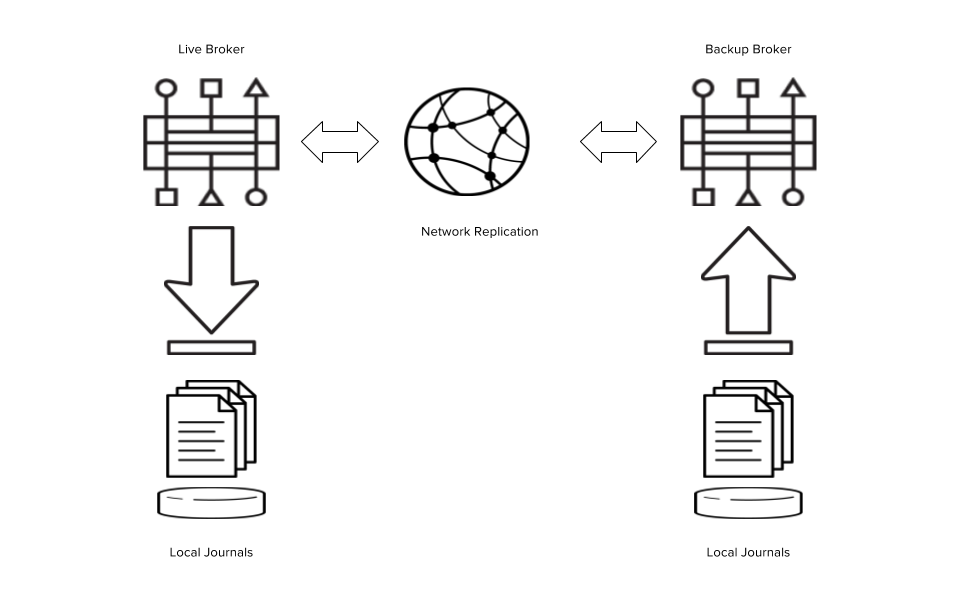
Red Hat JBoss AMQ 7 provides fast, lightweight, and secure messaging for Internet-scale applications. AMQ 7 components use industry-standard message protocols and support a wide range of programming languages and operating environments. AMQ 7 gives you the strong foundation you need to build modern distributed applications. Multiple instances of AMQ 7 brokers can be grouped together to share message processing load. Each broker manages its own messages and connections and is connected to other brokers with "cluster bridges" that are used to send topology information, such as queues and consumers, as well as load balancing messages. AMQ 7 supports two different strategies for backing up a server: shared store and replication.
This is a demostration of the new AMQ 7 replicated high availability feature to avoid using a shared store.
Red Hat JBoss AMQ 7 allows servers to be linked together as live - backup groups where each live server can have 1 or more backup servers. A backup server is owned by only one live server. Backup servers are not operational until failover occurs, however 1 chosen backup, which will be in passive mode, announces its status and waits to take over the live servers work.
Before failover, only the live server is serving the AMQ clients while the backup servers remain passive or awaiting to become a backup server. When a live server crashes or is brought down in the correct mode, the backup server currently in passive mode will become live and another backup server will become passive. If a live server restarts after a failover then it will have priority and be the next server to become live when the current live server goes down, if the current live server is configured to allow automatic failback then it will detect the live server coming back up and automatically stop.
When using replication, the live and the backup servers do not share the same data directories, all data synchronization is done over the network. Therefore all (persistent) data received by the live server will be duplicated to the backup.
Notice that upon start-up the backup server will first need to synchronize all existing data from the live server before becoming capable of replacing the live server should it fail. So unlike when using shared storage, a replicating backup will not be a fully operational backup right after start-up, but only after it finishes synchronizing the data with its live server.
This project demostrate how to set up a 2 clustered brokers using CLI and the replicated journal feature.
This workshop requires you to use your own laptop and have the following prerequisites installed:
- Operating System
- Mac OS X (10.8 or later) or
- Windows 7 (SP1) or
- Fedora (21 or later) or
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
- Memory: At least 2 GB+, preferred 4 GB
- Web Browser (preferably Chrome or Firefox)
- Git client -- download here
- http://github.com access
For running JBoss AMQ 7 Broker
- Java Runtime Engine (JRE) 1.8 --download here
- LibAIO (Optional)
If installing from supported version of Red Hat Enterprise Linux you can use yum command to install pre-requisites.
$ sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel git
Git clone this repository and then change directory to amq-ha-replicated-dem.
Download AMQ 7 Broker from Red Hat Developer Portal: --download here
Place the downloaded amq zip in the installs directory.
This demo can be deployed using the automated installation based on the init.sh script.
The init.sh script automates the installation and instantiation of the components contained within this demo. It will deploy an HA Broker configuration with a master broker running as the Live Broker and a second broker, the slave broker, running as a Backup for the Live Broker.
First, execute the init.sh script
./init.sh
After successfully deployed, you can test the failover
To send messages to the master broker, execute the following command:
$ target/amq-broker-7.0.1/instances/replicatedMaster/bin/artemis producer --message-count 10 --url "tcp://127.0.0.1:61616" --destination queue://haQueue
To check the messages were successfully send to the broker, check the queue in the broker web console.
- Open a web browser and navigate to the AMQ web console http://localhost:8161/hawtio
- In the left tree navigate to 127.0.0.1 > addresses > haQueue > queues > anycast > haQueue
- Click on Browse (refresh if necessary)
You will see the 10 messages send by the producer script.
As the replicatedSlave broker is running as a backup broker for replicatedMaster, there are no active addresses or queues listening.
- Open a web browser and navigate to the AMQ web console http://localhost:8261/hawtio
- In the left tree navigate to 127.0.0.1 > addresses > haQueue > queues > anycast > haQueue
You will only see the information regarding the cluster broadcast configuration.
To shutdown the master broker, execute the following command:
$ target/amq-broker-7.0.1/instances/replicatedMaster/bin/artemis-service stop
While the master is shutting down, the backup broker will notice the disconnection from the master and bwill become live.
To check the messages were successfully replicated to the slave broker, check the queue in the slave broker web console.
- Refresh the AMQ web console http://localhost:8261/hawtio
- In the left tree navigate to 127.0.0.1 > addresses > haQueue > queues > anycast > haQueue
- Click on Browse (refresh if necessary)
You will see the 10 messages send by the producer script to the master broker.
If you want, you can start again the replicatedMaster broker to see how the backup failbacks to the master.
$ target/amq-broker-7.0.1/instances/replicatedMaster/bin/artemis-service start
The master will start and check if there is a live broker, when the backup detects that the master has become availbale again, it failsback going in a backup mode again.
We welcome all forms of contribution (content, issues/bugs, feedback).
None yet...
See the tagged releases for the following versions of the product: