Enhancing Instruction-Following Capabilities in Seq2Seq Models: A Novel Adaptation of DoLA in T5 and FLAN-T5
Code for the paper "Enhancing Instruction-Following Capabilities in Seq2Seq Models: A Novel Adaptation of DoLA in T5 and FLAN-T5"
Authors: Huey Sun
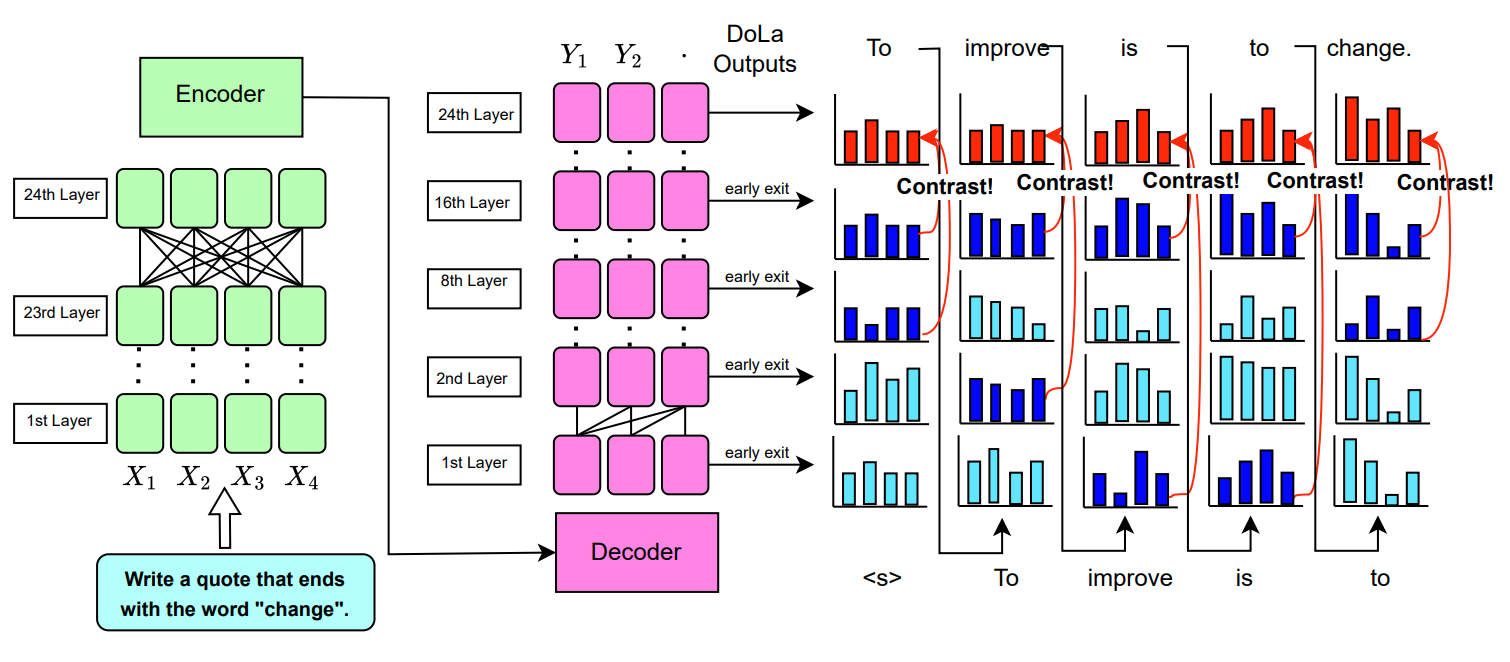
We adapted the DoLa to T5 and instruction-tuned FLAN-T5 models, and investigated how DoLa can improve keyword inclusion by analysing logit evolution through the model layers. You can upload running_dola.ipynb to Google Colab to test it out yourself.
pip install -e transformers-4.28.1
pip install datasets
pip install accelerate
-
dola_t5.pyThe class DoLa supports various generation and scoring methods, including baseline, DoLa-static, and DoLa modes. It's designed to run on either CPU or GPU, with support for multi-GPU setups. -
ifeval_eval.pyScript to evaluate the language model's performance on IFEval. It uses the Hugging Face Transformers library to load and interact with pre-trained models. It handles different configurations and modes of operation, including parallel processing and early exit strategies for efficient inference. -
memotrap_dataset_eval.pyScript to evaluate the performance of language models, specifically focusing on their ability to generate correct endings for given prompts. It utilizes a dataset loaded from a CSV file and supports different configurations
-
Results:Model outputs, evaluations of the outputs and logit analyses can be found here -
Scripts and Usage:The provided scripts are straightforward to use, requiring only the specification of the model, dataset paths, and the desired decoding strategy through command-line arguments. This design makes it easy to replicate the experiments or apply DoLa to new models and tasks. -
Evaluation Framework:The inclusion of evaluation scripts for specific tasks and datasets, along with instructions for using external tools for response comparison, offers a comprehensive framework for assessing the effectiveness of DoLa in enhancing the factuality of LLMs.
| Argument | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
--model-name |
google/flan-t5-large |
Specifies the model you want to use, currently we support LLaMA-v1 and the T5 family. |
--data-path |
/path/to/dataset |
Path to the dataset file or folder. |
--output-path |
output-path.json |
Where to store the output results. |
--num-gpus |
1 |
Number of GPUs to use |
--max_gpu_memory |
27 |
Maximum GPU memory size (in GiB) to allocate. Default: 27 (for 32G V100). |
--print-logits |
Adding this argument prints the top 5 logits in the premature layers for each token generated |
The --early-exit-layers argument takes a string containing a sequence of layer numbers separated by commas, with no spaces in between. By specifying different number of layers, we make the model decode at different modes.
| Number of Layers Specified | Example (str) | Description of Decoding Mode |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -1 |
Naive decoding from the final layer output. |
| 2 | 16,32 |
DoLa-static decoding with the second specified layer (i.e. 32) as the mature_layer and first specified layer (i.e. 16) as premature_layer. |
| >2 | 0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14,32 |
DoLa decoding with the last specified layer (i.e. 32) as the mature_layer and all the preceding layers (i.e. 0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14) as candidate_premature_layers. |
The dola_t5.py script defines a class DoLaT5 for working with a T5 model, supporting various generation and scoring methods, including baseline, DOLA-static, and DOLA modes. It's designed to run on either CPU or GPU, with support for multi-GPU setups. The script is structured into several key components:
-
Initialization: The init method initializes the class with model details, device configuration, and loads the model and tokenizer.
-
Model Loading:
load_modelloads the T5 model and tokenizer. It configures the model for efficient memory usage on GPUs and supports distributing the model across multiple GPUs if specified. -
Stopping Criteria:
set_stop_wordsallows setting custom stopping criteria for generation, using the T5StoppingCriteria. -
Text Generation: The
generatemethod supports text generation in three modes:-
baseline: Standard text generation. -
dola-static: Uses specified mature and premature layers for DOLA decoding. -
dola: Dynamically selects the premature layer based on divergence from the mature layer's output.
It supports various generation parameters like
max_new_tokens, top_p, top_k, andtemperature. The method can also remove specified stop words from the output. -
-
Relative Top Filtering:
get_relative_top_filteris a utility for applying a relative top filter based on the scores' softmax values, used in DOLA modes for filtering logits. -
Language Modeling Score:
lm_scorecalculates the language modeling score for a given text, supporting the same three modes as text generation. It can compute scores based on the difference in logits between layers (for DOLA modes) and supports PMI calculation. -
Utility Methods: The script includes methods for softmax normalization, KL divergence calculation, and JS divergence calculation for selecting the premature layer in DOLA mode.
Key functionalities include:
-
DoLa Decoding: Dynamically selects layers for decoding based on divergence, aiming to improve generation quality.
-
Efficient Memory Usage: Configures the model for low memory usage on CPUs and efficient distribution across multiple GPUs.
-
Custom Stopping Criteria: Allows specifying custom stopping words for generation tasks.
The input prompts can be found in data/ifeval-input-data.jsonl. Further instructions for analyzing model output can be found in evaluation/IfEval
python ifeval_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-small --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python ifeval_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-base --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python ifeval_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-large --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python ifeval_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-xl --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1python ifeval_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-small --early-exit-layers 0,2,4,6,8 --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python ifeval_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-base --early-exit-layers 0,2,4,6,8,10,12 --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python ifeval_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-large --early-exit-layers 0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24 --data-path ./data/--output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python ifeval_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-xl --early-exit-layers 0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24 --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1Script to evaluate the language model's performance on a given dataset. Uses the Hugging Face Transformers library to load and interact with pre-trained models. It handles different configurations and modes of operation, including parallel processing and early exit strategies for efficient inference.
It is structured as follows:
-
Imports and Setup: The script imports necessary libraries and sets up regular expressions and constants. It suppresses logging messages from the Transformers library to reduce clutter.
-
Functions:
-
load_jsonl(file_path): Loads a JSONL file and returns a list of prompts extracted from it.
-
create_demo_text(): Creates a demonstration text with questions and answers to be prepended to the input prompts.
-
build_prompt(input_text): Builds the final prompt by appending the input text to the demonstration text.
-
-
Argument Parsing: The script uses argparse to parse command-line arguments, allowing users to specify the model name, device, data path, and other configurations.
-
Data Preparation: It loads the dataset from a specified path and optionally limits the number of prompts for debugging or splits the dataset for parallel processing.
-
Model Initialization: Depending on the model name, it initializes DoLaT5 class to handle language model inference. The script sets stop words to signal the end of a generation.
-
Early Exit Layers Configuration: It configures early exit layers for the model, which is a technique to improve inference efficiency by exiting the model's forward pass early under certain conditions. The script supports three modes:
-
baseline: Standard decoding without early exit.
-
early_exit_contrastive: Uses a specific mature and premature layer for early exit.
-
dola: Dynamically chooses from a set of candidate premature layers based on certain criteria.
-
-
Inference Loop: For each prompt in the dataset, the script:
-
Builds the full prompt using build_prompt.
-
Generates a completion using the model with specified generation parameters.
-
Cleans up the generated text by removing stop words.
-
Optionally, tracks the usage of premature layers in dola mode.
-
Results Handling: The script collects the prompts and their corresponding model completions in a list of dictionaries.
-
-
Output: Finally, it saves the results to a JSONL file in the specified output path. If parallel processing is enabled, it appends the shard ID to the output filename.
The input prompts can be found in data/memotrap-input-data.jsonl. Further instructions for analyzing model output can be found in evaluation/MemoTrap
python memo_trap_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-small --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python memo_trap_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-base --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python memo_trap_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-large --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python memo_trap_eval.py--model-name google/flan-t5-xl --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1python memo_trap_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-small --early-exit-layers 0,2,4,6,8 --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python memo_trap_eval.py--model-name google/flan-t5-base --early-exit-layers 0,2,4,6,8,10,12 --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python memo_trap_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-large --early-exit-layers 0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24 --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1
python memo_trap_eval.py --model-name google/flan-t5-xl --early-exit-layers 0,2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,24 --data-path ./data/ --output-path output-path.json --num-gpus 1Script to evaluate the performance of language models, specifically focusing on their ability to generate correct endings for given prompts. It utilizes a dataset loaded from a CSV file and supports different configurations and modes for the language model, including the use of DoLa and DoLaT5 models for improved factuality.
-
Imports and Initial Setup: The script imports necessary libraries and sets up logging and constants. It defines regular expressions for parsing answers and initializes flags for debugging and other configurations.
-
Utility Functions:
-
parse_classes: Parses a string representation of a list into an actual list of strings.
-
load_csv: Loads data from a CSV file, parsing each line into a dictionary with keys for the prompt, possible classes (answers), and the correct answer index.
-
extract_and_compare_answer: Extracts the model's generated answer ending and compares it with the correct answer to determine correctness.
-
create_demo_text: Generates a demo text with example questions and answers to be used in the prompt construction.
-
build_prompt: Constructs the input prompt for the model by appending the demo text and the specific question to be answered.
-
-
Argument Parsing: The script uses argparse to handle command-line arguments for model configuration, dataset paths, and evaluation settings.
-
Model Selection and Configuration: Based on the provided model name, the script selects between the DoLa and DoLaT5 models. It also sets up model-specific configurations like stop words, early exit layers, and repetition penalties.
-
Data Preparation: The script loads the dataset from a CSV file. It supports debugging mode (which limits the data to the first 10 samples) and parallel processing mode (which divides the dataset into chunks based on shard IDs).
-
Evaluation Loop:
-
For each sample in the dataset, it constructs the input prompt and generates model completions based on the provided arguments.
-
It then cleans the model completion by removing any stop words and trims whitespace.
-
The script extracts the model's answer ending and compares it with the correct answer to determine correctness.
-
It accumulates results, including the model's completions, the generated answer endings, the correct answers, and correctness flags.
-
-
Results Reporting and Saving:
-
Calculates the overall accuracy of the model based on the correctness flags.
-
In "dola" mode with debugging enabled, it reports the usage statistics of premature layers.
-
Saves the evaluation results to a JSON file, with the filename optionally including the shard ID for parallel processing setups.
-