This repository contains the official implementation of the paper titled "Prompt Tuning Strikes Back: Customizing Foundation Models with Low-Rank Prompt Adaptation" accepted at NIPS 24.
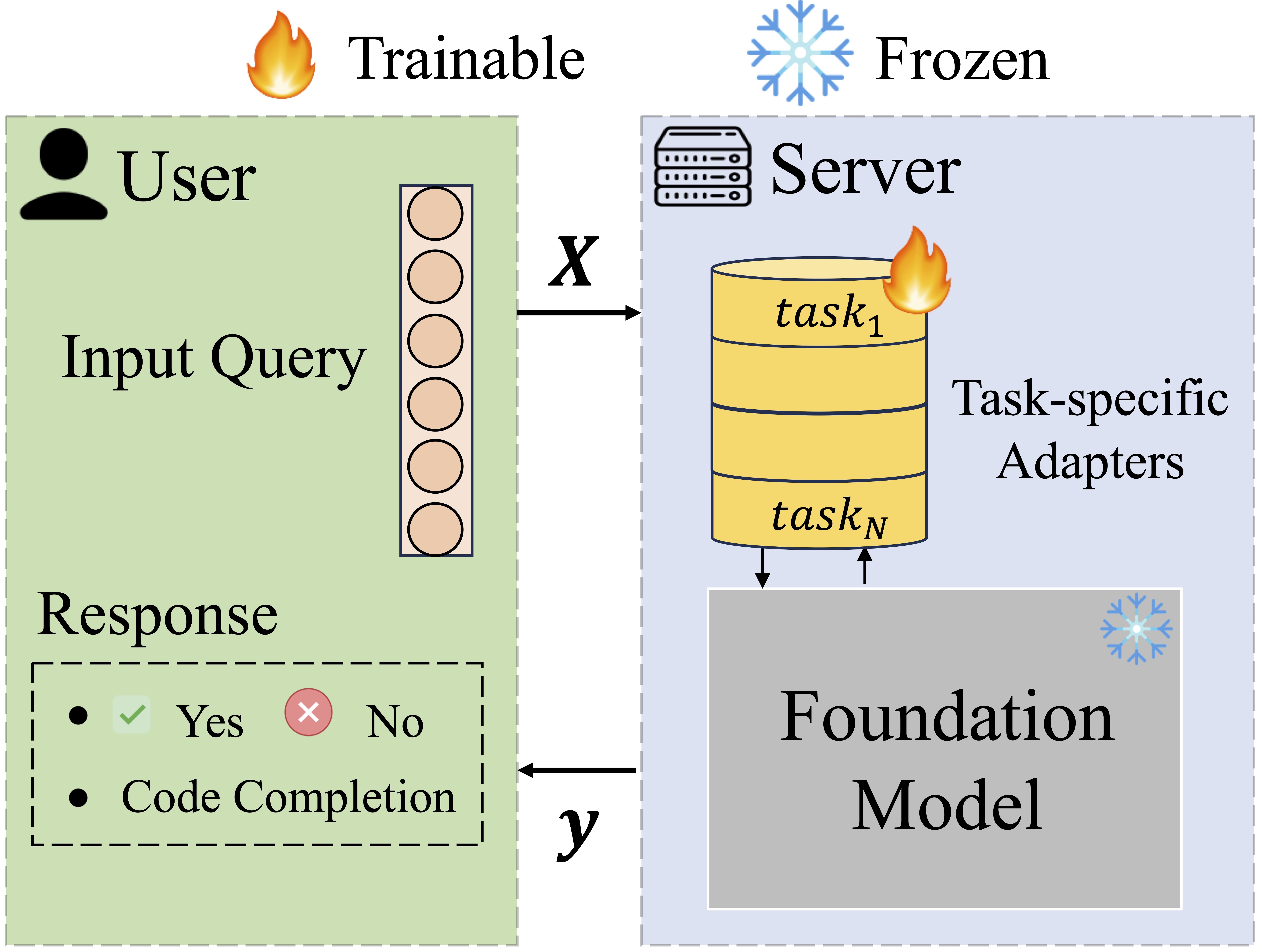 A schematic illustrating how typical PEFT methods like LoRA achieve personalization of a foundation model for multiple tasks.
A schematic illustrating how typical PEFT methods like LoRA achieve personalization of a foundation model for multiple tasks.
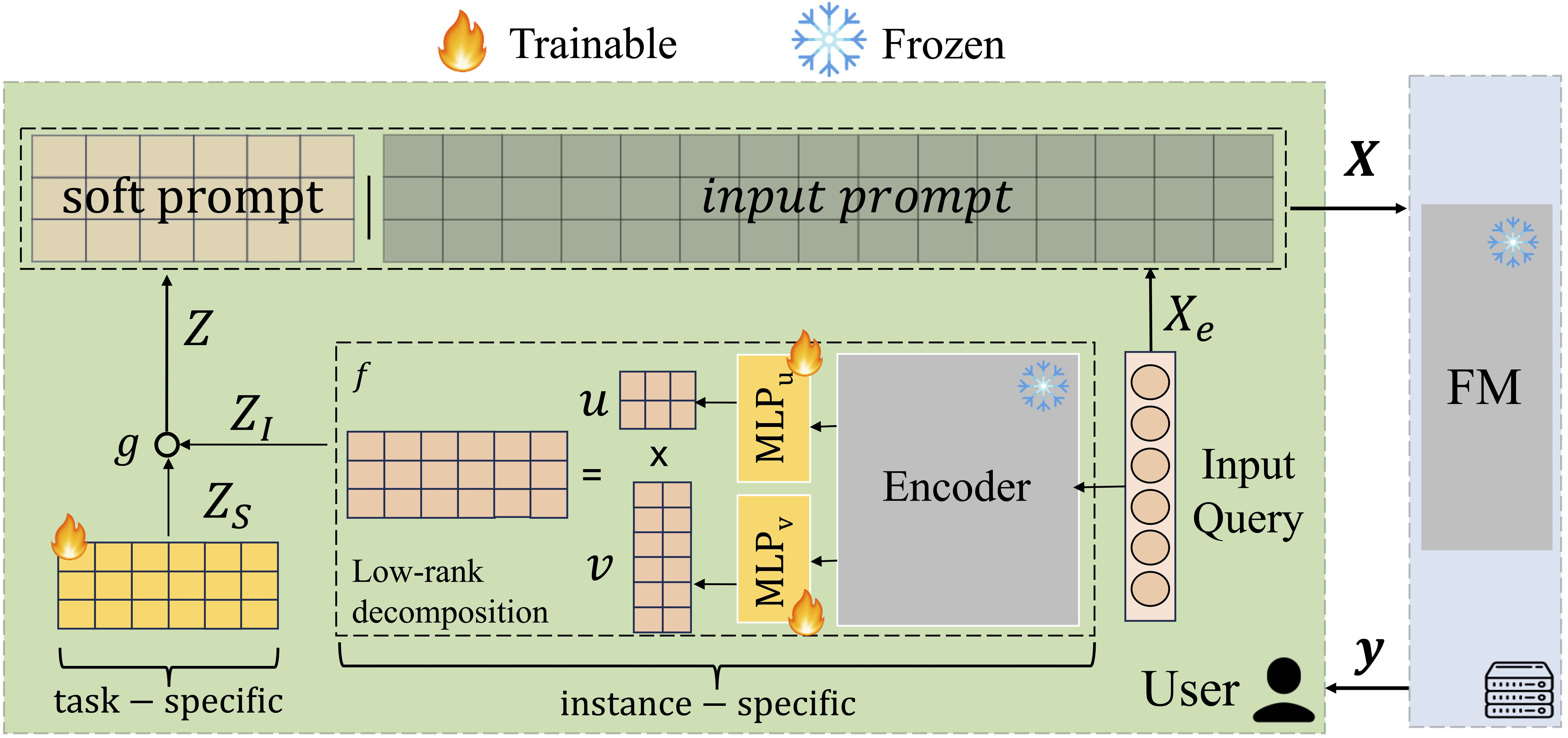 An illustration of LOPA. No task-specific adapters need to be stored on the server.
An illustration of LOPA. No task-specific adapters need to be stored on the server.
To set up the project dependencies, you have two options:
pip install -r requirements.txtAlternatively, you can use a Docker image with pre-installed dependencies.
docker pull aj0509/prog_synth:latestTo tune the model, you need to run the
tune_foundation_model.pyscript.
-
--peft_method: Specifies the PEFT method to be used.- Possible values:
lora,pt,idpg,lopa
- Possible values:
-
--task_name: Name of the task to be trained on.- Possible values:
mbpp,cruxeval_input_prediction,cruxeval_output_prediction
- Possible values:
-
--model_type: Specifies the type of foundation model to be used for PEFT.- Possible values:
phi-2,phi-3,codegen-350M,codegen2-3_7B,deepseek-coder-1.3b-base,deepseek-coder-7b-base,Meta-Llama-3-8B
- Possible values:
-
--enc_model_type: Specifies the type of encoder model to be used in lopa or idpg.- Possible values:
codebert-base,codesage-small,codesage-base,codesage-large
- Possible values:
-
--num_virtual_tokens: Length of soft prompt (=m)- Example:
5,10,25
- Example:
-
--lp_rank: Low-Rank for matrix factorization in LOPA (=r)- Example:
1,2,4
- Example:
-
--num_epochs: Number of epochs to train the model.- Example:
10
- Example:
-
--per_gpu_train_batch_size: Number of training samples per GPU.- Example:
2
- Example:
-
--lr: Learning rate for the optimizer.- Example:
0.001used for PT-based methods,0.0001used for LoRA and0.00001used for FFT.
- Example:
-
--log_dir: Directory to save logs. By default, the current timestamp is used as the name of the directory.- Example:
./logs
- Example:
-
--wandb_logging: Flag to enable logging to Weights and Biases.
Here is a sample command that tunes phi-2 for MBPP using LOPA with 10 virtual tokens and rank 1:
python tune_foundation_model.py --peft_method lopa --task_name mbpp --model_type phi-2 --enc_model_type codesage-small --num_virtual_tokens 10 --lp_rank 1 --num_epochs 10 --per_gpu_train_batch_size 2 --lr 0.001For using accelerator. Here is an example command that uses deepspeed-stage2 with accelerate:
accelerate launch --config_file config_files/config_ds_zero_stage2_no_fp16.yaml tune_foundation_model.pyRequirements:
- Setup
.yamlconfiguration file for the experiment. Example: config_ds_zero_stage2_no_fp16.yaml - Provide path to deepspeed-stage2 configuration file in the
.yamlfile. Example: zero_stage2_nofp16_config.json
Use the following link for more details: Huggingface Accelerator
We provide a separate script for full fine-tuning tune_fft_baseline.py
Recommendation: Use Deepspeed-stage3 for FFT training to tune large models.
deepspeed tune_fft_baseline.py --path_to_ds_config config_files/zero_stage3_config.json --fp16 True --gradient_accumulation_steps 2Requirements:
- Setup deepspeed configuration file for the experiment. Example: zero_stage3_config.json
To evaluate the model, you need to generate predictions using
generate_preds.pyscript.
Here is a sample command that generates predictions for phi-2 tuned on MBPP using LOPA with 10 virtual tokens and rank 1:
accelerate launch generate_preds.py --peft_method lopa --task_name mbpp --model_type phi-2 --enc_model_type codesage-small --num_virtual_tokens 10 --lp_rank 1Following arguments are needed to load the weights for the peft method.
--load_adapter_from: Path to directory containing the adapter weights for the foundation model. (Used by pt, lora, idpg, lopa)--clf_predictor_path: Path to the encoder model weights for. (Used by lopa, idpg)--load_base_from_path: Path to the base model weights. (Used by fft for un-sharded checkpoints)--sharded_checkpoint_dir: Path to the sharded checkpoint directory. (Used by fft)
Predictions of foundation models need to be post-processed before evaluation.
To run post-processing for MBPP, use the following command:
python postprocess_mbpp_preds.py --path "$path_to_mbxp_solutions_json"To run post-processing for CruxEval-I, use the following command:
python postprocess_cruxeval_preds.py --path "$path_to_output_raw_json" --mode inputThe processed predictions will be saved in the same directory as a different file.
Requirements:
- Setup the MBXP evaluation suite. Based of Amazon Science/mxeval.
pip install -e mxeval - Setup the CruxEval evaluation suite. Based of Facebook Research/CRUXEval.
cd cruxeval && pip install -r requirements.txt
To evaluate predictions for MBPP, use the following command:
evaluate_functional_correctness "$path_to_mbxp_solutions_post_processed" --problem_file mxeval/mbpp_test_release_v1.jsonlTo evaluate predictions for CruxEval-I, use the following command:
python cruxeval/evaluation/evaluate_generations.py --generations_path "$path_to_output_json" --scored_results_path "$path_to_output_scored_json" --mode inputWe provide the sample results (pass@1) of running different PEFT methods phi-2 across different tasks. For rest of the results, please refer to the paper.
| Tuning Method | CruxEval-I | CruxEval-O | MBPP |
|---|---|---|---|
| None | 33.5 | 33.0 | 45.17 |
| FFT | 40.2 | 37.0 | 55.03 |
| LoRA | 41.5 | 42.5 | 51.54 |
| PT | 35.0 | 34.0 | 49.69 |
| IDPG | 35.0 | 33.0 | 53.29 |
| LOPA | 43.0 | 37.2 | 52.15 |
We welcome contributions to the project. Please raise an issue or submit a pull request.
To run larger models, we recommend using the following resources: Huggingface GPU Inference
@article{jain2024prompt,
title={Prompt Tuning Strikes Back: Customizing Foundation Models with Low-Rank Prompt Adaptation},
author={Jain, Abhinav and Chaudhuri, Swarat and Reps, Thomas and Jermaine, Chris},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.15282},
year={2024}
}