This is the official Python implementation of our work: "DefakeHop: A Light-Weight High-Performance Deepfake Detector" accepted at ICME 2021.
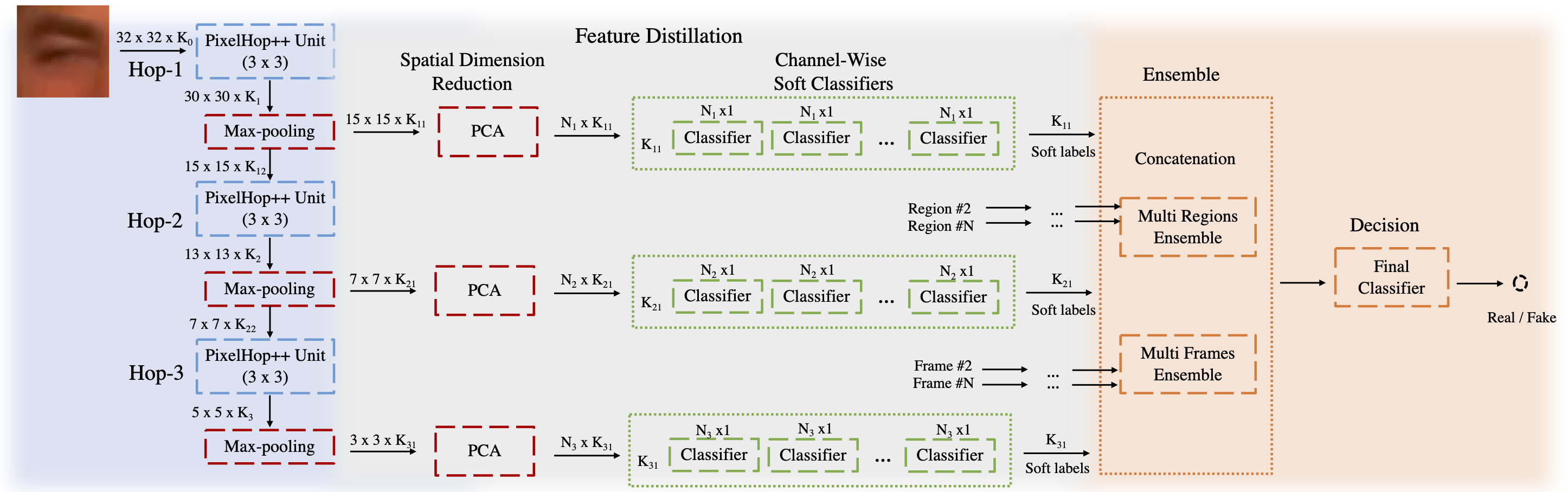
State-of-the-art Deepfake detection methods are built upon deep neural networks. In this work, we proposed a non deep learning method to detect Deepfake videos which use the successive subspace learning (SSL) principle to extract features from various parts of face images. The features are also further distilled by our feature distillation module to derive a concise representation of the fake and real faces.
conda install -c anaconda pandas
conda install -c conda-forge opencv
conda install -c conda-forge xgboost
conda install -c anaconda scikit-image
conda install -c conda-forge matplotlib
conda install -c conda-forge scikit-learnFeatureExtraction -f [video path] -out_dir [output directory]
- Face alignment and Crop the facial regions
python preprocessing/extract_facial_regions.py [videos folder] [landmarks folder] [output directory]
We use UADFV dataset as an example to show how to use our code to train and test the model.
python model.pyWhen we train the model, we use three items to train.
-
Images: 4D numpy array (N,H,W,C).
-
Labels: 1D numpy array where 1 is Fake and 0 is Real.
-
Names: 1D numpy array storing frame names.
The frame name should follow the format of {video_name}_{frame_number}.
Example: real/0047_0786.bmp, we can know it is the 786 th frame from real/0047.mp4
If you use this repository, please consider to cite.
@misc{chen2021defakehop,
title={DefakeHop: A Light-Weight High-Performance Deepfake Detector},
author={Hong-Shuo Chen and Mozhdeh Rouhsedaghat and Hamza Ghani and Shuowen Hu and Suya You and C. -C. Jay Kuo},
year={2021},
eprint={2103.06929},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
This work was supported by the Army Research Laboratory (ARL) under agreement W911NF2020157.