copied from https://github.com/hendisantika/SpringBoot-Security-JWT-Rest-API-Dynamic-Multi-Tenancy-MySQL-PostgreSQL.git
modified and reolved issue ################################################################################################################################
I wanted a solution where multi-tenancy is achieved by having a database per-tenant and all user information (username, password, client Id, etc.) for authentication and authorization stored in a user table in the respective tenant databases. This means that not only did I need a multi-tenant application, but also a secure application like any other web application secured by Spring Security.
I know how to use Spring Security to secure a web application and how to use Hibernate to connect to a database. The requirement further dictates that all users belonging to a tenant need to be stored in the tenant database and not a separate or central database. This would allow for complete data isolation for each tenant.
- Archive Application SaaS Model client wise different database.
- Focus Spring Security and JWT
- You can connect multiple schemas with a single database, like MySQL — testdb, testdb2.
- You can connect multiple databases, like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle.
Multi-tenancy is an architecture in which a single instance of a software application serves multiple customers. Each client is called a tenant. Tenants may be given the ability to customize some parts of the application.
A multi-tenant application is where a tenant (i.e. users in a company) feels that the application has been created and deployed for them. In reality, there are many such tenants, and they too are using the same application but get a feeling that it's built just for them.
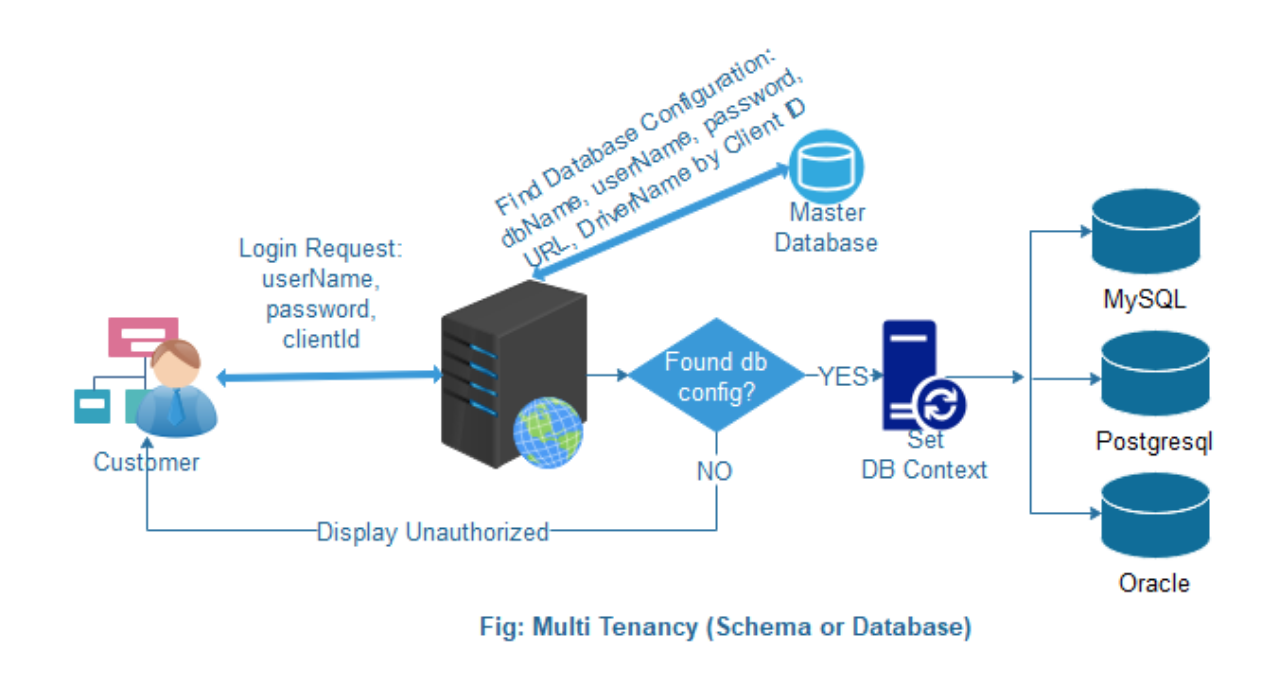
Dynamic Multi-Tenant High-Level Diagram:
Here,
- Client requests to login to the system.
- The system checks with the master database using client Id.
- If it's successful, set the current database to context based on the driver class name.
- If this fails, the user gets the message, "unauthorized".
- After successful authentication, the user gets a JWT for the next execution.
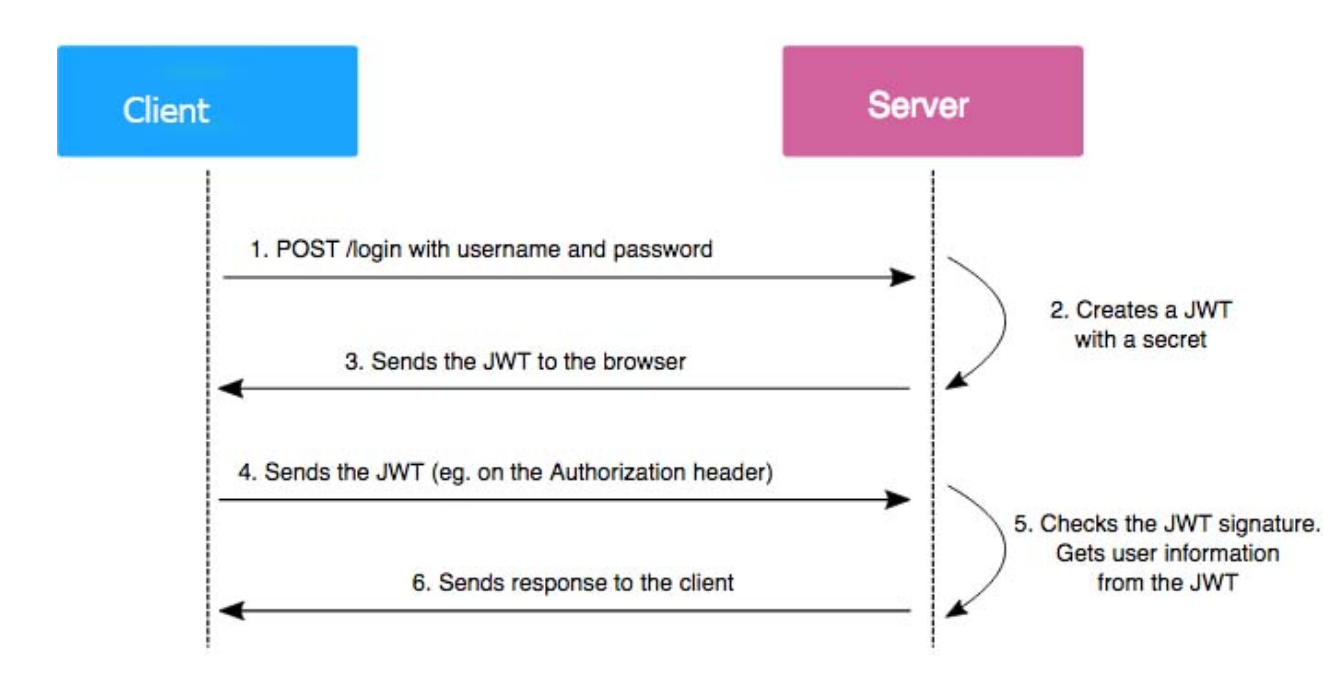
The whole process executes in the following workflow:
Technology and Project Structure:
- Java 11.
- Spring Boot.
- Spring Security.
- Spring AOP.
- Spring Data JPA.
- Hibernate.
- JWT.
- MySQ & PostgreSQL.
- IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate (2020.1).
Now, Create a Master Database and a tenant database.
Master Database:
In the master database, we only have one table (tbl_tenant_master), where all tenant information is storeed in the table. MySQL
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tbl_tenant_master`;
CREATE TABLE `tbl_tenant_master` (
`tenant_client_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL,
`db_name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`url` varchar(250) NOT NULL,
`user_name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`driver_class` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`status` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`tenant_client_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
INSERT INTO `tbl_tenant_master` (`tenant_client_id`, `db_name`, `url`, `user_name`, `password`, `driver_class`, `status`) VALUES
('100', 'tenant_db', 'jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tenant_db?useUnicode=true&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Jakarta&useSSL=false', 'root', 'root', 'com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver', 'ACTIVE'),
('200', 'tenant_db_pgs', 'jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/tenant_db_pgs', 'hendisantika', 'root', 'org.postgresql.Driver', 'ACTIVE'),
('300', 'tenant_db2', 'jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tenant_db?useUnicode=true&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Jakarta&useSSL=false', 'root', 'root', 'com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver', 'ACTIVE');
Tenant Database (1) in MySQL:
Create a table for client login authentication(tbl_user).
Create another table (tbl_product) to retrieve data using a JWT (for Authorization checks). MySQL
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tbl_product`;
CREATE TABLE `tbl_product` (
`product_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`product_name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`quantity` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`size` varchar(3) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`product_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tbl_user`;
CREATE TABLE `tbl_user` (
`user_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`full_name` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`gender` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`user_name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`status` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
INSERT INTO `tbl_product` (`product_id`, `product_name`, `quantity`, `size`) VALUES
('1', 'Apple MacOS', '5', 'M');
INSERT INTO `tbl_user` (`user_id`, `full_name`, `gender`, `user_name`, `password`, `status`) VALUES
('1', 'Uzumaki Naruto', 'Male', 'naruto', '$2y$12$/WhepH7JVYUCl4ujy6FFguiCi/x2q4dwXISD.WJTXYIN2QAhv6Zky', 'ACTIVE'); -- password=narutoTenant Database (2) in PostgreSQL:
Create a table for client login authentication (tbl_user).
Create another table (tbl_product) to retrieve data using a JWT (for authorization checks). PostgreSQL
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS "public"."tbl_product";
-- This script only contains the table creation statements and does not fully represent the table in the database. It's still missing: indices, triggers. Do not use it as a backup.
-- Table Definition
CREATE TABLE "public"."tbl_product" (
"product_id" int4 NOT NULL,
"product_name" varchar(50) NOT NULL,
"quantity" int4 NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
"size" varchar(3) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ("product_id")
);
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS "public"."tbl_user";
-- This script only contains the table creation statements and does not fully represent the table in the database. It's still missing: indices, triggers. Do not use it as a backup.
-- Table Definition
CREATE TABLE "public"."tbl_user" (
"user_id" int4 NOT NULL,
"full_name" varchar(100) NOT NULL,
"gender" varchar(10) NOT NULL,
"user_name" varchar(50) NOT NULL,
"password" varchar(100) NOT NULL,
"status" varchar(10) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ("user_id")
);
INSERT INTO "public"."tbl_product" ("product_id", "product_name", "quantity", "size") VALUES
('1', 'Apple MacOS', '5', 'M');
INSERT INTO "public"."tbl_user" ("user_id", "full_name", "gender", "user_name", "password", "status") VALUES
('1', 'Uzumaki Naruto', 'Male', 'naruto', '$2y$12$/WhepH7JVYUCl4ujy6FFguiCi/x2q4dwXISD.WJTXYIN2QAhv6Zky', 'ACTIVE');Database creation and table creation are done!
In this section, we'll work to understand multitenancy in Hibernate. There are three approaches to multitenancy in Hibernate:
- Separate Schema — one schema per tenant in the same physical database instance.
- Separate Database — one separate physical database instance per tenant.
- Partitioned (Discriminator) Data — the data for each tenant is partitioned by a discriminator value.
Master Database data:
tbl_tenant_master
MariaDB [master_db]> select * from tbl_tenant_master;
+------------------+---------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+----------+--------------------------+--------+
| tenant_client_id | db_name | url | user_name | password | driver_class | status |
+------------------+---------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+----------+--------------------------+--------+
| 100 | tenant_db | jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tenant_db?useUnicode=true&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Jakarta&useSSL=false | root | root | com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver | ACTIVE |
| 200 | tenant_db_pgs | jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/tenant_db_pgs | hendisantika | root | org.Postgresql.Driver | ACTIVE |
| 300 | tenant_db2 | jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tenant_db?useUnicode=true&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Jakarta&useSSL=false | root | root | com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver | ACTIVE |
+------------------+---------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+----------+--------------------------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.010 sec)
Tenant Database (MySQL) Table Data:
tbl_user
tbl_product
MariaDB [tenant_db]> select * from tbl_user;
+---------+----------------+--------+-----------+--------------------------------------------------------------+--------+
| user_id | full_name | gender | user_name | password | status |
+---------+----------------+--------+-----------+--------------------------------------------------------------+--------+
| 1 | Uzumaki Naruto | Male | naruto | $2y$12$/WhepH7JVYUCl4ujy6FFguiCi/x2q4dwXISD.WJTXYIN2QAhv6Zky | ACTIVE |
+---------+----------------+--------+-----------+--------------------------------------------------------------+--------+
1 row in set (0.002 sec)
MariaDB [tenant_db]> select * from tbl_product;
+------------+--------------+----------+------+
| product_id | product_name | quantity | size |
+------------+--------------+----------+------+
| 1 | Apple MacOS | 5 | M |
+------------+--------------+----------+------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
tbl_user
tbl_product
tenant_db_pgs=# select * from tbl_user;
user_id | full_name | gender | user_name | password | status
---------+----------------+--------+-----------+--------------------------------------------------------------+--------
1 | Uzumaki Naruto | Male | naruto | $2y$12$/WhepH7JVYUCl4ujy6FFguiCi/x2q4dwXISD.WJTXYIN2QAhv6Zky | ACTIVE
(1 row)
tenant_db_pgs=# select * from tbl_product;
product_id | product_name | quantity | size
------------+--------------+----------+------
1 | Apple MacOS | 5 | M
(1 row)
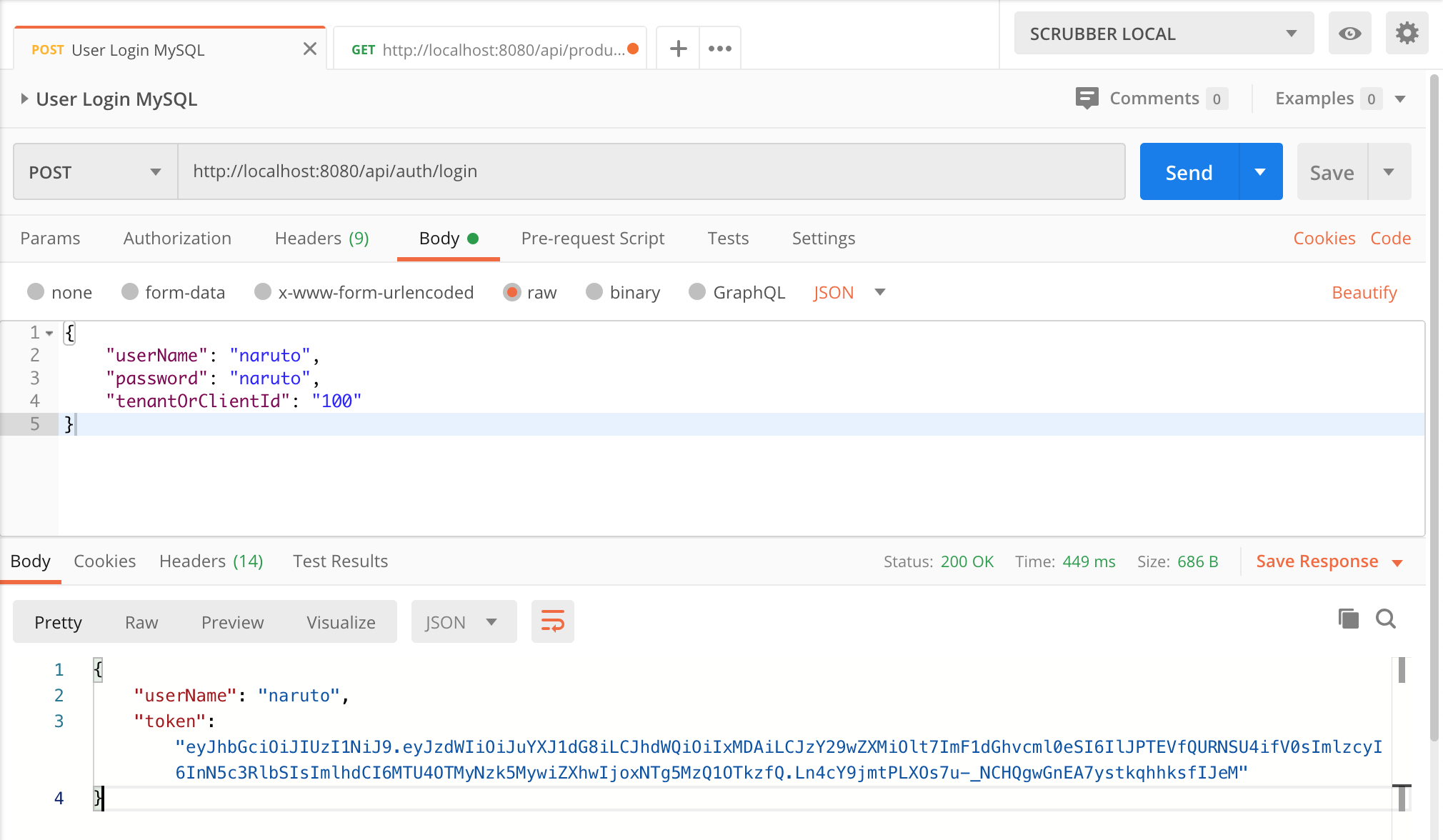
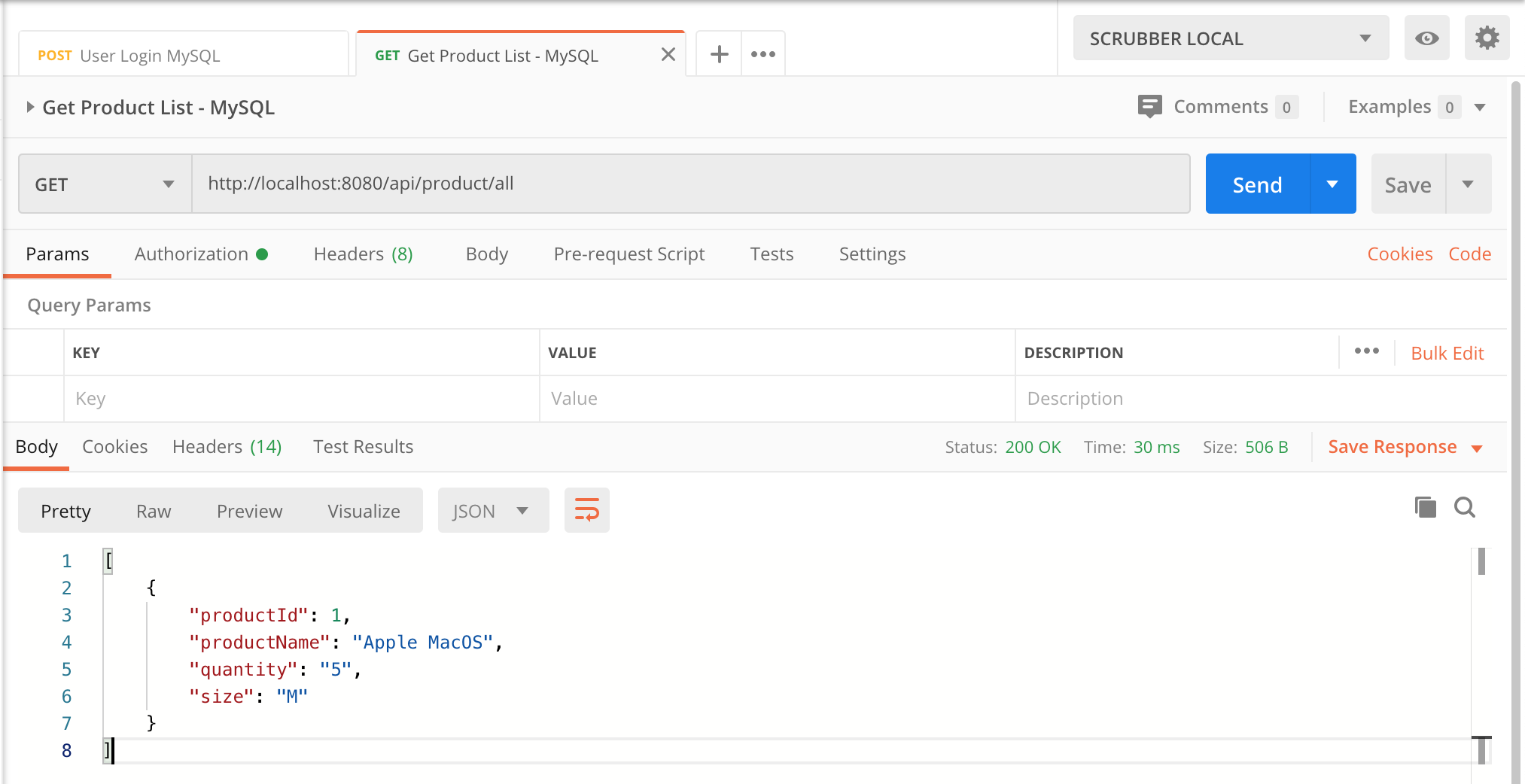
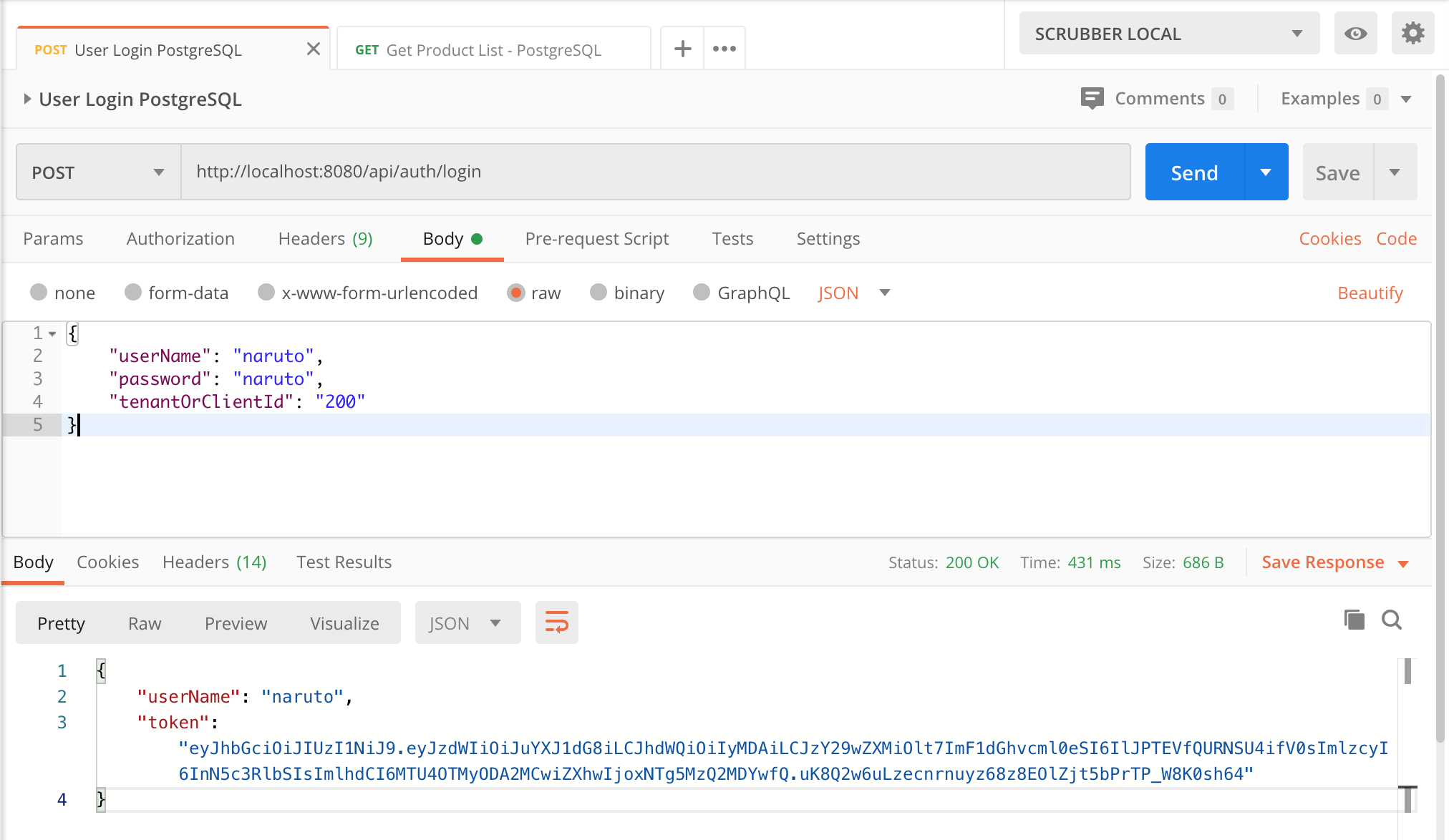
Now, test that everything works as we expect using Postman:
Target MySQL:
User Login in MySQL
Get Product List in MySQL
Target PostgreSQL:
User Login in PostgreSQL
Get Product List in PostgreSQL
NOTE: BCrypt Online Generator:
- https://bcrypt-generator.com/
- Lupa lagi. Nanti diupdate dech