- NOTE: envdb is still beta software.
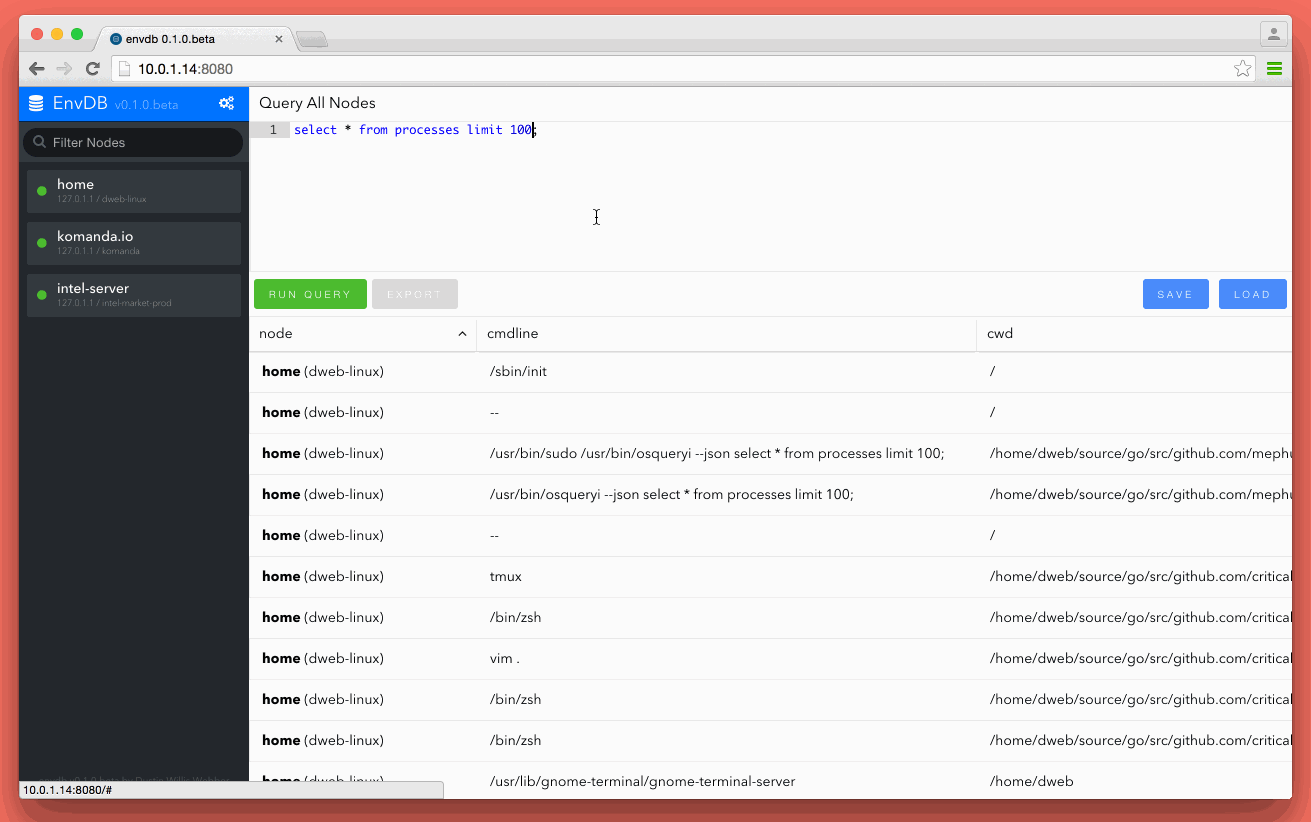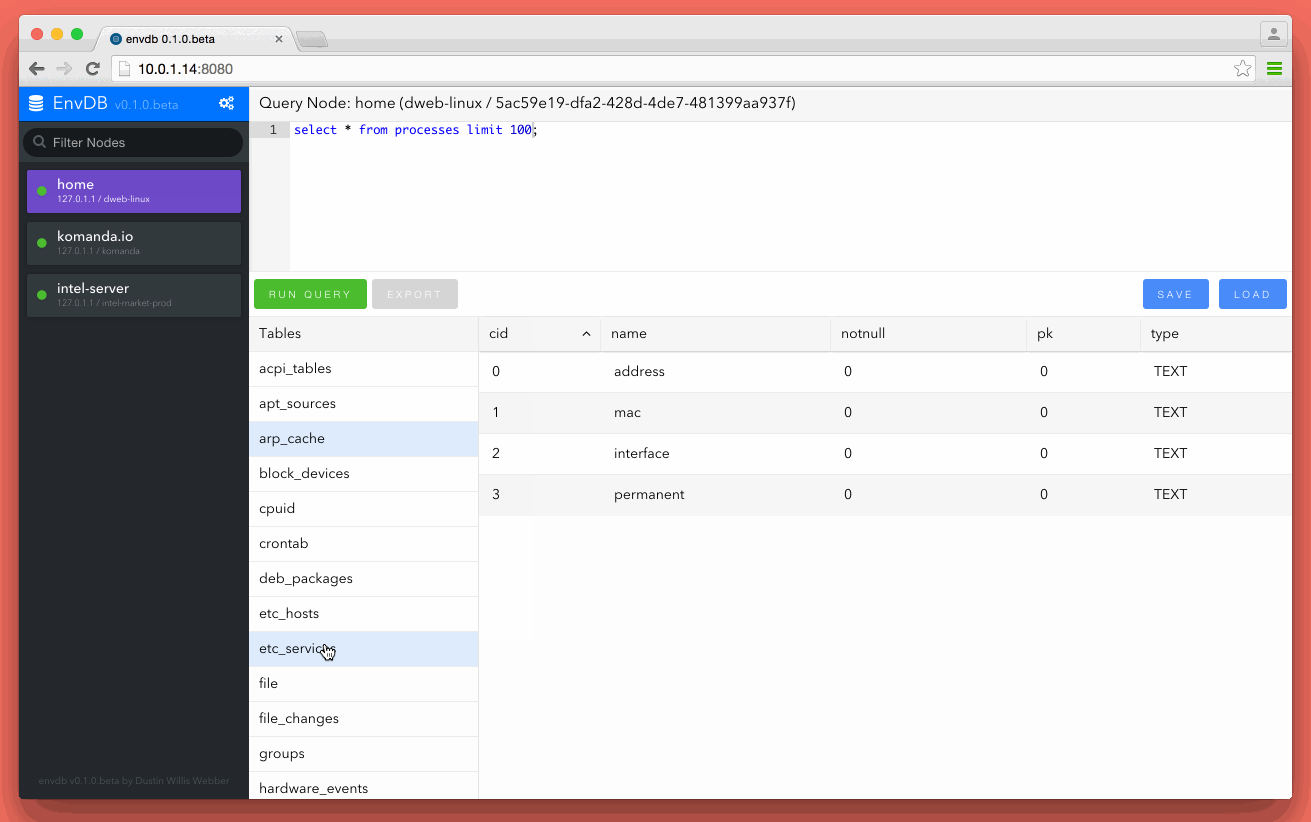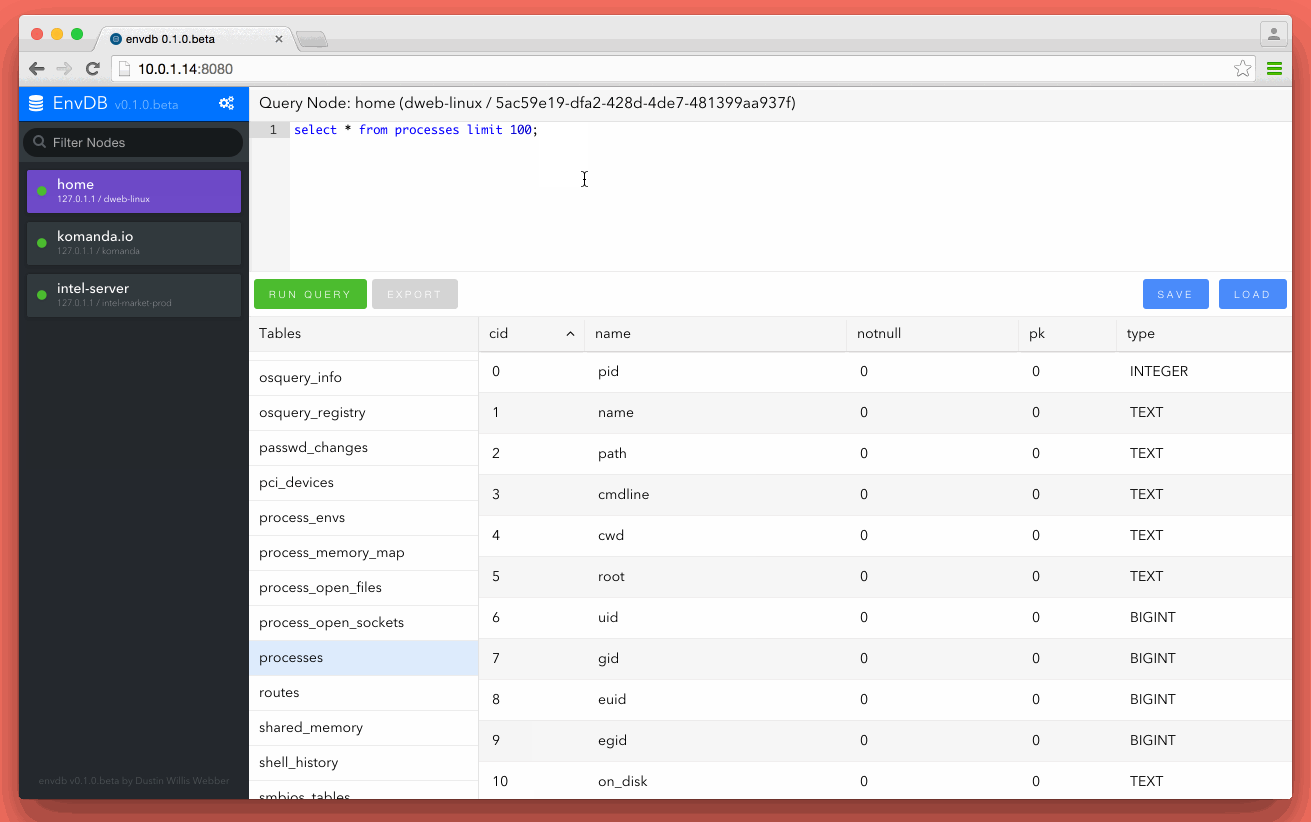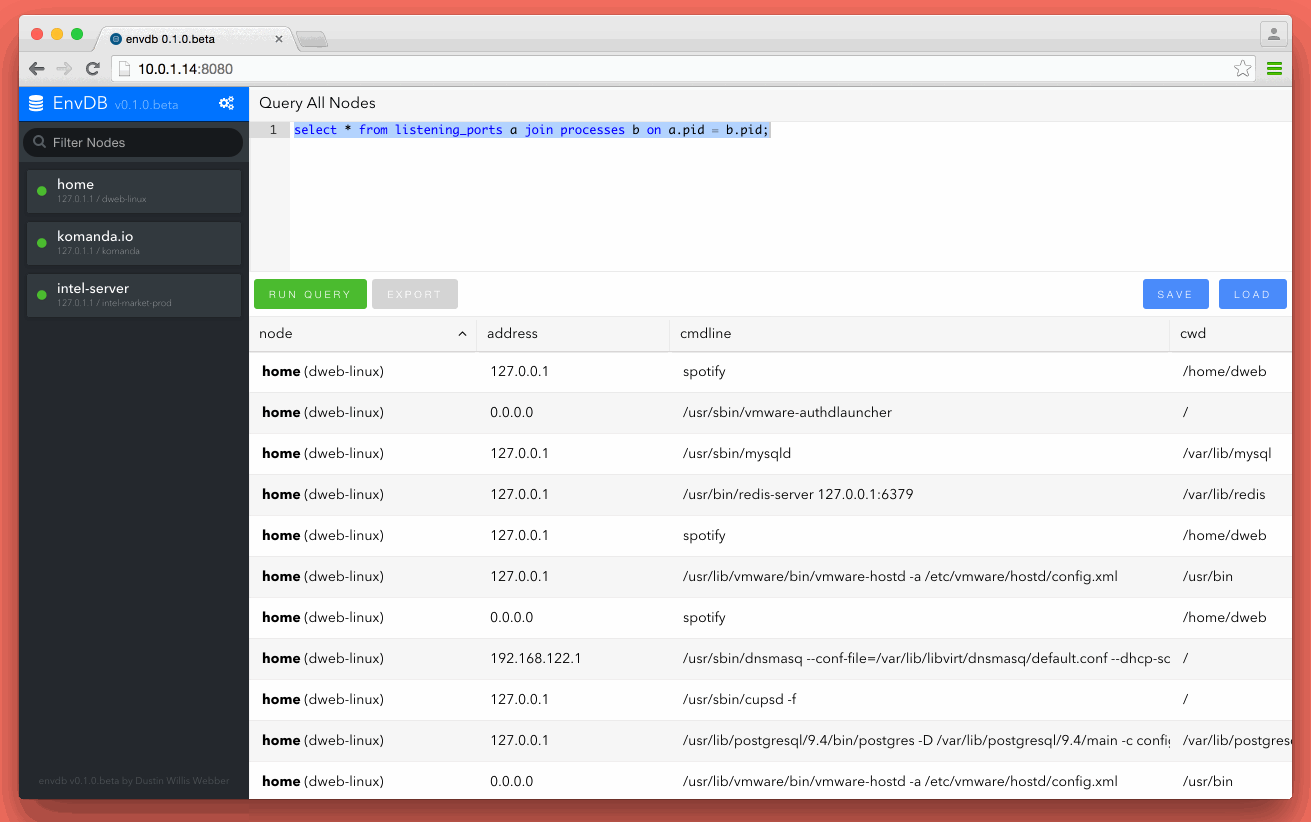
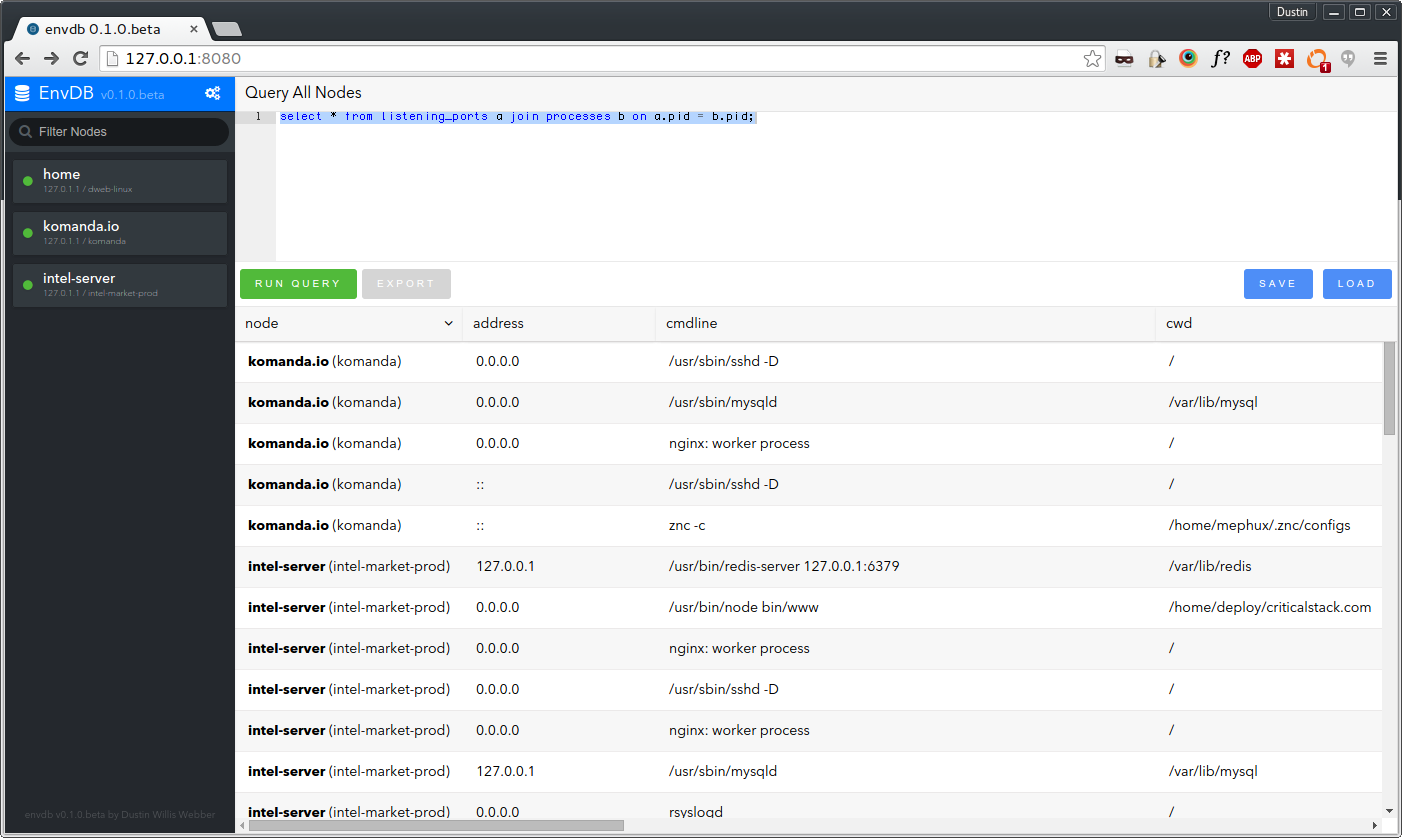
Envdb turns your production, dev, cloud, etc environments into a database cluster you can search using osquery as the foundation.
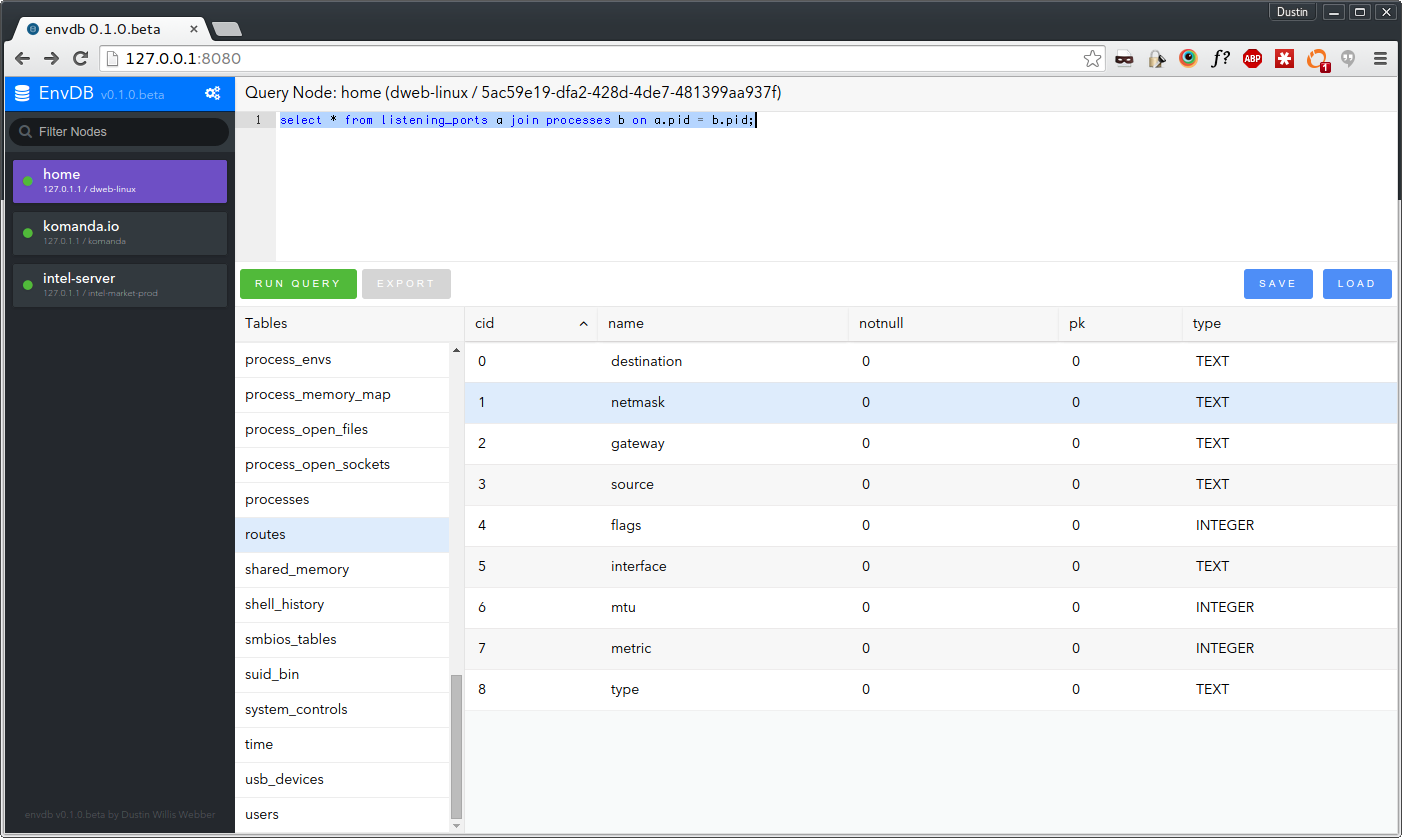
Envdb allows you to register each computer, server or asset as a node in a cluster. Once a new node is connected it becomes available for search from the Envdb ui. Envdb was built using golang so the whole application, node client and server comes as one single binary. This makes it really easy to deploy and get working in seconds.
Video Intro: https://youtu.be/ydYr7Ykwzy8
Envdb wraps the osquery process with a node agent (node as in cluster node) that can communicate back to a central location. When that node gets a new query, it's executed and then sent back to the tcp server for rendering. Once the request is processed it's then sent to any avaliable web clients using websockets.
Envdb has an embedded sqlite database for node storage and saved searches.
ui --websockets--> server --tcp--> node client.
Pre-built versions (deb/tar.gz) of envdb are avaliable for linux 386/amd64. linux downloads
Building on macosx is easy tho, checkout the section below.
Make sure you have Go installed. I used Go version 1.4.1.
go get github.com/jteeuwen/go-bindata/...go get github.com/elazarl/go-bindata-assetfsgo get github.com/tools/godep
git clone https://github.com/mephux/envdb.gitcd envdbmake
- NOTICE: The default username and password for the UI.
- username: admin@envdb.io
- password: envdb
usage: envdb [<flags>] <command> [<flags>] [<args> ...]
The Environment Database - Ask your environment questions
Flags:
--help Show help.
--debug Enable debug logging.
--dev Enable dev mode. (read assets from disk and
enable debug output)
-q, --quiet Remove all output logging.
--version Show application version.
Commands:
help [<command>]
Show help for a command.
server [<flags>]
Start the tcp server for node connections.
node --server=127.0.0.1 [<flags>] <node-name>
Register a new node.
users [<flags>]
User Management (Default lists all users).
$ envdb help server
usage: envdb [<flags>] server [<flags>] [<command>]
Start the tcp server for node connections.
Flags:
-p, --port=3636 Port for the server to listen on.
-P, --http-port=8080
Port for the web server to listen on.
Args:
[<command>] Daemon command. (start,status,stop)
Running the server without a `command` (start, stop or status) will run the server in the foreground.
* Note: By default this will start the tcp server on port 3636 and the web server on port 8080.
$ envdb help node
usage: envdb [<flags>] node --server=127.0.0.1 [<flags>] <node-name>
Register a new node.
Flags:
-s, --server=127.0.0.1
Address for server to connect to.
-p, --port=PORT Port to use for connection.
Args:
<node-name> A name used to uniquely identify this node.
`sudo envdb node --server <ip to server> SomeBoxName`
- That's it - it's really that simple.
-
list users
envdb users -
add a new user
envdb users --add -
remove a new user
envdb users --remove <email>
Like envdb? Follow the repository on GitHub and if you would like to stalk me, follow mephux on Twitter and GitHub.
- add in memeory pagination for results.
- Node/Server auth, verification and validation.
- Code cleanup (will continue forever).