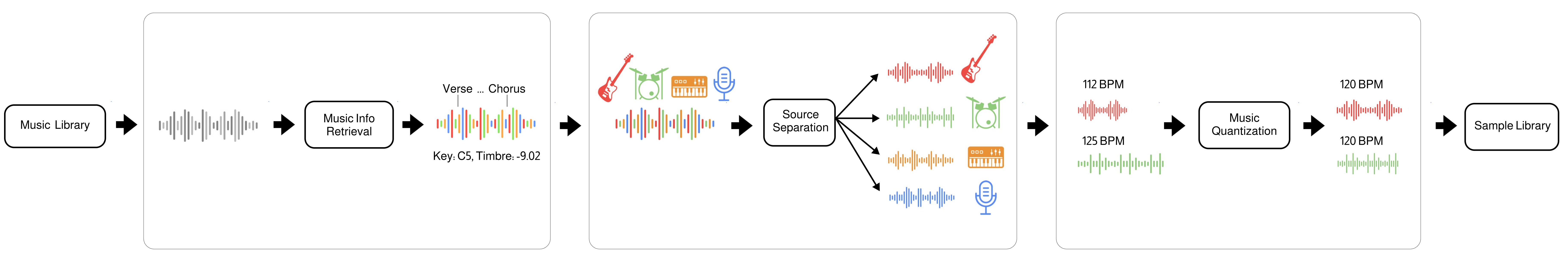
Polymath uses machine learning to convert any music library (e.g from Hard-Drive or YouTube) into a music production sample-library. The tool automatically separates songs into stems (beats, bass, etc.), quantizes them to the same tempo and beat-grid (e.g. 120bpm) and analyzes musical structure (e.g. verse, chorus, etc.), key (e.g C4, E3, etc.) and other infos (timbre, loudness, etc.). The result is a searchable sample library that streamlines the workflow for music producers, DJs, and ML audio developers.
Polymath makes it effortless to combine elements from different songs to create unique new compositions: Simply grab a beat from a Funkadelic track, a bassline from a Tito Puente piece, and fitting horns from a Fela Kuti song, and seamlessly integrate them into your DAW in record time. Using Polymath's search capability to discover related tracks, it is a breeze to create a polished, hour-long mash-up DJ set. For ML developers, Polymath simplifies the process of creating a large music dataset, for training generative models, etc.
- Music Source Separation is performed with the Demucs neural network
- Music Structure Segmentation/Labeling is performed with the sf_segmenter neural network
- Music Pitch Tracking and Key Detection are performed with Crepe neural network
- Music Quantization and Alignment are performed with pyrubberband
- Music Info retrieval and processing is performed with librosa
You will need at least Python 3.7. From your terminal run:
git clone https://github.com/samim23/polymath
cd polymath
pip install -r requirements.txtIf you are on MacOS, run these commands before installation:
pip install tensorflow-macos
pip install tensorflow-metalpython polymath.py -a n6DAqMFe97Epython polymath.py -a /path/to/audiolib/song.wavpython polymath.py -a n6DAqMFe97E,eaPzCHEQExs,RijB8wnJCN0
python polymath.py -a /path/to/audiolib/song1.wav,/path/to/audiolib/song2.wav
python polymath.py -a /path/to/audiolib/Songs are automatically analyzed once which takes some time. Once in the database, they can be access rapidly. The database is stored in the folder "/library/database.p". To reset everything, simply delete it.
Quantize a specific songs in the library to tempo 120 BPM (-q = database audio file ID, -t = tempo in BPM)
python polymath.py -q n6DAqMFe97E -t 120python polymath.py -q all -t 120python polymath.py -q n6DAqMFe97E -kSongs are automatically quantized to the same tempo and beat-grid and saved to the folder “/processed”.
Search for 10 similar songs based on a specific songs in the library (-s = database audio file ID, -sa = results amount)
python polymath.py -s n6DAqMFe97E -sa 10Search for similar songs based on a specific songs in the library and quantize all of them to tempo 120 BPM
python polymath.py -s n6DAqMFe97E -sa 10 -q all -t 120python polymath.py -s n6DAqMFe97E -sa 10 -q all -t 120 -st -kSimilar songs are automatically found and optionally quantized and saved to the folder "/processed". This makes it easy to create for example an hour long mix of songs that perfectly match one after the other.
The Demucs Neural Net has settings that can be adjusted in the python file
- bass
- drum
- guitare
- other
- piano
- vocalsThe audio feature extractors have settings that can be adjusted in the python file
- tempo
- duration
- timbre
- timbre_frames
- pitch
- pitch_frames
- intensity
- intensity_frames
- volume
- avg_volume
- loudness
- beats
- segments_boundaries
- segments_labels
- frequency_frames
- frequency
- keyPolymath is released under the MIT license as found in the LICENSE file.