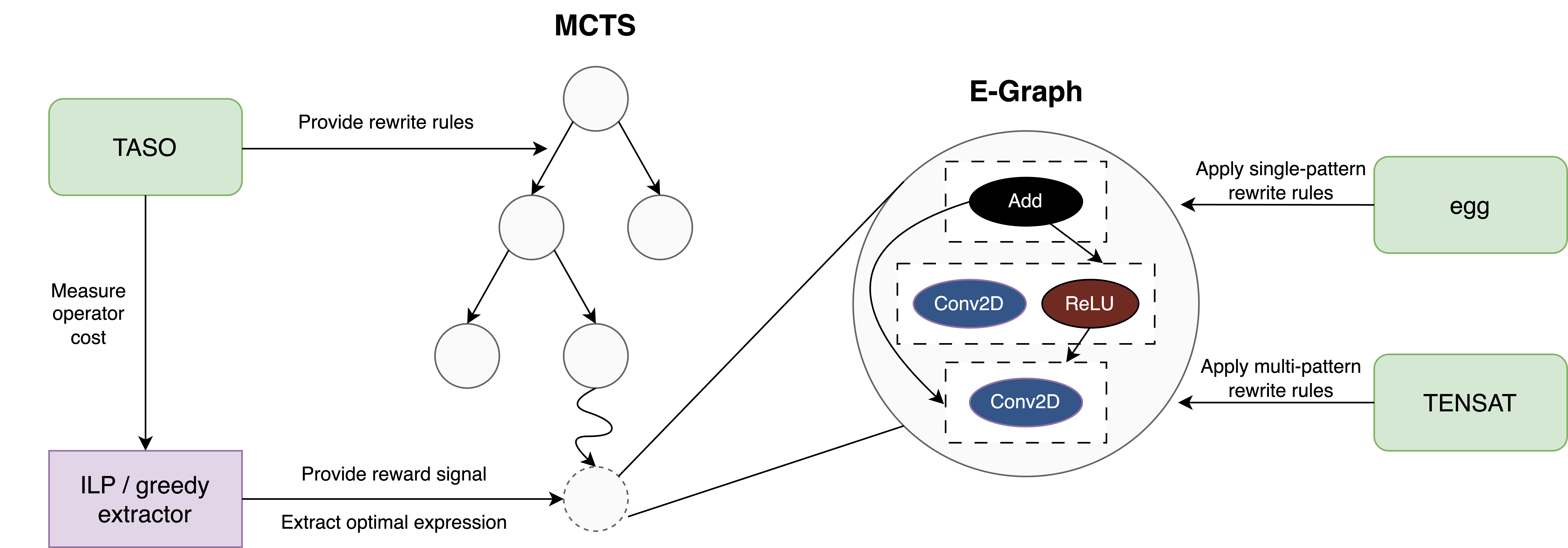
This repository accompanies the paper "Optimizing Tensor Computation Graphs with Equality Saturation and Monte Carlo Tree Search" which was submitted to the International Conference on Parallel Architectures and Compilation Techniques (PACT) 2024. The repository builds on top of four other projects:
- Z. Jia et al., TASO: Optimizing Deep Learning Computation with Automatic Generation of Graph Substitutions, SOSP ’19, 2019. TASO provides the rewrite rules, and measures the operator and graph runtimes on our hardware. We use this version of TASO without any modifications.
- M. Willsey et al., egg: Fast and extensible equality saturation, POPL, 2021. egg is the equality saturation framework underyling our work. We have slightly modified this version to fit our needs.
- Y. Yang et al., Equality Saturation for Tensor Graph Superoptimization, MLSys, 2021. TENSAT serves as our baseline and provides important functionality such as the application of multi-pattern rewrite rules. We have modified this version to implement, among other things, our proposed cost function.
- He et al., MCTS-GEB: Monte Carlo Tree Search is a Good E-graph Builder, EuroMLSys, 2023. Our tensor program optimizer is built on top of the Rust-based implementation of MCTS-GEB.
Below is an overview of our tensor program optimizer using equality saturation and MCTS. We have added TASO, egg, TENSAT, and rmcts as folders to this repository.
To run our optimizer, an NVIDIA GPU with appropriate drivers and the NVIDIA Container Toolkit are required. Below are three example setups that have been shown to work with our optimizer.
Setup 1
- Hardware:
- CPU: Intel Xeon Gold 6142 CPU @ 2.60GHz with 8 cores
- RAM: 64 GB
- GPU: NVIDIA P100 16GB
- Software:
- OS: Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- NVIDIA driver version: 525.125.06
- CUDA version: 12.0
Setup 2
- Hardware:
- CPU: Intel Xeon Silver 4210R CPU @ 2.40GHz with 8 cores
- RAM: 64 GB
- GPU: NVIDIA A100 80GB
- Software:
- OS: Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- NVIDIA driver version: 525.125.06
- CUDA version: 12.0
Setup 3
- Hardware:
- CPU: Intel Xeon CPU @ 2.20GHz with 6 cores
- RAM: 89 GB
- GPU: NVIDIA Tesla A100 40GB
- Software:
- OS: Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- NVIDIA driver version: 550.90.07
- CUDA version: 12.4
- Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/jakobhartmann/tensor-eqs-mcts.git - Change directory:
cd tensor-eqs-mcts/tensat/docker - Run the Dockerfile to install the dependencies:
docker build --tag tensat:1.0 . - In the
run_docker.shfile, change the source parameters to the correct folder paths. - Start the Docker container:
./run_docker.sh - Inside the Docker container, install TASO:
cd /usr/TASO mkdir -p build cd build cmake .. sudo make install -j10 cd /usr/TASO/python python setup.py install - Inside the Docker container, install the ILP solver:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install coinor-libcbc-dev
If you receive this error message libstdc++.so.6: version 'GLIBCXX_3.4.20' not found when trying to run the experiments, please follow the steps below to resolve the issue:
-
Find the latest version of the libstdc++ library. The version is probably 6.0.30.
find / -name "libstdc++.so*" -
Copy the respective file to the conda library folder.
cp /usr/lib32/libstdc++.so.6.0.30 /opt/conda/lib/ -
Remove the old versions and link the latest library.
cd /opt/conda/lib/ rm libstdc++.so.6.0.29 rm libstdc++.so.6.0 ln -s libstdc++.so.6.0.30 libstdc++.so.6
If you receive a Cuda failure: 804 error message when trying to run the experiments, please use the driver and CUDA versions from one of the setups listed above.
- In our experiments, we evaluate a) our proposed cost function for greedy extractors and b) compare the performance of our tensor program optimizer to TENSAT. We use the following neural networks architectures as benchmarks: BERT, Inception-v3, MobileNet-v2, NASNet-A, NASRNN, ResNet-50, ResNeXt-50, SqueezeNet, and VGG-19. All neural networks are included in this repository. We repeat all experiments five times to account for the randomness of MCTS and the stochasticity of the cost model.
- To run our optimizer with the default settings, use
/usr/rmcts/run_experiments.sh. The script will automatically run experiments across different cost functions, neural network architectures, and seeds. The hyperparameters of our optimizer can be changed in/usr/rmcts/src/main.rs. - For TENSAT, use
/usr/tensat/run_exp_main.shto automatically run all experiments with the default settings. The hyperparameters can be changed in the script.
-
The experimental results for TENSAT are saved in
/usr/experiments/tensatand follow the naming convention{model}_{k_multi}_{run}. Each folder contains the following files:stats.txt: Optimization results including original graph runtime, optimized graph runtime, and optimization time.iteration_data.txt: Detailed information for each iteration including which single-pattern rewrite rules were applied to the e-graph.hook_iteration_data.txt: Information for each iteration on which multi-pattern rewrite rules were applied to the e-graph.start.modelandoptimized.model: Serialized version of the input and output tensor program.start.svgandext.svg: Visualization of the original and final e-graph.settings.txt: Settings for the experiment.ilp_data_main.jsonandsolved_main.json: Files used and outputed by the ILP solver.
-
The experimental results for our optimizer are saved in
/usr/experiments/tensor_eqs_mcts. Each folder corresponds to a combination of main and final extraction method and each subfolder corresponds to one model and seed. Each subfolder contains the following files:rmcts_stats.txt: Optimization results including original graph runtime, optimized graph runtime, and optimization time.rmcts_iteration_data.txt: Detailed information for each MCTS iteration including which single- and multi-pattern rewrite rules were applied to the e-graph.start.modelandoptimized.model: Serialized version of the input and output tensor program.start.svgandext.svg: Visualization of the original and final e-graph.settings.txt: Settings for the experiment.ilp: The folder includes files used and outputed by the ILP solver. Only present for experiments that use an ILP solver.
-
This Juyper notebook can be used to analyze the experimental results and reproduce the Tables and Figures in our paper. To use the notebook, please follow the steps below. We recommend to run these steps on the host machine outside the Docker container.
-
Ensure you have Python >=3.8 installed. You can download different versions of Python here.
python -V -
Install virtualenv:
pip install virtualenv -
Change directory:
cd tensor-eqs-mcts/experiments -
Create a virtual environment:
virtualenv venv -
Activate the virtual environment:
source venv/bin/activate -
Install the dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt -
Follow the instructions in the Juyper notebook.
-
-
If you had to restart the experiments, it is possible that the
.txtresult files contain duplicates. This can cause the JSON decoder in the analysis notebook to throw an error. You can use this Juyper notebook to deduplicate the data.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. However, it includes components that are licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
- egg is licensed under the MIT License. See egg/LICENSE for details.
- TENSAT is licensed under the MIT License. See tensat/LICENSE for details.
- rmcts is licensed under the MIT License. See rmcts/LICENSE for details.
- TASO is licensed under the Apache License 2.0. See TASO/LICENSE for details.
Please consult the specific LICENSE file in each project directory for the full terms of that project's license.