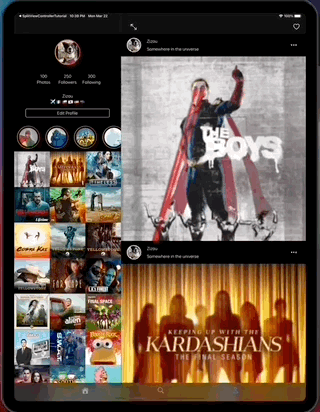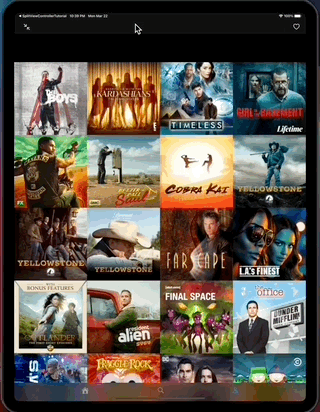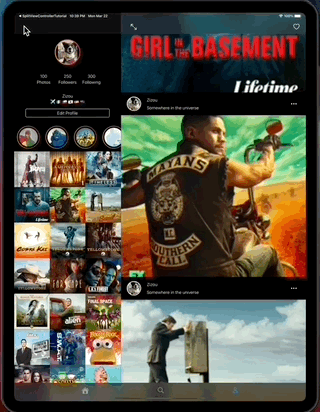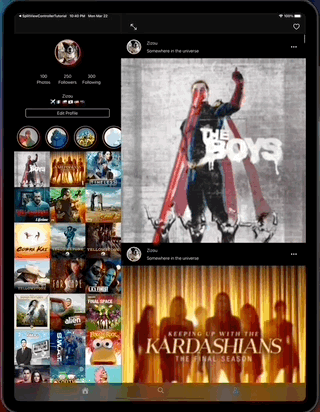
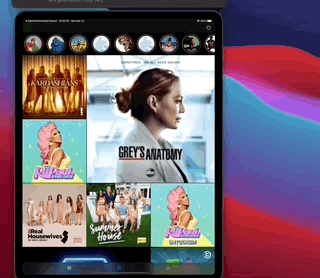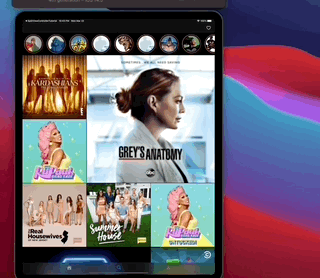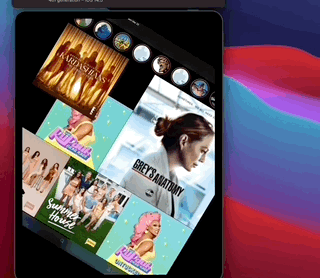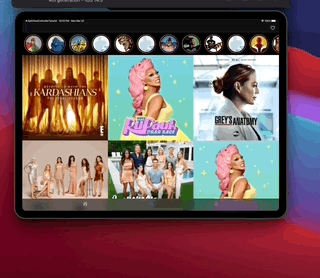
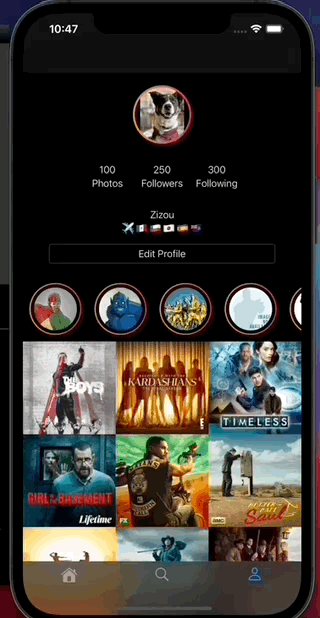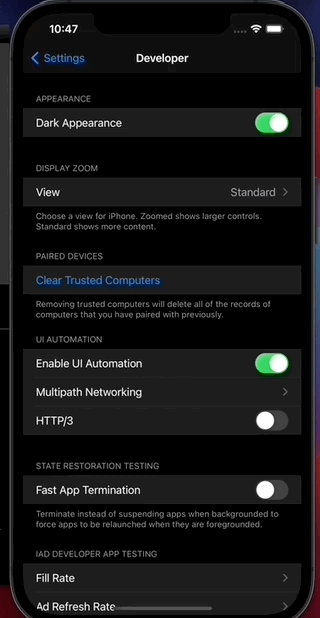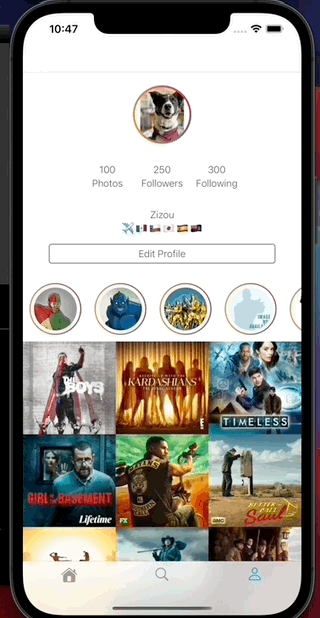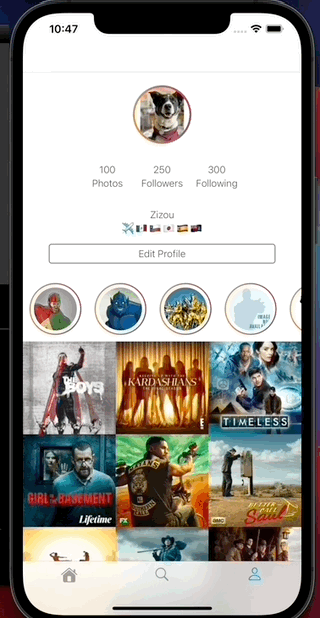
SimpleFeed App is a simple app that uses the RSS Feed Itunes Generator API and Marvel API to display feeds with layouts that adapts to iPad and iPhone, taking advantage of generics, protocols, meta types and enums to create reusable components.
Its main purpose is to build a project using some concepts from my personal blog posts where I will like to highlight:
- Using Generics and Protocols to create Reusable UI
- Using Generics and Protocols to create Reusable Networking layers
- Adapting your App for iPad and iPhone
- iOS 13.0 or later
- Supports Dynamic layout for iPad and iPhone.
- Supports adapting UI to any kind of custom layout.
- Uses MarvelClient a personal Swift Package that fetches data from Marvel API.
- Fetches data from RSS Feed Generator API's.
- Supports Dark mode.
- Supports insert/delete of sections and cell identifiers.
- Swift
- Combine
- Diffable Data Source
- Compositional Layout
- Swift Package.
- (Disclaimer, this project uses SDWebImage framework for loading images, it was used for convenience and because the project is not intended to showcase best way to load images. 🤷🏽♂️
- MVVM and Combine.
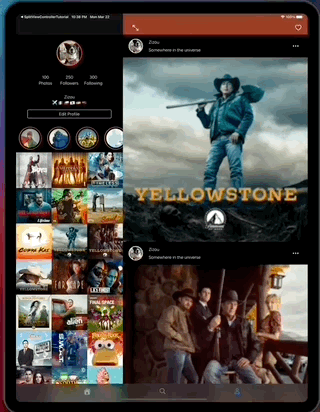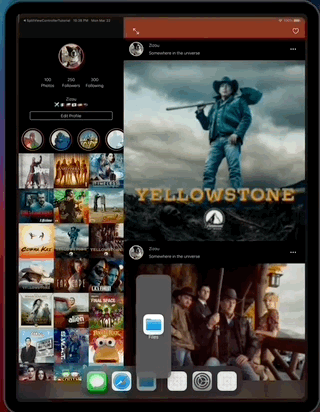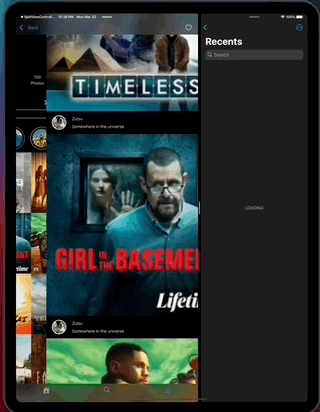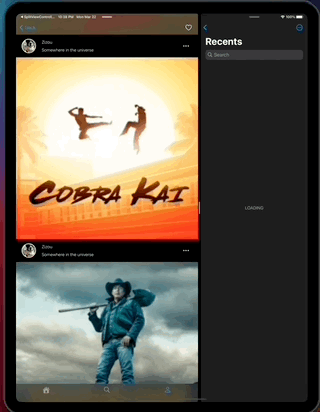
The app displays a feed of items from the RSS itunes API and uses the Marvel API to display content in headers.
The app Uses a Tab bar controller as main root, each of its tabs display a view controller sub class of GenericFeedViewController the super class definition looks like this:
class GenericFeedViewController<Content: SectionIdentifierViewModel, Remote: RemoteObservableObject>: ViewController {
}- This class inherits from
ViewControllerwhich is in charge of the theming of the app. - This view controller contains a
DiffableCollectionView<SectionContentViewModel: SectionIdentifierViewModel>view, which is the one that displays the items in a collectionview. - This class has two generic constraints,
RemoteObservableObjectwhich is an object that conforms toObservableObjectand its in charge of providing the updated content, andSectionIdentifierViewModelwhich is in charge of displaying the content.
SectionIdentifierViewModel is a PAT that represents the structure of a section in a collectionview its definition looks like this...
protocol SectionIdentifierViewModel {
associatedtype SectionIdentifier: Hashable <- A section in a diffable Collection view.
associatedtype CellIdentifier: Hashable <- A model in a section.
var sectionIdentifier: SectionIdentifier { get }
var cellIdentifiers: [CellIdentifier] { get }
}RemoteObservableObject is a protocol that inherits from ObservableObject its definition looks like this...
protocol RemoteObservableObject : ObservableObject {
init()
}For Example, for the home feed view controller we will display a feed of items using the itunes music endpoint...
1 - Create an instance that inherits from GenericFeedViewController and declare the types for the two generic constraints.
/// A
// MARK:- Home Feed Diffable Section Identifier
enum HomeFeedSectionIdentifier {
case popular
case adds
}
/// C
final class HomeViewController: GenericFeedViewController<HomeViewController.SectionModel, ItunesRemote> {
// MARK:- Section ViewModel
/// - Typealias that describes the structure of a section in the Home feed.
/// B
typealias SectionModel = GenericSectionIdentifierViewModel<HomeFeedSectionIdentifier, FeedItemViewModel>
...
}- A) Define the section identifier, it can be anything as long it conforms to
Hashable - B) Define the types of an object that conforms to
SectionIdentifierViewModel, we can find a generic object in the repo that conforms to this protocol its definition looks like this...
struct GenericSectionIdentifierViewModel<SectionIdentifier: Hashable, CellIdentifier: Hashable>: SectionIdentifierViewModel {
/// The Hashable Section identifier in a Diffable CollectionView
public let sectionIdentifier: SectionIdentifier
/// The Hashable section items in a Section in a Diffable CollectionView
public var cellIdentifiers: [CellIdentifier]
}You can use it or create your own, the benefit of this approach is that you can reuse this type, it has 2 generic constraints and we need to fill those placeholders, with the types that we want to use, for example, for the HomeViewController we want HomeFeedSectionIdentifier as a section identifier and a FeedItemViewModel as a cell identifier.
- C) Now that we have the type definition for the sections we can use it to define the types for the view controller, here we will use the section we defined in point B and also the
ItunesRemotewhich provides different kind of data like apps, apple books, movies, podcasts etc.
With the types defined we can now fetch the object from the remote, configure cells and supplementary views and display the data in the collection view, the full implementation of a simple feed looks like this...
/// A
enum HomeFeedSectionIdentifier {
case popular
}
/// C
final class HomeViewController: GenericFeedViewController<HomeFeedSectionModel.SectionModel, ItunesRemote> {
/// B
typealias SectionModel = GenericSectionIdentifierViewModel<HomeFeedSectionIdentifier, FeedItemViewModel>
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
}
override func fetchData() {
/// D
remote.fetch(.itunesMusic(feedType: .recentReleases(genre: .all), limit: 100))
}
override func setUpUI() {
/// E
collectionView.cellProvider { collectionView, indexPath, model in
collectionView.dequeueAndConfigureReusableCell(with: model, at: indexPath) as ArtworkCell
}
/// F
collectionView.assignHedearFooter { collectionView, model, kind, indexPath in
switch model {
case .popular:
/// G
let reusableView: HomeFeedSupplementaryView = collectionView.dequeueAndConfigureSuplementaryView(with: model, of: kind, at: indexPath)
reusableView.layout = HorizontalLayoutKind.horizontalStorySnippetLayout.layout
return reusableView
default:
assert(false, "Section identifier \(String(describing: model)) not implemented \(self)")
return UICollectionReusableView()
}
}
}
override func updateUI() {
/// H
remote.$sectionFeedViewModels.sink { [weak self] models in
guard let self = self else { return }
self.collectionView.content {
/// I
SectionModel(sectionIdentifier: .popular, cellIdentifiers: models)
}
}.store(in: &cancellables)
}
}- A) Define the section identifier for a Diffable DataSource, it can be anything as long it conforms to
Hashable - B) Define the type that conforms to
SectionIdentifierViewModel - C) Subclass
GenericFeedViewControllerand define the constraints, here it will useHomeFeedSectionModel.SectionModelas a section, and theItunesRemoteobject to fetch itunes feed data. - D) Call the remote fetch request,
ItunesRemoteuses theItunesClientclass that uses generics, protocols and meta types to decode from apps to podcasts. - E) Here we define the cell,
- F) Here we define the headers, footers for the collection view, this will work based on the layout definition, if the layout asked for a footer the view returned here will be placed as a footer, to give an example.
- G) Use the section identifier to switch and provide a certain header or footer for a section.
- H) Use the
Publisherto get the content for updating the UI. - I) DiffableCollectionView uses a function builder that expects
SectionModelobjects.
For more about generic UI you can go to:
- Advanced Generics to create reusable UI
- Using Generic code in UIKit to construct a compositional List in SwiftUI
Itunes Client uses CombineAPI its architechture uses Combine to perform networking requests and publish changes.
The Itunes RSS feed loads from apps, to movies and we can fetch any kind of data by using generic code like this...
public struct Author: Decodable {
let name: String
let uri: String
}
public protocol ItunesResource: Decodable {
associatedtype Model
var title: String? { get }
var id: String? { get }
var author: Author? { get }
var copyright: String? { get }
var country: String? { get }
var icon: String? { get }
var updated: String? { get }
var results: [Model]? { get }
}
public struct ItunesResources<Model: Decodable>: ItunesResource {
public let title: String?
public let id: String?
public let author: Author?
public let copyright: String?
public let country: String?
public let icon: String?
public let updated: String?
public let results: [Model]?
}
public protocol FeedProtocol: Decodable {
associatedtype FeedResource: ItunesResource
var feed: FeedResource? { get }
}
public struct Feed<FeedResource: ItunesResource>: FeedProtocol {
public let feed: FeedResource?
}We can also model the paths for a certain request using enums, like this...
enum MediaType {
case appleMusic(feedType: AppleMusicFeedType, limit: Int)
case itunesMusic(feedType: ItunesMusicFeedType, limit: Int)
case apps(feedType: AppsFeedType, limit: Int)
case audioBooks(feedType: AudioBooksFeedType, limit: Int)
case books(feedType: BooksFeedType, limit: Int)
case tvShows(feedType: TVShowFeedType, limit: Int)
case movies(feedType: MovieFeedType, limit: Int)
case podcast(feedType: PodcastFeedType, limit: Int)
case musicVideos(feedType: MusicVideoFeedType, limit: Int)
var path: String {
switch self {
case .appleMusic(let feedType, let limit): return "/apple-music/\(feedType.path)/\(limit)/explicit.json"
case .itunesMusic(let feedType, let limit): return "/itunes-music/\(feedType.path)/\(limit)/explicit.json"
case .apps(let feedType, let limit): return "/ios-apps/\(feedType.path)/\(limit)/explicit.json"
case .audioBooks(let feedType, let limit): return "/audiobooks/\(feedType.path)/\(limit)/explicit.json"
case .books(let feedType, let limit): return "/books/\(feedType.path)/\(limit)/explicit.json"
case .tvShows(let feedType, let limit): return "/tv-shows/\(feedType.path)/\(limit)/explicit.json"
case .movies(let feedType, let limit): return "/movies/\(feedType.path)/\(limit)/explicit.json"
case .podcast(let feedType, let limit): return "/podcasts/\(feedType.path)/\(limit)/explicit.json"
case .musicVideos(let feedType, let limit): return "/music-videos/\(feedType.path)/\(limit)/explicit.json"
}
}
}
.....more.....The method to perform a request will look as simple as this...
func fetch(_ mediaType: MediaType) {
cancellable = service.fetch(Feed<ItunesResources<FeedItem>>.self, mediaType: mediaType).sink(receiveCompletion: { value in
}, receiveValue: { [weak self] resource in
/// the resource...
})
}But even better it will look very descriptive at the moment of consumption...
remote.fetch(.itunesMusic(feedType: .recentReleases(genre: .all), limit: 100))
/// you can read this and understand what you are requesting.For more of generic networking you can go...
- Generic Networking layer using Combine in SwiftUI
- Advanced Generics and protocols in Swift <- Explains how to model decodable objects to avoid code duplication.
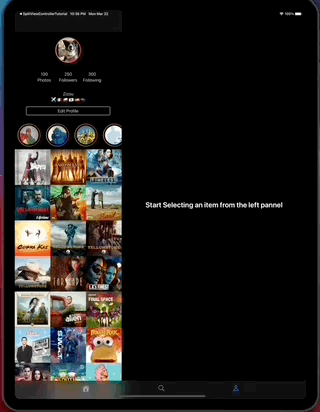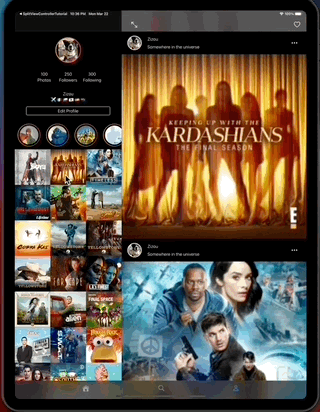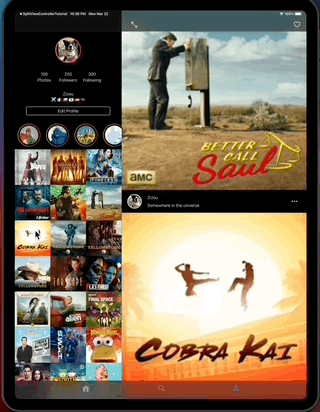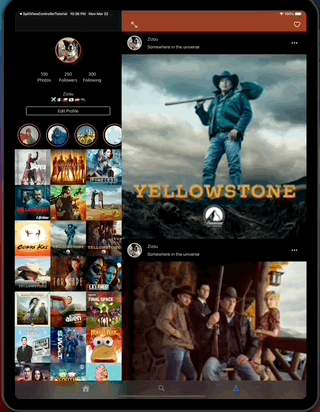
This app also contains layout implementations that supports iPad and iPhone on different contexts including iPad multitasking, the result looks like this...
- The app on iPad.
- Navigation to a selected feed item, on expanded mode.
- Navigation to a selected feed item, on collapsed mode.
- Adaptive your layout to split view controller display mode changes.
- Adapt your layout on trait collection changes
- Adapt your layout on device orientation
- The app in iPhone
- Dark/Light Mode
More on Building for iPad you can go:
- [] Fix Some layout bugs.