverged
channel: "1.6.0"
EOFThen, create the HyperConverged custom resource to complete the installation.
Further information about the HyperConverged CR and its possible configuration options can be found
in the Cluster Configuration doc.
Using the HCO without OLM or Marketplace
Run the following script to apply the HCO operator:
$ curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubevirt/hyperconverged-cluster-operator/main/deploy/deploy.sh | bashDeveloper Workflow
If you want to make changes to the HCO, here's how you can test your changes through OLM.
Build the HCO container using the Makefile recipes make container-build and
make container-push with vars IMAGE_REGISTRY, REGISTRY_NAMESPACE, and CONTAINER_TAG
to direct it's location.
To use the HCO's container, we'll use a registry image to serve metadata to OLM. Build and push the HCO's registry image.
# e.g. quay.io, docker.io
export IMAGE_REGISTRY=<image_registry>
export REGISTRY_NAMESPACE=<container_org>
export CONTAINER_TAG=example
# builds the registry image and pushes it to
# $IMAGE_REGISTRY/$REGISTRY_NAMESPACE/hco-container-registry:$CONTAINER_TAG
make bundleRegistryCreate the namespace for the HCO.
kubectl create ns kubevirt-hyperconvergedCreate an OperatorGroup that watches all namespaces.
cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f -
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1
kind: OperatorGroup
metadata:
name: hco-operatorgroup
namespace: kubevirt-hyperconverged
spec: {}
EOFCreate a CatalogSource and a Subscription.
If OLM Operator and Catalog Operator run in a namespace different than
openshift-marketplace, replaceopenshift-marketplacewith it in the CatalogSource and Subscription below.
cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f -
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: CatalogSource
metadata:
name: hco-catalogsource
namespace: openshift-marketplace
spec:
sourceType: grpc
image: $IMAGE_REGISTRY/$REGISTRY_NAMESPACE/hco-container-registry:$CONTAINER_TAG
displayName: KubeVirt HyperConverged
publisher: Red Hat
EOFcat <<EOF | kubectl create -f -
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: hco-subscription
namespace: kubevirt-hyperconverged
spec:
channel: "1.6.0"
name: community-kubevirt-hyperconverged
source: hco-catalogsource
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
EOFCreate an HCO CustomResource, which creates the KubeVirt CR, launching KubeVirt, CDI, Network-addons, VM import and SSP.
kubectl create -f deploy/hco.cr.yaml -n kubevirt-hyperconvergedCreate a Cluster & Launch the HCO
- Choose the provider
#For k8s cluster:
$ export KUBEVIRT_PROVIDER="k8s-1.17"#For okd cluster:
$ export KUBEVIRT_PROVIDER="okd-4.1"- Navigate to the project's directory
$ cd <path>/hyperconverged-cluster-operator- Remove an old cluster
$ make cluster-down- Create a new cluster
$ make cluster-up- Clean previous HCO deployment and re-deploy HCO
(When making a change, execute only this command - no need to repeat steps 1-3)
$ make cluster-syncCommand-Line Tool
Use ./cluster/kubectl.sh as the command-line tool.
For example:
$ ./cluster/kubectl.sh get pods --all-namespaces