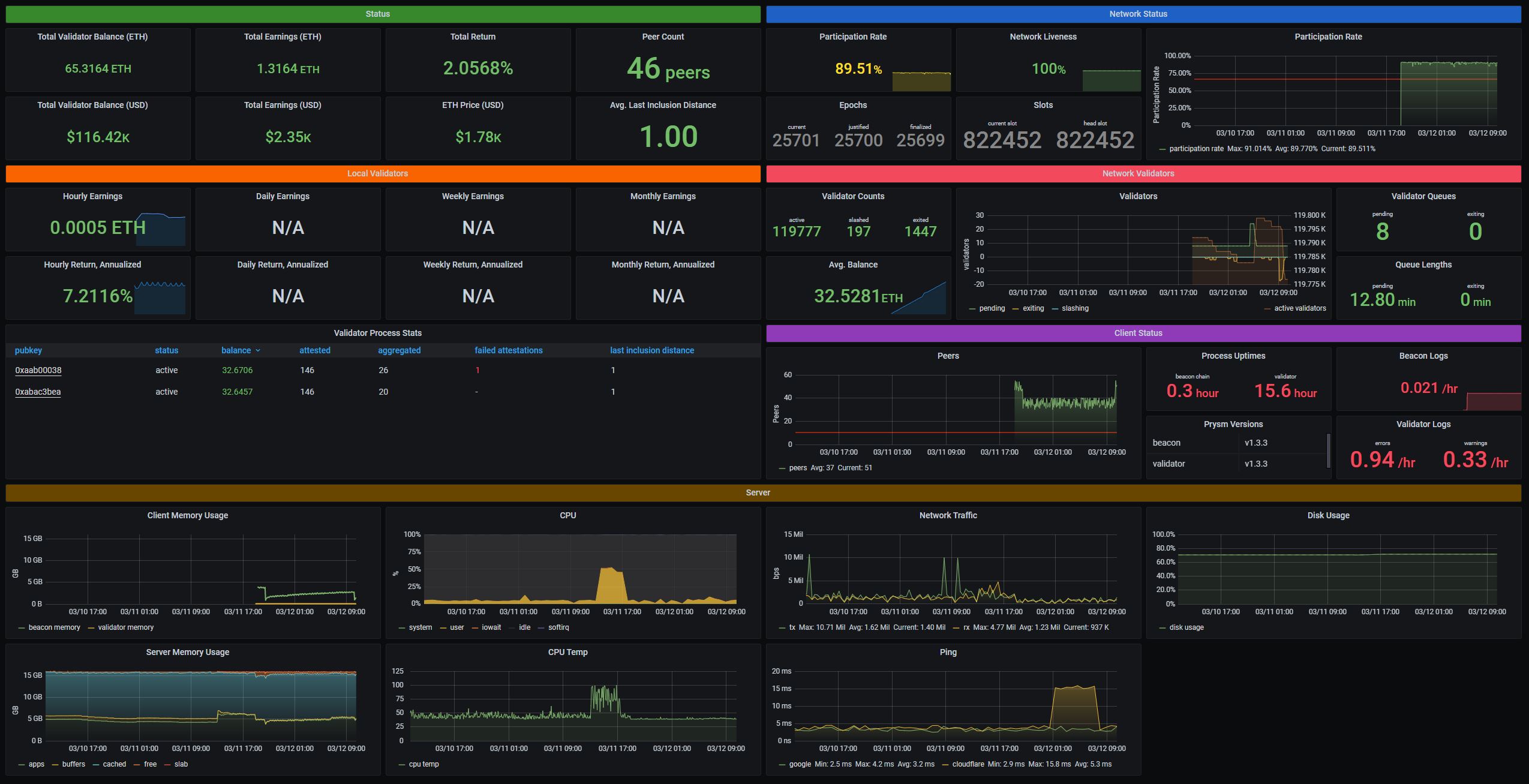
Grafana dashboards for Prysmatic Labs Prysm Eth2 client.
Host stats require node_exporter, ping stats require blackbox_exporter, and ETH price requires blackbox_exporter. Panels requiring these modules can be manually removed from the dashboard after installation if you choose not to install these additional components.
This installation assumes that you are running Prysm, Grafana, Prometheus, node_exporter, blackbox_exporter, and json_exporter on the same system, and that only default ports are used.
- Install node_exporter if you would like to see system information, such as CPU utilization, memory use, CPU temperature, disk usage, and network traffic.
- If you would like to see ping (network latency) information, install blackbox_exporter using the following configuration file.
modules:
icmp:
prober: icmp
timeout: 10s
icmp:
preferred_ip_protocol: ipv4
- Install go
- Install json_exporter if you would like to see ETH price information. Use the following configuration file.
metrics:
- name: ethusd
path: $.ethereum.usd
help: Ethereum (ETH) price in USD
- Install Prometheus using the following configuration file.
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'prometheus'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['127.0.0.1:9090']
- job_name: 'beacon node'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['127.0.0.1:8080']
- job_name: 'node_exporter'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['127.0.0.1:9100']
- job_name: 'validator'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['127.0.0.1:8081']
- job_name: 'ping_google'
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module: [icmp]
static_configs:
- targets:
- 8.8.8.8
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- target_label: __address__
replacement: 127.0.0.1:9115 # The blackbox exporter's real hostname:port.
- job_name: 'ping_cloudflare'
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module: [icmp]
static_configs:
- targets:
- 1.1.1.1
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- target_label: __address__
replacement: 127.0.0.1:9115 # The blackbox exporter's real hostname:port.
- job_name: json_exporter
static_configs:
- targets:
- 127.0.0.1:7979
- job_name: json
metrics_path: /probe
static_configs:
- targets:
- https://api.coingecko.com/api/v3/simple/price?ids=ethereum&vs_currencies=usd
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- target_label: __address__
replacement: 127.0.0.1:7979
- Install Grafana.
- Login to Grafana and add
http://XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX:9090/as a Prometheus data source. - Add the Prysm dashboard to Grafana.
Adapted from my instructions for setting up a Prysm staking system on Ubuntu 20.04.
sudo adduser --system prometheus --group --no-create-homeFind the URL to the latest amd64 version of Prometheus at https://prometheus.io/download/. In the commands below, replace any references to the version 2.22.1 to the latest version available.
cd
wget https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.22.1/prometheus-2.22.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar xzvf prometheus-2.22.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
cd prometheus-2.22.1.linux-amd64
sudo cp promtool /usr/local/bin/
sudo cp prometheus /usr/local/bin/
sudo chown root:root /usr/local/bin/promtool /usr/local/bin/prometheus
sudo chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/promtool /usr/local/bin/prometheus
cd
rm prometheus-2.22.1.linux-amd64.tar.gzCreate directories that prometheus will be expecting to find.
sudo mkdir -p /etc/prometheus/console_libraries /etc/prometheus/consoles /etc/prometheus/files_sd /etc/prometheus/rules /etc/prometheus/rules.dCreate the prometheus configuration files. Open a new configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/prometheus/prometheus.ymlCopy and paste the following text into the prometheus.yml configuration file:
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'prometheus'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['127.0.0.1:9090']
- job_name: 'beacon node'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['127.0.0.1:8080']
- job_name: 'node_exporter'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['127.0.0.1:9100']
- job_name: 'validator'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['127.0.0.1:8081']
- job_name: 'ping_google'
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module: [icmp]
static_configs:
- targets:
- 8.8.8.8
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- target_label: __address__
replacement: 127.0.0.1:9115 # The blackbox exporter's real hostname:port.
- job_name: 'ping_cloudflare'
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module: [icmp]
static_configs:
- targets:
- 1.1.1.1
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- target_label: __address__
replacement: 127.0.0.1:9115 # The blackbox exporter's real hostname:port.
- job_name: json_exporter
static_configs:
- targets:
- 127.0.0.1:7979
- job_name: json
metrics_path: /probe
static_configs:
- targets:
- https://api.coingecko.com/api/v3/simple/price?ids=ethereum&vs_currencies=usd
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- target_label: __address__
replacement: 127.0.0.1:7979
Note: Users of earlier versions of these instructions may have the beacon node job name set to "beacon" instead of "beacon node". When choosing a Grafana dashboard from this repository, please select this dashboard if you are using "beacon" as the job name, and this dashboard if you are using "beacon node" as the job name.
Change the ownership of the prometheus configuration directory to the prometheus user.
sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheusMake a directory for prometheus files, owned by the prometheus user account, and with appropriate privileges.
sudo mkdir /var/lib/prometheus
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /var/lib/prometheus
sudo chmod 755 /var/lib/prometheusSet up systemd to automatically start Prometheus. It will also restart the software if it stops.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/prometheus.serviceCopy and paste the following text into the prometheus.service file.
[Unit]
Description=Prometheus
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
[Service]
User=prometheus
Group=prometheus
Type=simple
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/prometheus \
--config.file /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \
--storage.tsdb.path /var/lib/prometheus/ \
--web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles \
--web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Reload the systemd service file configurations, start prometheus, then enable the prometheus service to have it start automatically on reboot.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start prometheus.service
sudo systemctl enable prometheus.serviceSetup and install Grafana using apt-get.
cd
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https
sudo apt-get install -y software-properties-common wget
wget -q -O - https://packages.grafana.com/gpg.key | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository "deb https://packages.grafana.com/oss/deb stable main"
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install grafana-enterpriseReload the systemd service file configurations, start Grafana, then enable the Grafana service to have it start automatically on reboot.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start grafana-server
sudo systemctl enable grafana-serverLogin to Grafana at http://XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX:3000/, replacing XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX with the IP address of your server. If you do not know the IP address, run ifconfig.
Default username admin. Default password admin. Grafana will ask you to set a new password.
- On the left-hand menu, hover over the gear menu and click on Data Sources.
- Then click on the Add Data Source button.
- Hover over the Prometheus card on screen, then click on the Select button.
- Enter
http://127.0.0.1:9090/into the URL field, then click Save & Test.
- Hover over the plus symbol icon in the left-hand menu, then click on Import.
- Copy and paste the dashboard at https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metanull-operator/eth2-grafana/master/eth2-grafana-dashboard-single-source-beacon_node.json into the "Import via panel json" text box on the screen. If you used an older version of these instructions, where the Prometheus configuration file uses the beacon node job name of "beacon" instead of "beacon node", please use this dashboard instead for backwards compatibility.
- Then click the Load button.
- Then click the Import button.
Note: Some panels will not display data until all required software is running. Various portions of this dashboard are directly or indirectly dependent on Prometheus, Prysm beacon chain, Prysm validator, node_exporter, and blackbox exporter.
A few of the queries driving the Grafana dashboard may need different settings, depending on your hardware.
To ensure that network traffic is correctly reflected on your Grafana dashboard, update the network interface in the Network Traffic widget. Run the following command to find your Linux network device.
ifconfigOutput of the command should look like the following:
eno1: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.1.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255
inet6 fe80::1e69:7aff:fe63:14b0 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 1c:69:7a:63:14:b0 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 238936 bytes 78487335 (78.4 MB)
RX errors 0 dropped 1819 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 257824 bytes 112513038 (112.5 MB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
device interrupt 16 memory 0x96300000-96320000
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 39805 bytes 29126770 (29.1 MB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 39805 bytes 29126770 (29.1 MB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
Of the two entries shows above, the first lists my IP address on the second line, network interface eno1. Find the entry that represents the network connection you want to monitor and copy the device name, which is the part before the colon on the first line of each entry. In my case the value is eno1.
- Go to the Grafana dashboard previously installed
- Find the Network Traffic widget, and open the drop down that can be found by the Network Traffic title.
- Click Edit.
- There will be four references to
eno1in the queries that appear. Replace all four with the name of the network interface you found in theifconfigcommand.
Node exporter allows Prometheus to record system data, such as CPU utilization, memory use, CPU temperature, and disk usage.
Setup and install node_exporter using apt-get.
sudo adduser --system node_exporter --group --no-create-homecd
wget https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v1.0.1/node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar xzvf node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo cp node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64/node_exporter /usr/local/bin/
sudo chown node_exporter:node_exporter /usr/local/bin/node_exporter
rm node_exporter-1.0.1.linux-amd64.tar.gzSet up systemd to automatically start node_exporter. It will also restart the software if it stops.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/node_exporter.serviceCopy and paste the following text into the node_exporter.service file.
[Unit]
Description=Node Exporter
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
User=node_exporter
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/node_exporter
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Reload the systemd service file configurations, start node_exporter, then enable the node_exporter service to have it start automatically on reboot.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start node_exporter.service
sudo systemctl enable node_exporter.servicesudo apt-get install golang-1.14-go
# Create a symlink from /usr/bin/go to the new go installation
sudo ln -s /usr/lib/go-1.14/bin/go /usr/bin/gosudo apt-get install gitsudo adduser --system json_exporter --group --no-create-homecd
git clone https://github.com/prometheus-community/json_exporter.git
cd json_exporter
make build
sudo cp json_exporter /usr/local/bin/
sudo chown json_exporter:json_exporter /usr/local/bin/json_exporterCreate a directory for the json_exporter configuration file, and make it owned by the json_exporter account.
sudo mkdir /etc/json_exporter
sudo chown json_exporter:json_exporter /etc/json_exporterEdit the json_exporter configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/json_exporter/json_exporter.ymlCopy and paste the following text into the json_exporter.yml file.
metrics:
- name: ethusd
path: $.ethereum.usd
help: Ethereum (ETH) price in USD
Change ownership of the configuration file to the json_exporter account.
sudo chown json_exporter:json_exporter /etc/json_exporter/json_exporter.ymlSet up systemd to automatically start json_exporter. It will also restart the software if it stops.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/json_exporter.serviceCopy and paste the following text into the json_exporter.service file.
[Unit]
Description=JSON Exporter
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
User=json_exporter
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/json_exporter --config.file /etc/json_exporter/json_exporter.yml
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Reload the systemd service file configurations, start node_exporter, then enable the json_exporter service to have it start automatically on reboot.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start json_exporter.service
sudo systemctl enable json_exporter.serviceI use blackbox_exporter to provide ping (network latency) data between my staking system and two DNS providers. This can also be used to see network downtime.
The Grafana dashboard in these instructions includes a panel with a ping time graph. If you choose not to install blackbox_exporter, simply remove that panel from your Grafana dashboard. It will not show data.
sudo adduser --system blackbox_exporter --group --no-create-homecd
wget https://github.com/prometheus/blackbox_exporter/releases/download/v0.18.0/blackbox_exporter-0.18.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar xvzf blackbox_exporter-0.18.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo cp blackbox_exporter-0.18.0.linux-amd64/blackbox_exporter /usr/local/bin/
sudo chown blackbox_exporter:blackbox_exporter /usr/local/bin/blackbox_exporter
sudo chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/blackbox_exporterGives blackbox_exporter special network packet creation abilities to allow for pinging servers.
sudo setcap cap_net_raw+ep /usr/local/bin/blackbox_exporterRemove the original blackbox_exporter package.
rm blackbox_exporter-0.18.0.linux-amd64.tar.gzsudo mkdir /etc/blackbox_exporter
sudo chown blackbox_exporter:blackbox_exporter /etc/blackbox_exporterEdit the blackbox_exporter configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/blackbox_exporter/blackbox.ymlCopy and paste the following text into the blackbox.yml file.
modules:
icmp:
prober: icmp
timeout: 10s
icmp:
preferred_ip_protocol: ipv4
Change ownership of the configuration file to the blackbox_exporter account.
sudo chown blackbox_exporter:blackbox_exporter /etc/blackbox_exporter/blackbox.ymlSet up systemd to automatically start blackbox_exporter. It will also restart the software if it stops.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/blackbox_exporter.service
Copy and paste the following text into the blackbox_exporter.service file.
[Unit]
Description=Blackbox Exporter
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
User=blackbox_exporter
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/blackbox_exporter --config.file /etc/blackbox_exporter/blackbox.yml
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Reload the systemd service file configurations, start blackbox_exporter, then enable the blackbox_exporter service to have it start automatically on reboot.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start blackbox_exporter.service
sudo systemctl enable blackbox_exporter.service