A simple process profiler. propro can be used in many different ways. Conveniently it can be used on the command line:
$ propro --fmt=png <command>For more options, call:
$ propro --helpAnother option is to call the profiling programmatically:
import propro
x = propro.profile_cmd("ufig --background-type=chunked_map ufig.config.random")The returned profiling result can then, for instance, be used for custom plotting.
propro offers the option to profile a single Python function using a decorator:
import propro
import numpy as np
@propro.profile(sample_rate=0.1, fmt="txt")
def mem_hungry(size):
a = []
for i in range(size):
a.append(np.random.random())
b = []
for i in range(size):
t = []
for j in range(size):
t.append(i * a[j])
b.append(t)
b = np.array(b)The profiling output is stored in the folder where the Python code was launched.
Finally, propro can be embedded in your IPython notebooks. Load the extension with:
import propro
%load_ext proproThe profiling can be done on a line level:
%propro -r 0.1 load_pixels(path, PIXEL_COUNT)or on a cell level:
%%propro -r 0.1
X = np.random.normal(size=(200,200,1000))
P, D, Q = np.linalg.svd(X, full_matrices=False)
X_a = np.dot(np.dot(P, np.diag(D)), Q)
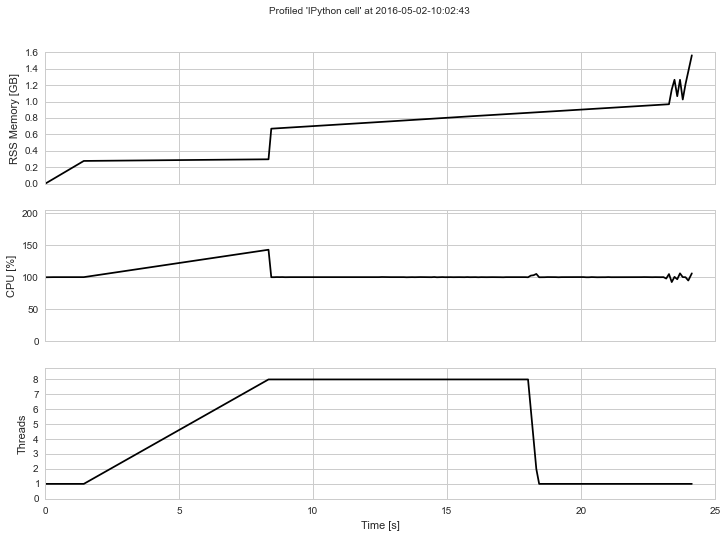
print(np.std(X), np.std(X_a), np.std(X - X_a))The output will look something like this if rendered into an image: