This is a sample implementation for running an AWS Batch job that automatically scales up required memory using the Serverless framework.s To achieve this, a simple AWS Step Function state machine is used to orchestrate the job running process. An AWS Lambda is used to process failed jobs. When the job failure is due to a Memory Error , it then creates a job specification with more memory available and the job is executed again.
All components are serverless keeping the cost down for some scenarios like Data Science pipelines and ETL/ELT pipelines.
This example also show how to run multiple jobs on different schedules. This relies on AWS EventBridge Rules, so keep in mind currently there is a limit of 300 Rules per Bus (which can be increased).
Here is a representation of the state machine:
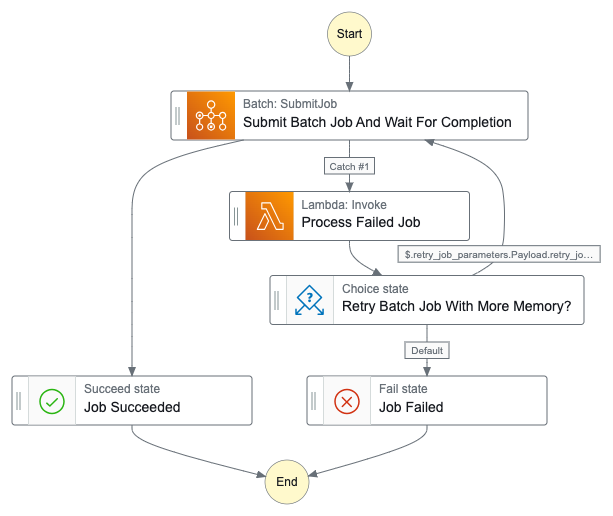
In addition to Step Function and Lambdas, other CloudFormation resources are created as part of this implementation (under resources.yml):
- Step Functions IAM Role
- Batch Compute Environment
- Batch Job Queue
- Batch Job Definition
- Install the serverless framework
- Install the required serverless plugins:
> serverless plugin install -n serverless-step-functions
✔ Plugin "serverless-step-functions" installed (17s)- Choose a subnet and security group, then deploy a new stack:
> sls deploy --param="subnet_id=subnet-12345678" --param="security_group_id=sg-12345678"
Running "serverless" from node_modules
Deploying memory-autoscaling-example to stage dev (us-east-1)
✓ State machine "JobRunner" definition is valid
✔ Service deployed to stack memory-autoscaling-example-dev (162s)
functions:
processFailedBatchJob: memory-autoscaling-example-dev-processFailedBatchJob (137 kB)- Retrieve the ARN of the state machine and start a manual state machine execution (can also be done from AWS Management Console):
> aws stepfunctions start-execution --state-machine-arn arn:aws:states:us-east-1:ACCOUNT_ID:stateMachine:JobRunnerStepFunctionsStateMachine-eB75gE2choxG --input "{
\"job_name\": \"bonjour\",
\"job_vcpus\": \"0.25\",
\"job_memory\": \"512\",
\"job_command\": [
\"echo\",
\"bonjour\"
]
}"
{
"executionArn": "arn:aws:states:us-east-1:ACCOUNT_ID:execution:JobRunnerStepFunctionsStateMachine-eB75gE2choxG:6bb5676c-4fe0-4754-8eac-6cca606d1476",
"startDate": 1702081624.749
}To schedule a new job to run automatically you need to add a new object to the end of the file jobs.yml with these required parameters:
- schedule:
rate: rate(1 hour)
input:
job_name: the-aws-batch-job-name
job_vcpus: "0.25"
job_memory: "512"
job_command: ["echo", "howdy"]After that you just need to re-deploy the changes using serverless.