AWS do EKS (aws-do-eks)
Create and Manage your Amazon EKS clusters using the do-framework
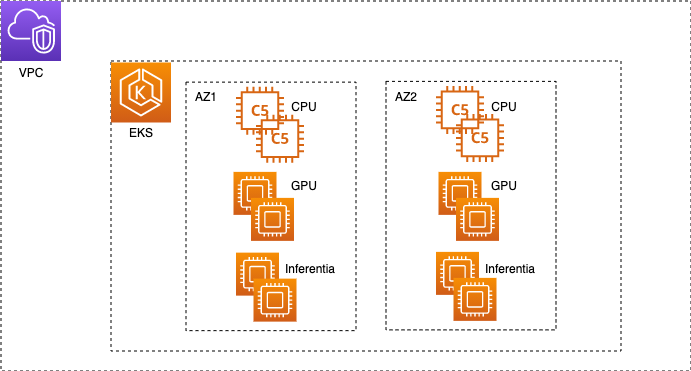
Fig. 1 - EKS cluster sample
As described in the Amazon EKS User Guide, creating an EKS cluster can be done using eksctl, the AWS console, or the aws cli. There are also other options, however typically each tool has a learning curve and requires some proficiency.
The Do framework strives to simplify DevOps and MLOps tasks by automating complex operations into intuitive action scripts. For example, instead of running an eksctl command with several command line arguments to create an EKS cluster, aws-do-eks provides an eks-create.sh script which wraps a collection of tools including eksctl and provides the end user with a simplified and intuitive experience. The only prerequisite needed to build and run this project is Docker. The main use case of this project is to specify a desired cluster configuration, then create or manage the EKS cluster by executing a script. This process is described in further detail below.
All necessary configuration items are centralized in two configuration files. The .env file in the project's root contains all project-specific items and is used when building and running the project container. The wd/conf/eks.conf file contains all EKS specific configuration items and is used when running the action scripts to create, scale, or delete your EKS cluster. Heterogeneous clusters are supported. In eks.conf you can specify the list of nodegroups to be added to the cluster and at what scale. AWS Credentials can be configured at the instance level through an instance role or injected into the container that runs aws-do-eks using volume or secrets mounting. To configure credentials, run aws configure. Credentials you configure on the host will be mounted into the aws-do-eks container according to the VOL_MAP setting in .env.
Alternatively to eks.conf you may use a cluster manifest file wd/conf/eks.yaml. To use the manifest file instead of eks.conf, set the CONFIG variable in eks.conf to yaml instead of conf. The advantage of using a manifest file for defining the cluster is that it supports advanced options, which are not available through eksctl. For example, enabling of EFA networking is only supported via the manifest file. All supported options in the manifest are documented in the eks.yaml schema.
This project follows the Depend on Docker template to build a container including all needed tools and utilities for creation and management of your EKS clusters. Please execute the ./build.sh script to create the aws-do-eks container image. If desired, the image name or registry address can be modified in the project configuration file .env.
The ./run.sh script starts the project container. After the container is started, use the ./exec.sh script to open a bash shell in the container. All necessary tools to allow creation, management, and operation of EKS are available in this shell.
Execute the ./eks-create.sh script to create the configured cluster. This operation will take a while as it involves creation of a VPC, Subnets, Autoscaling groups, the EKS cluster, its nodes and any other necessary resources. Upon successful completion of this process, your shell will be configured for kubectl access to the created EKS cluster.
To view the current status of the cluster execute the eks-status.sh script. It will display the cluster information as well as details about any CPU, GPU, Inferentia nodegroups and fargate profiles in the cluster.
To set the sizes of your cluster node groups, update the eks.conf file, then run ./eks-scale.sh.
To decomission your cluster and remove all AWS resources associated with it, execute the ./eks-delete.sh script. This is a destructive operation. If there is anything in your cluster that you need saved, please persist it outside of the cluster VPC before executing this script.
When you open a shell into a running aws-do-eks container via ./exec.sh, you will be able to execute kubectl, aws, and eksctl commands. There are other tools and shell customizations that are installed in the container for convenience.
- kubectx - show or set current Kubernetes context
- kubens - show or set current namespace
- kubetail - tail the logs of pods that have a name matching a specified pattern
- kubectl-node-shell - open an interactive shell into a kubernetes node using a privileged mode (Do not use in production)
- kubeps1 - customize shell prompt with cluster info
ll='ls -alh --color=auto'
k=kubectl
kc=kubectx
kn=kubens
kt=kubetail
ks=kube-shell
kon=kubeon
koff=kubeoff
The eks folder contains vpc, nodegroup, and fargateprofile subfolders. These subfolders contain module-level scripts that are used by the scripts in the main folder, however they can also be executed independently. To run one of those scripts independently, ensure that the environment variables tha are needed by the scripts are set before executing them. One way to do that is to source the eks.conf file. Running a module script individually will display information about any environment variables that are missing and could be defined with export ENV_VAR=value.
The deployment folder contains scripts for deploying system-level capabilities like cluster-autoscaler, aws-load-balancer-controller, horizontal-pod-autoscaler, etc. to the EKS cluster. If you would like cluster-autoscaler deployed automatically when the cluster is created, set CLUSTER_AUTOSCALER_DEPLOY="true" in eks.conf. To deploy the cluster-autoscaler to an EKS cluster that has already been created, change your current directory to deployment/cluster-autoscaler, then execute ./deploy-cluster-autoscaler.sh. Follow a similar pattern for other deployments.
The ops folder contains scripts for management and operation of workloads on the EKS cluster. The goal of these scripts is to provide shorthand for commonly used kubectl command lines.
The project home folder offers a number of additional scripts for management of the aws-do-eks container.
./login.sh- use the currently configured node aws settings to authenticate with the configured registry./push.sh- push aws-do-eks container image to configured registry./pull.sh- pull aws-do-eks container image from a configured existing registry./status.sh- show current status of aws-do-eks container./start.sh- start the aws-do-eks container if is currently in "Exited" status./stop.sh- stop and remove the aws-do-eks container./test.sh- run container unit tests
- eksctl authentication errors - execute "aws configure --profile <profile_name>" and provide access key id and secret access key to configure access.
Create a new profile, different than default:
aws configure --profile <profile-name>
Update kubeconfig with profile::
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region <region> --name <cluster-name> --profile <profile-name>
Check that <profile-name> is in ~/.kube/config
user:
exec:
apiVersion: client.authentication.k8s.io/v1alpha1
args:
- --region
- <region>
- eks
- get-token
- --cluster-name
- <cluster-name>
command: aws
env:
- name: AWS_PROFILE
value: <profile-name>
- timeouts from eksctl api - the cloudformation apis used by eksctl are throttled, normally eksctl will retry when a timeout occurs
- context deadline exceeded - when executing eksctl commands you may see this error message. In this case please retry running the same command after the failure occurs. The cloud formation stack may have completed successfully already, but that information may not be known to eksctl. Running the command again updates the status and checks if all necessary objects have been created.
See CONTRIBUTING for more information.
This library is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file.