Getting started with ansible cloudformation module
The below requirements are needed on the host that executes this module.
1.boto 2.boto3 3.botocore>=1.5.45 4.python >= 2.6
ansible-vault create <name-of-file.yml> add your access and secret keys to the yml file.
ansible-playbook ansible-cloudformation-cluster.yml --vault-id @prompt
ansible-playbook ansible-cloudformation-service.yml --vault-id @prompt
Several combinations of template are available in this folder. You can deploy containers with two different networking approaches:
- Public VPC subnet with direct internet access
- A public facing load balancer that accepts traffic from anyone on the internet (ideal for a public facing web service)
To use this template to launch a EC2 instance cluster Then launch a service template for the EC2 Instance service you want to run in the cluster. When launching a service template its important to make sure the "StackName" value is filled in with the same name that you selected for the name of your cluster stack.
Each of the service stacks has default values prefilled for launching a simple Nginx container, but can be adjusted to launch your own container.
This architecture deploys your container into its own VPC, inside a public facing network subnet. The containers are hosted with direct access to the internet, and they are also accessible to other clients on the internet via a public facing appliation load balancer.
- Launch the [fully public](ansible-playbook ansible-cloudformation-cluster.yml --vault-id @prompt)
- Launch the [public facing service template](ansible-playbook ansible-cloudformation-service.yml --vault-id @prompt).
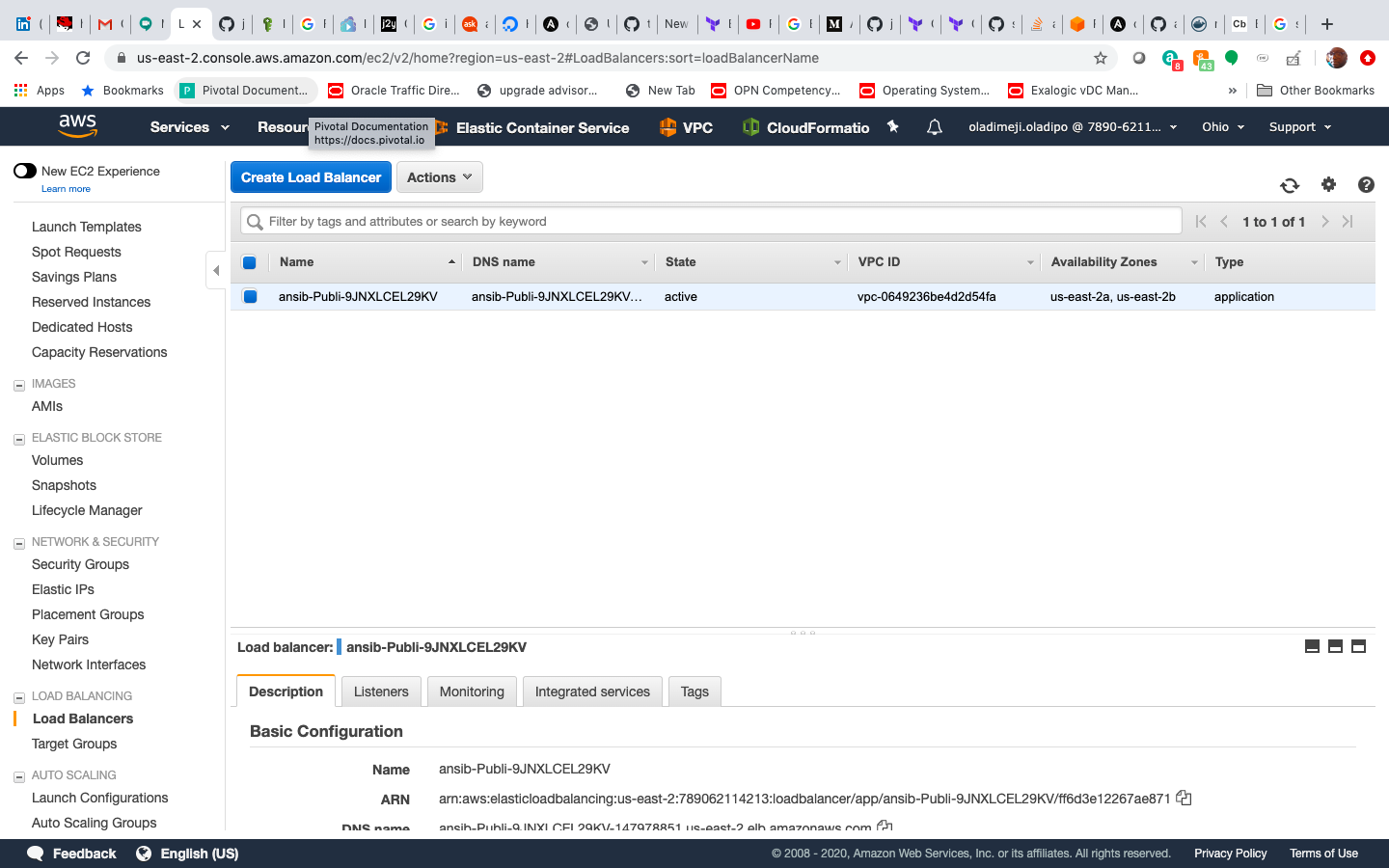
Look up the Elastic Loadbalancer DNS under the EC2 service a DNS A record has been created, kindly refer to the images.
Access cloudformation service and delete the service stack first and then the cluster created
Explore using ec2_elb_info ansible module – Gather information about EC2 Elastic Load Balancers in AWS so we could display ELB info in the console