mud is a multi-directory git runner which allows you to run git commands in a multiple repositories. It has multiple powerful tools filtering tools and support of aliasing. This tool is not limited to git commands only, you can run any commands as you wish, but this tool was primarily designed to be used with git, so each referenced directory should have .git.
For PyPI
pip install mud-gitFor Arch Linux
paru -S mud-git- Run
mud configto start interactive wizard which help you to set the preferable settings. Check settings section for more. At the end,.mudsettingsfile will appear at your home directory that you can alter in the future. - Locate to your preferable directory with repositories.
- Run
mud initcommand to create.mudconfigfile. This file is important to keep references to repositories. All repositories in current dictionary would be included to.mudconfig. - Optional: Run
mud set-globalto make current configuration default and reachable from any directory.
All entries are stored in .mudconfig in TSV format. After making your first entry, you can open .mudconfig in a text editor and modify it according to your needs.
mud set-global- sets current.mudconfigas a global configuration, so it would be used as a fallback configuration to run from any directory.mud get-config- prints closest.mudconfiglocation.
mud <FILTER> <COMMAND> will execute bash command across all repositories. To filter repositories check arguments section.
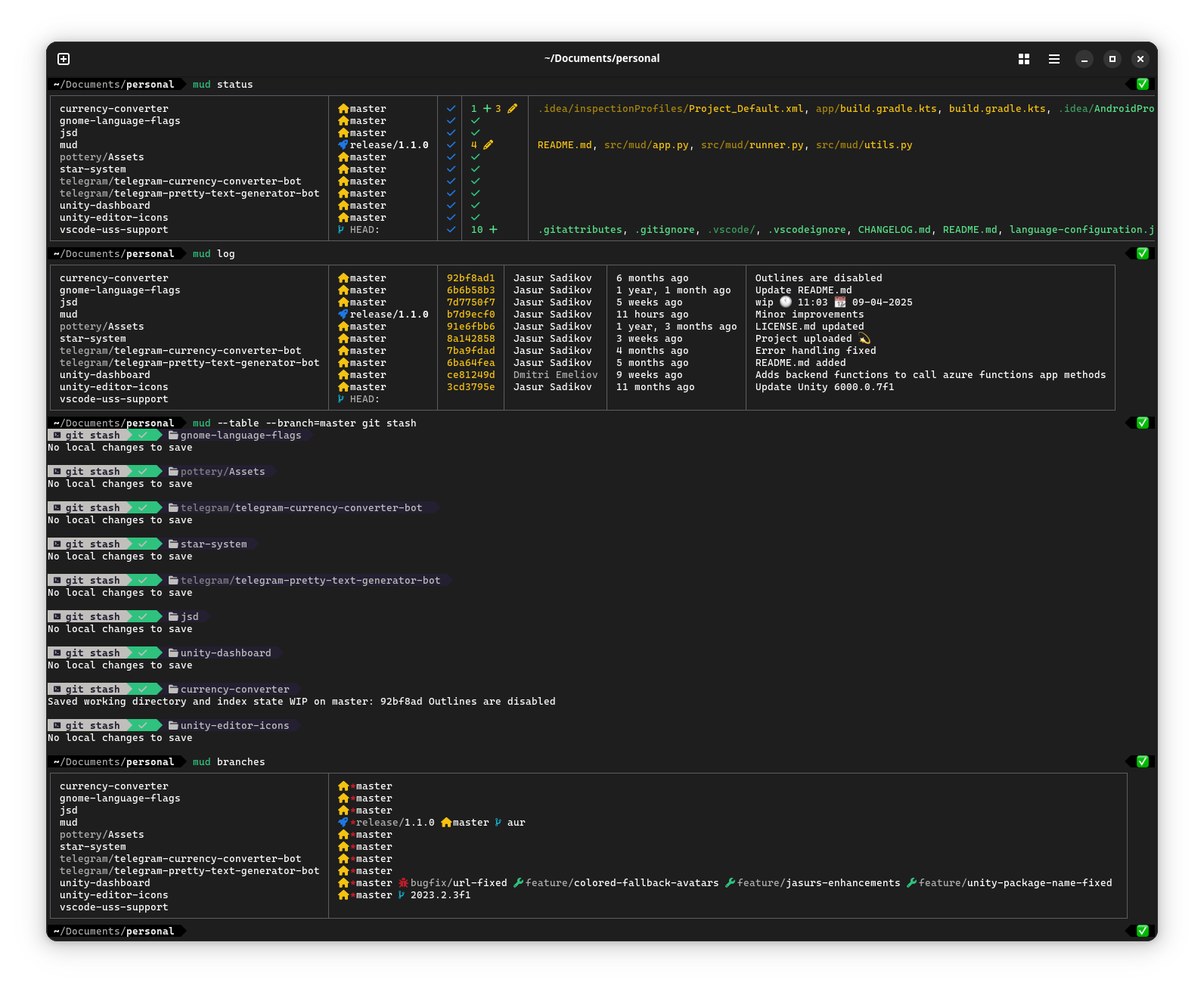
mud info/mud i- displays branch divergence and working directory changes.mud status/mud st- displays working directory changes.mud log/mud l- displays latest commit message, it's time and it's author.mud labels/mud lb- displays mud labels across repositories.mud branch/mud br- displays all branches in repositories.mud remote-branch/mud rbr- displays all branches in repositories.mud tags/mud t- displays git tags in repositories.
-l=<label>or--label=<label>- includes repositories with provided label.-nl=<label>or--not-label=<label>- excludes repositories with provided label.-b=<branch>or--branch=<branch>- includes repositories with provided branch.-nb=<branch>or--not-branch=<branch>- excludes repositories with provided label.-cor--command- explicit command argument. Use this whenever you're trying to run a complex command.-mor--modified- filters out modified repositories.-dor--diverged- filters repositories with diverged branches.-tor--table- toggles default table view setting for run.-aor--async- toggles asynchronous run feature.
Example:
# Filters out all repos with master branch and diverged branches and then runs pull command.
mud -b=master -d git pull
# Fetches all repositories that are not on master branch and have "personal" label but excluding ones with "work" label
mud -nb=master -l=personal -nl=work git fetchSettings are stored in your home directory in .mudsettings file.
run_async = 0/1- enables asynchronous commands.run_table = 0/1- enables asynchronous commands in a table view. Requiresrun_async.nerd_fonts = 0/1- use nerd fonts in the output 💅.show_borders = 0/1- enables borders in table view.collapse_paths = 0/1- simplifies branch name in the branch view.config_path = /home/user/path/.mudconfig- this is set up bymud --set-globalcommand.
You can create your own aliases for commands. To create your own aliases, edit .mudsettings file, [alias] section. .mudsettings has the following aliases by default:
[alias]
to = git checkout
fetch = git fetch
pull = git pull
push = git pushYou can modify your .mudconfig file by using following commands:
mud add <label> <path>- adds path with an optional label.mud add <path>- adds path without a label.
mud remove <label>- removes label from all directories.mud remove <path>- removes directory with a specified path.mud remove <label> <path>- removes label from a directory.