Watt is a runtime for executing Rust procedural macros compiled as WebAssembly.
I assume you are familiar with watt, dtolnay's crate for executing procedural macros in a web assembly interpreter.
There, tooling improvements are listed as remaining work, and this cargo subcommand aims to achieve that. Its purposes are
- compile existing proc-macro crates without manual intervention for the watt runtime
- verify that a wasm file is compiled from a particular source
A list of some popular procedural macros compiled with cargo watt is available here.
To use cargo watt you will need to install rustc's wasm32 toolchain:
$ rustup target add wasm32-unknown-unknownAlso, for optimizing the size of the wasm-file, wasm-strip (wabt) and wasm-opt (binaryen) will be used. To opt out, use --no-wasm-opt or --no-wasm-strip.
Building works by first copying a crate (either from a local directory, a git repository or crates.io) into /tmp.
The crate type is then changed to cdylib, proc-macro2 is being patched to dtolnay's proc_macro2.
Next, all procedural macros in it are being replaced with pub #[no_mangle] extern "C" fns and proc_macro is replaced with proc_macro2, see this.
At this point, simple crates already compile, but there is more to be done to support a wider range of crates. Since we just change some signatures and hope for the best, sometimes stuff stops working. To 'fix' that (altough it's more of a hack), we do the following:
- replace
synwith this syn patch, which basically has all instances ofproc_macroreplaced withproc_macro2(see here) and the conditional compilation forwasm32-unknown-unknownis removed - do a literal search and replace of
proc_macrotoproc_macro2. This may sound stupid, but in my testing this works alright.
Of course, some crates still don't compile, in that case you need tweak things yourself.
Notably, anything depending on synstructure or proc_macro_error won't work, maybe patches for those will be provided in the future aswell.
Lastly, a shim crate is generated which calls into the generated web assembly file and executes the token tree transformation.
As a user, all you need to do is
$ cargo watt build --crate serde-derive
INFO cargo_watt > download crate 'serde-derive' into temporary directory...
INFO cargo_watt > begin compiling crate...
Updating git repository `https://github.com/dtolnay/watt`
Updating git repository `https://github.com/jakobhellermann/syn-watt`
Updating crates.io index
Compiling syn v1.0.22 (https://github.com/jakobhellermann/syn-watt#0f0ace5e)
Compiling serde_derive v1.0.110 (/tmp/cargo-watt-crate)
Finished release [optimized] target(s) in 19.65s
INFO cargo_watt > finished in 19.65s
INFO cargo_watt > compiled wasm file is 2.65mb large
INFO cargo_watt > generated crate in "serde_derive-watt"Alternatively you can fetch a git repository (cargo watt build --git https://github.com/idanarye/rust-typed-builder) or use a local path (cargo watt build ./path/to/crate).
By default, cargo watt will include all files of original crate (i.e. tests, documentation etc.) in the newly generated one.
If you'd like to only have Cargo.toml, src/lib.rs and src/the-macro.wasm there is the --only-copy-essential option.
Some proc-macro crates need to export other things then the actual macros, so they are split into a regular rust crate exporting some Traits/Functions, which then reexports the macros from another crate.
This is why for example cargo watt --crate thiserror will tell you that thiserror is not a proc macro crate. Instead, what you need to do is run cargo watt --crate thiserror-impl and [patch] thiserror-impl to your generated crate.
Also, if the syn version specified in the Cargo.lock file is newer than my patched version, that will result in a compilation error.
In most cases updating is as easy as rebasing the fork on upstream, but there should be some kind of automation for that which there isn't so far.
The isolation properties of running the macro inside web assembly ensure that it doesn't have unwanted access to files or the network, but the code it generates can still be mailcious. Therefor it is important to be able to verify that a compiled binary wasm file was indeed compiled by some source, which can then be audited manually.
Just as the build subcommand, cargo watt verify works with local projects, remote git repos and crates.io crates, you can use it like this:
$ cargo watt build --crate serde-derive
...
$ cargo watt verify serde-derive_watt/src/serde-derive.wasm --crate serde-derive
INFO cargo_watt::wasm > finished in 17.3s
Success!Currently though, a crate compiled an linux will be different than on macos. If you know why this is and how to fix it, let me know.
$ cargo install cargo-wattHow much of a difference does this make regarding compile times?
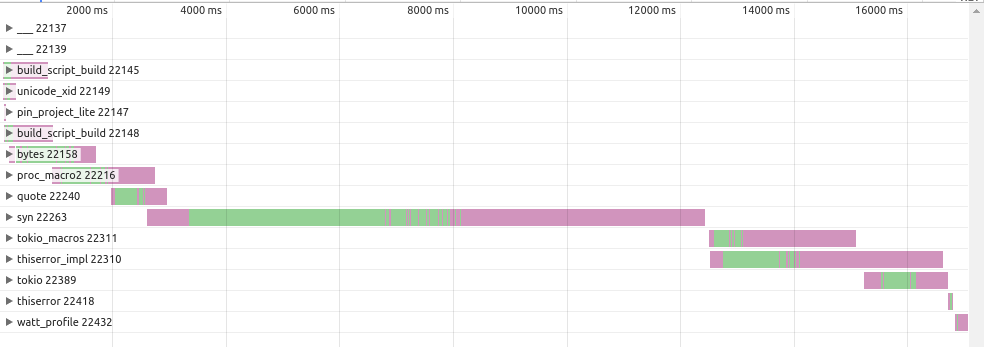
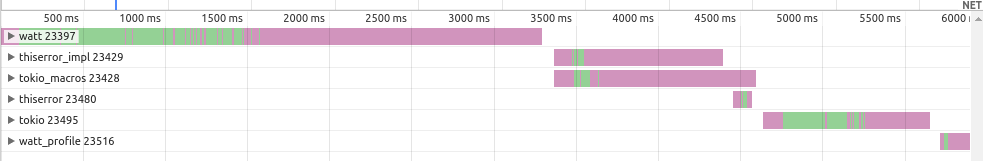
I profiled a crate with the following dependencies:
tokio = { version = "0.2", features = ["macros"] }
thiserror = "1.0"
[patch.crates-io]
tokio-macros = { git = "https://github.com/jakobhellermann/watt-contrib" }
thiserror-impl = { git = "https://github.com/jakobhellermann/watt-contrib" }Without the patches:
With patches:
That's a difference of 6 seconds vs 17 seconds, so not bad. Of course, in a real project you're gonna have a more non-macro crates so the speed-up is less noticable, but it's still faster.
MIT © Jakob Hellermann