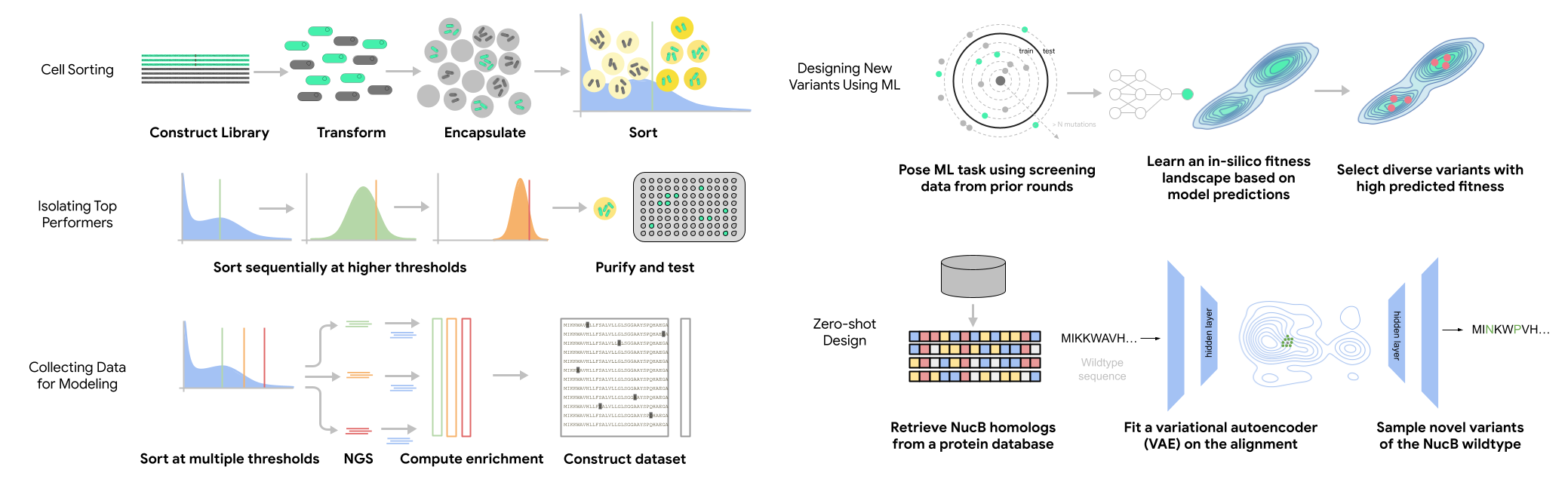
This repository accompanies the paper: Engineering highly active and diverse nuclease enzymes by combining machine learning and ultra-high-throughput screening
You can use our dataset of estimated enzyme activity for 55,760 NucB variants to develop new machine learning models or to generate new insights about NucB.
A simple notebook has been provided to load and analyze the data:
All figures and tables in the paper can be reproduced by notebooks in notebooks/.
Each notebooks can be run as-is, since it loads pre-computed enrichment factor data from GCS (see below). To regenerate the analysis from the raw NGS count data, run
get_enrichment_factor_data.ipynb
with a local value of LOCAL_OUTPUT_DATA_DIR.
These notebooks, and the library code they call, can be used to dig deeper into our results or to provide a jumping-off point for creating your own genotype-phenotype dataset based on count data from high-throughput sorting.
Some useful starting points:
- Analyze the hit rates of various library design methods
- Analyze the diversity of hits from these libraries
- Play with the CNN model used for the final round of sequence design
All data is available in a Google cloud storage (GCS) bucket. We don't recommend directly downloading it; the above scripts use helper functions for loading from the bucket.
The bucket contains the following sub-directories:
-
raw_count_data: raw NGS count data for pre-sort and post-sort populations. -
processed_fiducial_data: enrichment factors for synonyms of various 'fiducial' sequences. Each row represents a distinct DNA sequence that translates to the same amino acid sequence. -
processed_data: enrichment factors computed from the raw count data and the processed fiducial data. Each row represents a unique amino acid sequence. For each row and each fiducial, the row is assigned a p-value for observing its enrichment factor under the null distribution of enrichment factors from the fiducial. -
processed_data/landscape.csv: A single file that merges data from all 4 rounds of experiments and provides a multi-class catalytic activity labels for 56K distinct amino acid sequences. -
plate_data: Data from the low-throughput purified protein experiments used to confirm hits. -
library_designs: A mapping from amino acid sequences to the list of the names of the sub-libraries (corresponding to different sequence design methods) that proposed it. Note that some sequences were proposed by multiple methods. -
analysis: Data used for creating certain tables and results in the paper that require expensive computations, such as clustering hits in order to quantify diversity. -
alignments: A multiple sequence alignment used to fit our VAE model.
The notebooks directly install this package from GitHub, so no installation is necessary. However, you can locally install this package in order to run tests using the following commands:
Note that our package requires python >= 3.10.
venv=/tmp/nuclease_design_venv
python3 -m venv $venv
source $venv/bin/activate
pip install -e .
python -m pytest nuclease_design/*test.py
Please cite the accompanying paper:
@article {thomasbelanger2024,
author = {Neil Thomas and David Belanger and Chenling Xu and Hanson Lee and Kat Hirano and Kosuke Iwai and Vanja Polic and Kendra D Nyberg and Kevin Hoff and Lucas Frenz and Charlie A Emrich and Jun W Kim and Mariya Chavarha and Abi Ramanan and Jeremy J Agresti and Lucy J Colwell},
title = {Engineering of highly active and diverse nuclease enzymes by combining machine learning and ultra-high-throughput screening},,
year = {2024},
doi = {10.1101/2024.03.21.585615},
journal = {bioRxiv}
}
Copyright 2023 DeepMind Technologies Limited
All software is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (Apache 2.0); you may not use this file except in compliance with the Apache 2.0 license. You may obtain a copy of the Apache 2.0 license at: https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
All other materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY). You may obtain a copy of the CC-BY license at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, all software and materials distributed here under the Apache 2.0 or CC-BY licenses are distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the licenses for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under those licenses.
This is not an official Google product.