This project demonstrates usage of the New Relic Java agent distributed tracing APIs. In this example, we use Java agent APIs to propagate W3C Trace Context headers (transported over Kafka records) between two SpringBoot services resulting in them being linked together in a distributed trace.
The Java agent's Spring instrumentation automatically starts a
transaction when the kafka/produce (GET) controller route in the kafka-producer service is executed. This controller creates a Kafka record, generates W3C
Trace Context headers and inserts them into a map of headers using the insertDistributedTraceHeaders(Headers headers) API, finally it manually retrieves the
W3C headers and inserts them into the Kafka record headers before publishing the record to a Kafka broker.
/**
* This method illustrates usage of New Relic Java agent APIs for propagating distributed tracing headers over Kafka records.
* NewRelic.getAgent().getTransaction().insertDistributedTraceHeaders(Headers) is used to generate distributed tracing headers and insert them into
* a provided Headers map. This API generates a New Relic header (`newrelic`) as well as W3C Trace Context headers (`traceparent`, `tracestate`).
*
* @param producerRecord Kafka record
*/
@Trace
private void addDistributedTraceHeadersToKafkaRecord(ProducerRecord<String, String> producerRecord) {
// ConcurrentHashMapHeaders provides a concrete implementation of com.newrelic.api.agent.Headers
Headers distributedTraceHeaders = ConcurrentHashMapHeaders.build(HeaderType.MESSAGE);
// Generate W3C Trace Context headers and insert them into the distributedTraceHeaders map
NewRelic.getAgent().getTransaction().insertDistributedTraceHeaders(distributedTraceHeaders);
// Retrieve the generated W3C Trace Context headers and insert them into the ProducerRecord headers
if (distributedTraceHeaders.containsHeader(W3C_TRACE_PARENT)) {
producerRecord.headers().add(W3C_TRACE_PARENT, distributedTraceHeaders.getHeader(W3C_TRACE_PARENT).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
if (distributedTraceHeaders.containsHeader(W3C_TRACE_STATE)) {
producerRecord.headers().add(W3C_TRACE_STATE, distributedTraceHeaders.getHeader(W3C_TRACE_STATE).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}Additionally, the agent's Kafka client instrumentation
automatically applies to the Kafka producer client and generates a span named MessageBroker/Kafka/Topic/Produce/Named/example-topic that is included in the
distributed trace. The Kafka client instrumentation also injects the newrelic distributed tracing header into each record to link distributed
traces with other services monitored by New Relic APM agents.
The kafka-producer service logs a line similar to the following each time it publishes a Kafka record to the broker:
Published Kafka Record:
topic = example-topic, key = example-key-935, value = example-value-935
The kafka-consumer service continuously polls the Kafka broker and individually processes each record that is retrieved. When the method that processes each
record is executed a transaction is started using the Java agent's custom instrumentation APIs. During the processing W3C Trace Context headers are accessed
from each record and passed to the acceptDistributedTraceHeaders(TransportType transportType, Headers headers) API which links the transaction to the
distributed trace that originated in the kafka-producer service.
/**
* This method illustrates usage of New Relic Java agent APIs for propagating distributed tracing headers over Kafka records.
* NewRelic.getAgent().getTransaction().acceptDistributedTraceHeaders(TransportType, Headers) is used to accept distributed tracing headers from an
* incoming request and link the requests together into a single distributed trace.
*
* @param record Kafka record
*/
@Trace
private static void acceptDistributedTraceHeadersFromKafkaRecord(ConsumerRecord<String, String> record) {
// ConcurrentHashMapHeaders provides a concrete implementation of com.newrelic.api.agent.Headers
Headers distributedTraceHeaders = ConcurrentHashMapHeaders.build(HeaderType.MESSAGE);
// Iterate through each Kafka record header and insert the W3C Trace Context headers into the distributedTraceHeaders map
for (Header kafkaRecordHeader : record.headers()) {
String kafkaRecordHeaderValue = new String(kafkaRecordHeader.value(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.printf("\tKafka record header: key = %s, value = %s%n", kafkaRecordHeader.key(), kafkaRecordHeaderValue);
if (kafkaRecordHeader.key().equals(NEWRELIC_HEADER)) {
distributedTraceHeaders.addHeader(NEWRELIC_HEADER, kafkaRecordHeaderValue);
}
if (kafkaRecordHeader.key().equals(W3C_TRACE_PARENT_HEADER)) {
distributedTraceHeaders.addHeader(W3C_TRACE_PARENT_HEADER, kafkaRecordHeaderValue);
}
if (kafkaRecordHeader.key().equals(W3C_TRACE_STATE_HEADER)) {
distributedTraceHeaders.addHeader(W3C_TRACE_STATE_HEADER, kafkaRecordHeaderValue);
}
// Accept distributed tracing headers to link this request to the originating request
NewRelic.getAgent().getTransaction().acceptDistributedTraceHeaders(TransportType.Kafka, distributedTraceHeaders);
}
}The kafka-consumer service logs a line similar to the following each time it processes a Kafka record:
Consuming Kafka Record:
topic = example-topic, key = example-key-935, value = example-value-935, offset = 865
Kafka record header: key = traceparent, value = 00-025be10f5f64e6ee009e3d0df7e8c474-128bc7290a7f5d8e-00
Kafka record header: key = tracestate, value = 1939595@nr=0-0-2212864-1279685854-128bc7290a7f5d8e-f6b1ebb08dac2b50-0-0.916613-1610924459792
Kafka record header: key = newrelic, value = {"d":{"ac":"2212864","pr":0.916613,"tx":"f6b1ebb08dac2b50","ti":1610924459797,"ty":"App","tk":"1939595","tr":"025be10f5f64e6ee009e3d0df7e8c474","sa":false,"ap":"1279685854"},"v":[0,1]}
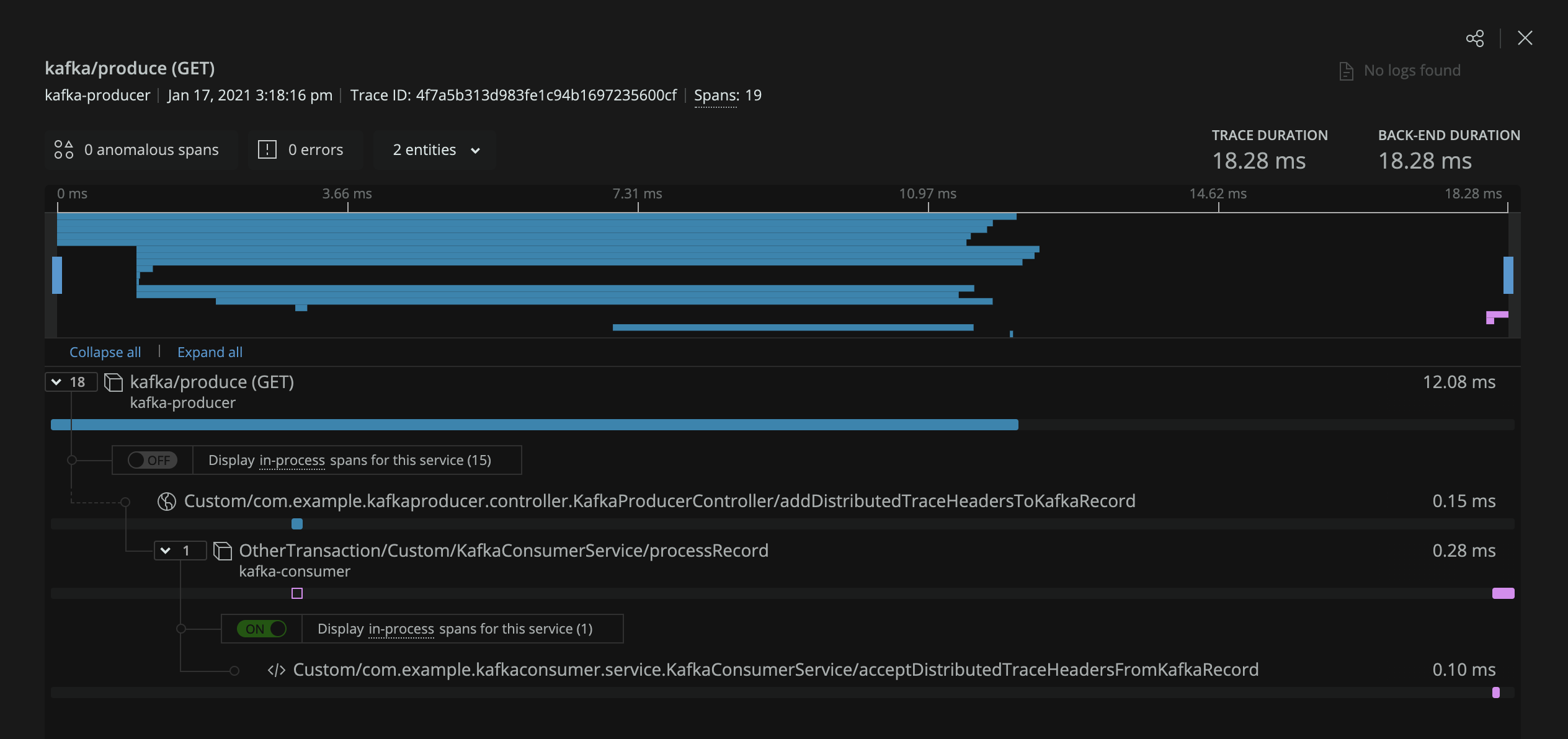
In this screenshot the kafka-producer and kafka-consumer services are connected in a single distributed trace.
Requires Java 8+
To build all artifacts run the following from the project root:
./gradlew clean build
Artifacts produced:
kafka-examples/kafka-producer/build/libs/kafka-producer-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jarkafka-examples/kafka-consumer/build/libs/kafka-consumer-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
A number of scripts have been provided in the kafka_2.13-2.6.0/ directory to streamline running Kafka.
- Start zookeeper in its own terminal window:
./start-zookeeper.sh - Start the Kafka broker in its own terminal window:
./start-kafka.sh - Create a topic on the Kafka broker in new terminal window:
./create-topic.sh - Run the Kafka producer and consumer services
KafkaProducerApplicationKafkaConsumerApplication
- Publish records to topic on the Kafka broker via one of the following options:
- Directly execute the route (publishes a single record each time): http://localhost:8080/kafka/produce
- Run
./produce-records.shin its own terminal window to batchcurlthe route
Each service has its own newrelic directory containing the agent jar, agent api jar, and agent config yaml file:
/path/to/kafka-examples/kafka-producer/newrelic//path/to/kafka-examples/kafka-consumer/newrelic/
In order to report data to your New Relic account you are required to configure your license_key in the newrelic.yml or via
the environment variable NEW_RELIC_LICENSE_KEY for each service.
The following config to enable
distributed tracing for kafka,
has already been added to the newrelic.yml file for each service:
common: &default_settings
license_key: 'key'
...
distributed_tracing:
enabled: true
class_transformer:
kafka-clients-spans:
enabled: true
...
Once each service has a configured license key you can start both of the services as follows:
kafka-producer (runs on port 8080):
java -javaagent:/path/to/kafka-examples/kafka-producer/newrelic/newrelic.jar -jar /path/to/kafka-examples/kafka-producer/build/libs/kafka-producer-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
kafka-consumer (runs on port 8081):
java -javaagent:/path/to/kafka-examples/kafka-consumer/newrelic/newrelic.jar -jar /path/to/kafka-examples/kafka-consumer/build/libs/kafka-consumer-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
This will result in two services reporting to New Relic One: kafka-producer and kafka-consumer