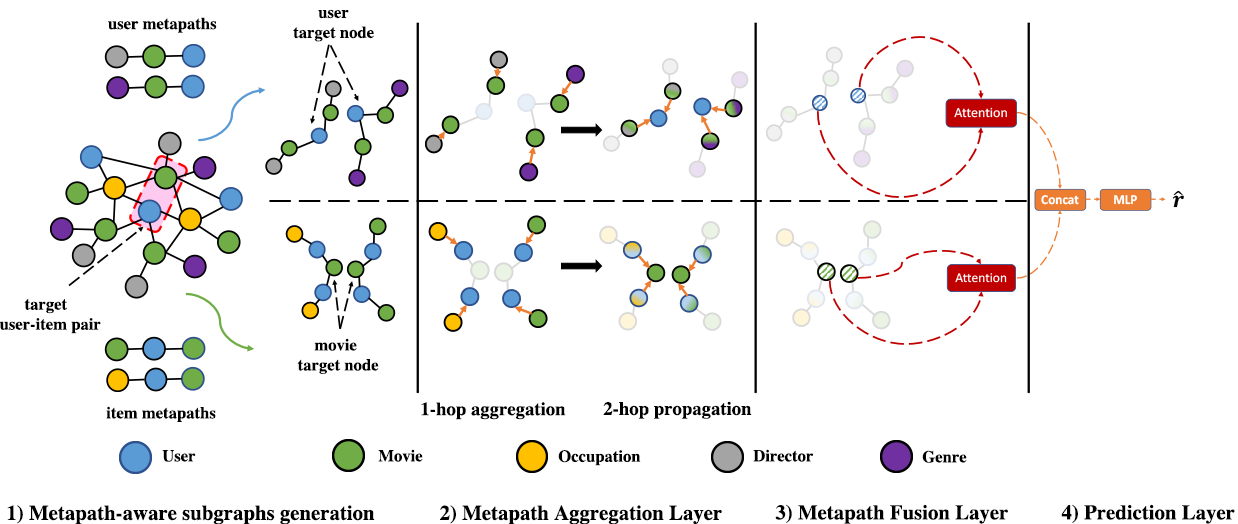
Integrating content information for user preference prediction remains a challenging task in the development of recommender systems. Due to the shallow structure, classic graph neural networks (GNNs) failed in modelling high-order graph structures that deliver critical insights of task relevant relations. A natural solution of capturing the inter- and intra-relations between content features and user-item pairs is to explore the high-order information encoded by metapaths, a set of composite relations designed for representing multi-hop structure and sequential semantics.
We propose Meta Path- and Entity-Aware Graph Neural Network (PEAGNN), a unified GNN framework tailored for recommendation tasks, which is capable of exploiting the rich semantics in metapaths. PEAGNN trains multilayer GNNs to perform metapath-aware information aggregation on collaborative subgraphs, h-hop subgraphs around the target user-item pairs. After the attentive fusion of aggregated information from different metapaths, a graph-level representation is then extracted for matching score prediction. To leverage the local structure of collaborative subgraphs, we present entity-awareness that regularizes node embedding with the presence of features in a contrastive manner. Further analysis indicates that trained PEAGNN automatically derives meaningful metapath combinations from the given metapaths.
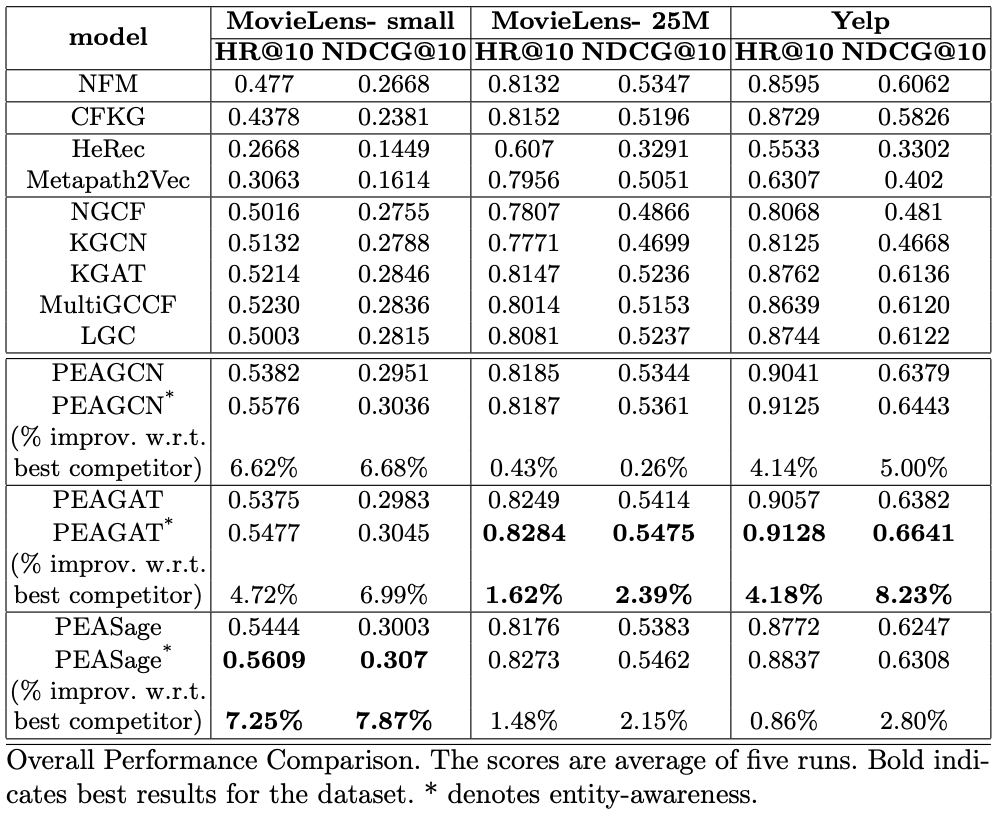
Our model is able to outperform the other competitive baselines on three public datasets, namely: MovieLens-small, MovieLens-25M and Yelp. We use Hit Ratio (HR) and Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG) metrics.
The performances of PEAGNN variants and baselines are presented below:
- Python 3.6
- PyTorch 1.5.1
- PyTorch Geometric 1.5.0
- Install all dependencies run
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
- our code can be installed by
python3 setup.py install
The basic skeleton of our source code will look like this :
├── datasets
│ └── Yelp
│ └── yelp_dataset.tar
├── experiments
│ ├── checkpoint
│ │ ├── data
│ │ │ ├── Movielenslatest-small
│ │ │ ├── Movielenslatest-25m
│ │ │ └── Yelp
│ │ ├── loggers
│ │ │ ├── Movielenslatest-small
│ │ │ ├── Movielenslatest-25m
│ │ │ └── Yelp
│ │ └── weights
│ │ ├── Movielenslatest-small
│ │ ├── Movielenslatest-25m
│ │ └── Yelp
│ ├── scripts
│ │ ├── **/*.ps1
│ └── **/*.py
├── graph_recsys_benchmark
│ ├── datasets
│ │ ├── **/*.py
│ ├── models
│ │ ├── **/*.py
│ ├── nn
│ │ ├── **/*.py
│ ├── parser
│ │ ├── **/*.py
│ ├── utils
│ │ ├── **/*.py
│ └── **/*.py
├── images
│ └── **/*.png
├── license.txt
├── README.md
├── requirements.txt
└── setup.pyThe code is based on PyTorch Geometric documentation.
experiments: contain experiment files for PEAGNN and baseline modelscheckpoint: contain processed data, logs and model weightsscripts: scripts to reproduce the results for each datasetdatasets: creates Heterogenous Information network for the datasetsmodels: creates PEAGNN and baseline modelsnn: contains convolutional networks for GNN based modelsparser: functions to parse the raw dataset filesutils: functions to save, load models and compute evaluation metrics
Dataset will be downloaded during experiment execution and saved in experiments/checkpoint/data folder. No need to explicity download the dataset. Weights of pre-trained Movielens-small dataset can be found here.
Download the dataset via this link and save yelp_dataset.tar in the datasets/Yelp folder.
Like MovieLens dataset, the extracted raw files will be saved in experiments/checkpoint/data folder during execution.
For training and testing PEAGNN and baseline models, pass the appropriate arguments to the experiments files.
To reproduce the benchmark results for particular dataset, use the arguments as mentioned in experiments/scripts folder.
For instance, for training PEAGAT model on MovieLens-small dataset run the following command:
python3 peagat_solver_bpr.py --dataset=Movielens --dataset_name=latest-small --num_core=10 --num_feat_core=10 --sampling_strategy=unseen --entity_aware=false --dropout=0 --emb_dim=64 --repr_dim=16 --hidden_size=64 --meta_path_steps=2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2 --entity_aware_coff=0.1 --init_eval=true --gpu_idx=0 --runs=5 --epochs=30 --batch_size=1024 --save_every_epoch=26 --metapath_test=false
For instance, for training PEAGAT model with entity awareness on MovieLens-small dataset run the following command:
python3 peagat_solver_bpr.py --dataset=Movielens --dataset_name=latest-small --num_core=10 --num_feat_core=10 --sampling_strategy=unseen --entity_aware=true --dropout=0 --emb_dim=64 --repr_dim=16 --hidden_size=64 --meta_path_steps=2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2 --entity_aware_coff=0.1 --init_eval=true --gpu_idx=0 --runs=5 --epochs=30 --batch_size=1024 --save_every_epoch=26 --metapath_test=true
For training other baselines e.g. KGAT on MovieLens-small dataset run the following command:
python3 kgat_solver_bpr.py --dataset=Movielens --dataset_name=latest-small --num_core=10 --num_feat_core=10 --sampling_strategy=unseen --entity_aware=false --dropout=0.1 --emb_dim=64 --hidden_size=64 --entity_aware_coff=0.1 --init_eval=false --gpu_idx=0 --runs=5 --epochs=30 --batch_size=1024 --save_every_epoch=26
The pre-trained models for all three datasets used in this paper can be accessed via this link.