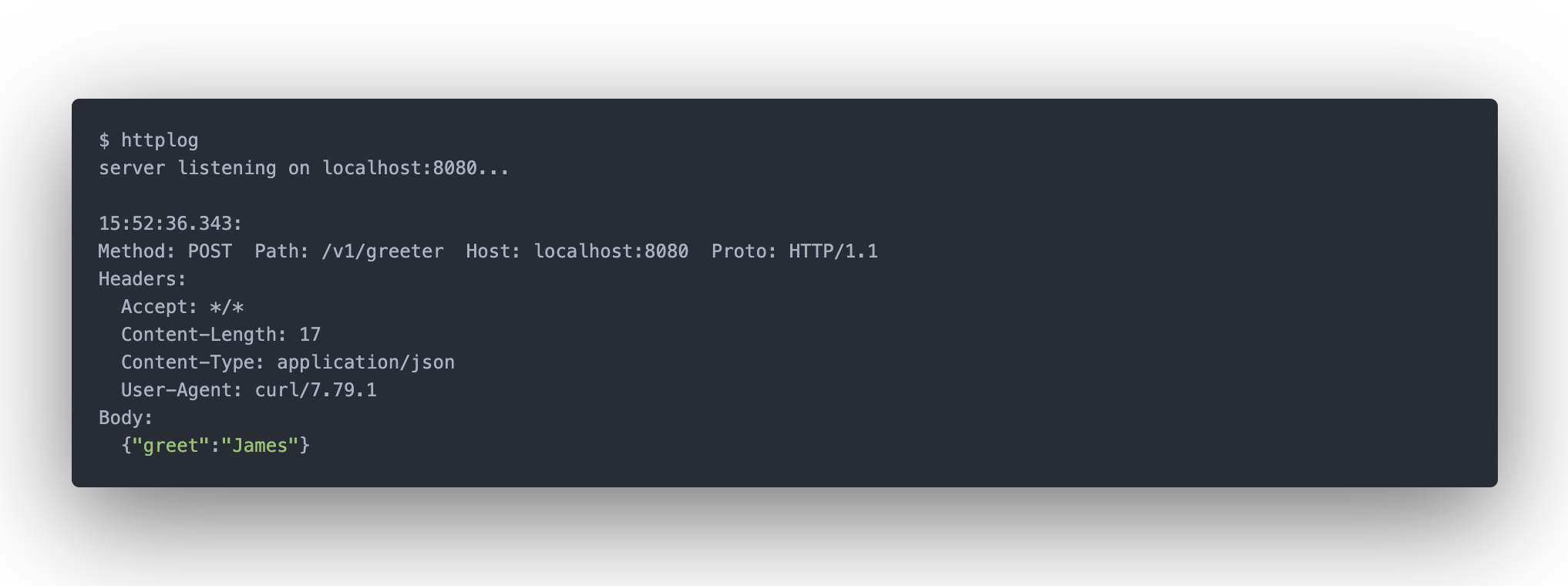
httplog is a command line tool that launches a local HTTP server that logs all requests it receives, replying with a canned response.
Either download a pre-built binary, or install from source (requires Go 1.19+):
go install github.com/jamescun/httplogAlternatively on macOS, you can install httplog using the Homebrew package manager:
brew install jamescun/formulas/httploghttplog v1.0.2
httplog is a command line tool that launches a local HTTP server that logs all
requests it receives, replying with a canned response.
Usage: httplog [options...]
Options:
--help show helpful information
--listen <host:port> configure the listening address for the HTTP
server (default localhost:8080)
--response <text> configure the canned body sent in response to
all requests (default none)
--response-code <code> configure the HTTP status code sent in response
to all requests (default 200)
--response-header <X=Y> configure one or more headers to be sent in the
response, may be specified more than once
--json log all requests as JSON rather than human
readable text
--tls-self-cert enable TLS with a self-signed certificate
### Examples
Run with no options, a server will be launched on localhost:8080, answering no body and an HTTP 200 status code to all requests.
To configure the HTTP status code, use the --response-code <code> option, i.e. for a HTTP 500 Internal Server code:
$ httplog --response-code 500
$ curl -v http://localhost:8080
HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server ErrorTo configure the response body, use the --response <text> option, i.e. to responsd the text hello world to all requests:
$ httplog --response "hello world"
$ curl http://localhost:8080
Hello WorldIf you would prefer JSON output, rather than human-readable text, use the --json option.