pybts (Python Behavior Tree) is a Python library for creating and managing behavior trees, which are used to model the decision-making process in artificial intelligence systems, such as in games or robotics. The library provides a structured way to organize complex behaviors through a hierarchy of nodes, each representing a specific action, decision, or condition.
- Node Hierarchy: Implements various node types such as
Action,Composite,Decorator, andCondition, allowing complex behavior modeling. - Extensible Framework: Users can define custom nodes by inheriting from base classes like
Node,Composite, orDecorator. - Memory Management: Nodes like
SequenceandSelectorcan have memory, maintaining state between ticks. - Parallel Execution: Supports parallel node execution with customizable policies (
SuccessOnOne,SuccessOnAll). - Behavior Tracking: Integrates with a
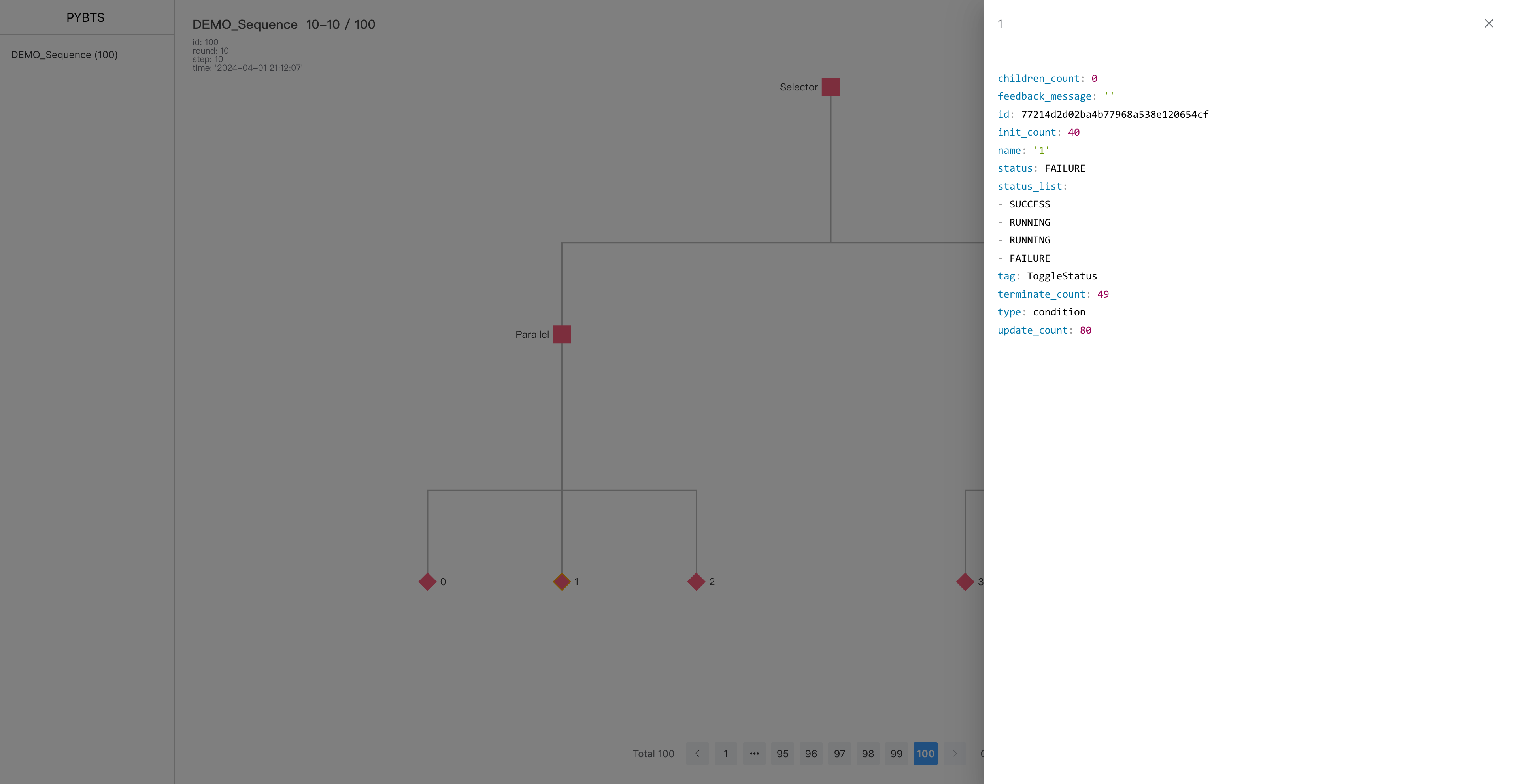
Boardclass to track and log the state of the tree during execution. - Web Interface: Features a web server (
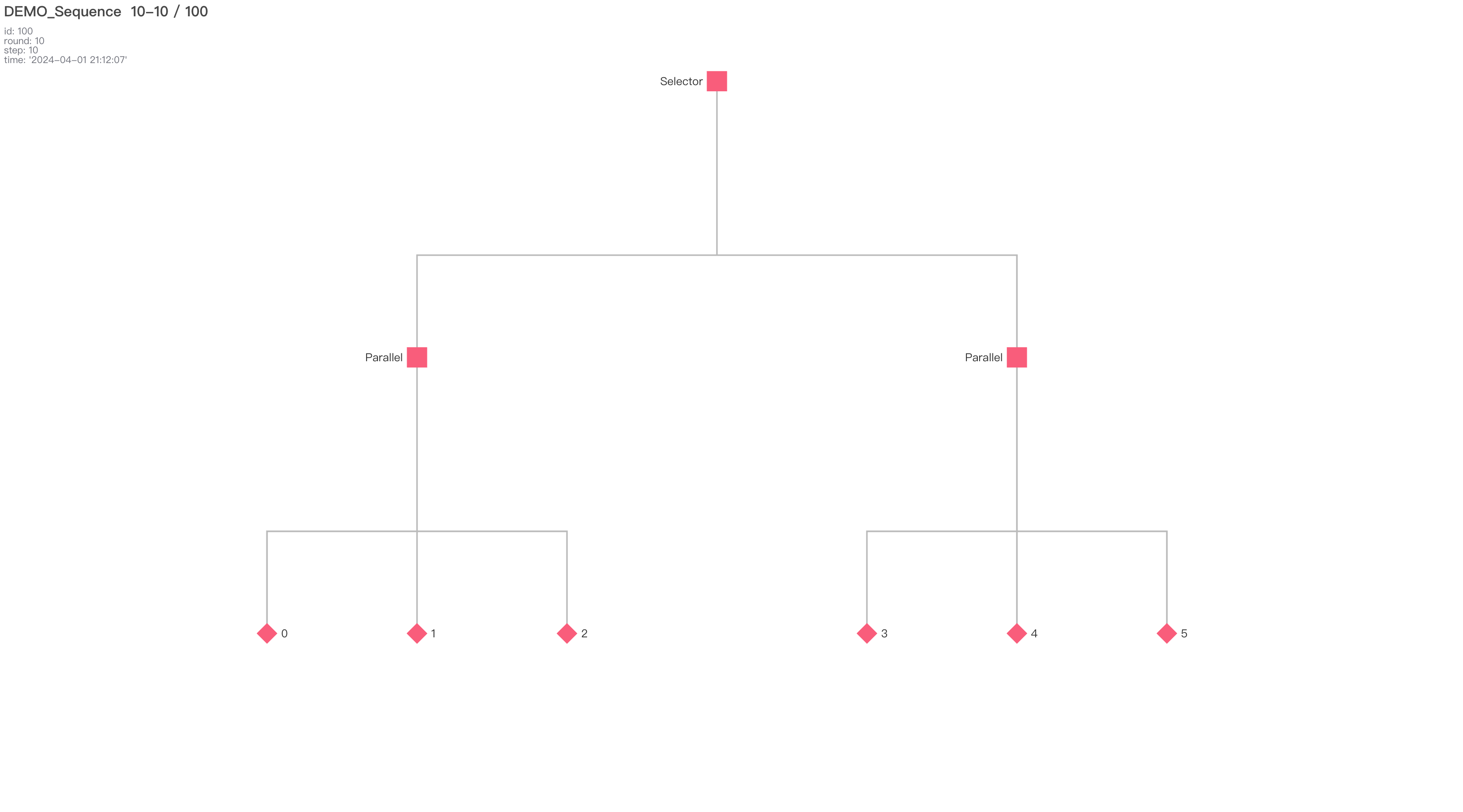
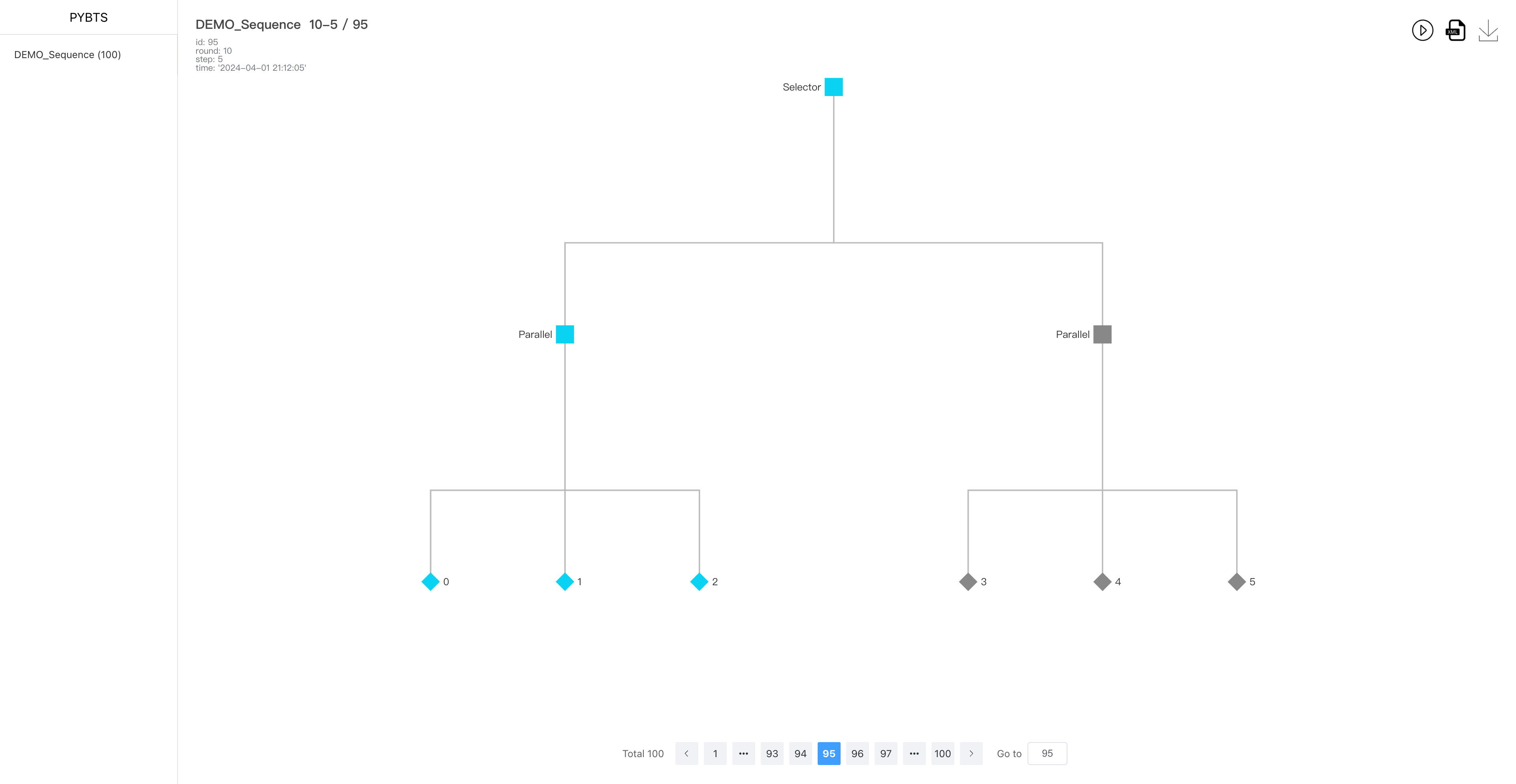
BoardServer) to visualize and manage behavior trees through a web interface, including real-time updates.
- Node Classes: Define the behavior and structure of the behavior tree.
Node: Base class for all behavior tree nodes.Composite,Decorator,Sequence,Parallel,Selector: Specialized node types for structuring tree logic.
- Tree Management
Tree: Represents the entire behavior tree, initialized with a root node.Board: Manages logging and tracking of tree state and history.
- Web Server
BoardServer: Flask-based web server for visualizing and managing behavior trees. Supports dynamic data updates and visualization through ECharts.
Currently, pybts is not available through package managers and must be installed by cloning the repository:
pip install pybts
pip install pybts[rl] # add reinforcement learning support
# or
git clone https://github.com/wangtong2015/pybts.git
cd pybts
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install .- Define Behavior Nodes: Create custom behavior nodes by extending
pybts.Nodeor other specific node types likeAction,Condition, etc. - Build the Behavior Tree: Use the
pybts.builder.Builderto create trees from your nodes. - Track and Log: Initialize a
Boardobject with your tree to enable tracking and logging. - Visualize and Manage: Start the
BoardServerto view and interact with the behavior tree in a web interface.
from pybts import Tree, board, builder
from pybts.node import Action
from py_trees import common
import time
# Define custom behavior node
class Person(Action):
def __init__(self, name: str, age: int):
super().__init__(name=name)
self.age = age
def update(self) -> common.Status:
self.age += 1
return common.Status.SUCCESS
# Build the behavior tree
builder = builder.Builder()
builder.register('Person', Person)
# or
builder.register_node(Person) # will register tag 'Person' and 'person'(snake case)
root = builder.build_from_file('demos/demo_bt.xml')
tree = Tree(root=root, name='Person')
# Initialize board for tracking
bt_board = board.Board(tree=tree, log_dir='logs')
bt_board.clear()
for i in range(10000):
tree.tick()
bt_board.track(info={
'test_info': i
}) # track the tree status
time.sleep(0.5)Running the Board Server:
Use the following command to start the BoardServer with the specified log directory, enabling debug mode, and setting the host and port:
python -m pybts.board_server --dir=logs --debug --host=localhost --port=10000
- This command starts the pybts board server using the
logsdirectory for storing and retrieving behavior tree logs. Debug mode is enabled, and the server is accessible athttp://localhost:10000. - Alternative Command: If you have a command line interface setup for
pybtsas a package, you can also start the server using a more direct command:
pybts --dir=logs --debug --host=localhost --port=10000- This assumes that
pybtsis configured as a command-line tool that internally callspybts.board_server.
After running the appropriate command, you can open a web browser and navigate to http://localhost:10000 to view and interact with the behavior tree visualizations and management tools provided by pybts.
This project, PYBTS (Python Behavior Tree), is developed based on the py_trees library, a powerful and flexible Python framework for building and managing behavior trees. We extend our heartfelt thanks to the py_trees project and its contributors for providing the foundational components and concepts upon which pybts is built.
For more information about py_trees and to access its source code, visit the official GitHub repository: py_trees on GitHub.
We appreciate the effort and expertise that has gone into py_trees, making it possible for us to develop advanced features in pybts and offer a comprehensive behavior tree solution in the Python ecosystem.
Contributions to pybts are welcome! You can contribute by submitting issues, providing updates to documentation, or submitting pull requests with new features or bug fixes.