This project aim is to create software to controls real self-driving car. It is based on architecture which is provided by Udacity as a base for final task.
| Team member | |
|---|---|
| Andrey Zabegaev | andronics@mail.ru |
| Pavel Silin | silinp@yandex.ru |
| Jens Kutschera | jenskutschera@gmail.com |
| Assem Sabbah | assem.sabbah@gmail.com |
The best and stable way to run this project would be to use docker. Docker installation instruction can be found here.
Clone this project repository
git clone https://github.com/Spinch/CarND-Capstone.gitGot to project directory
cd ./CarND-CapstoneBuild the docker container
docker build . -t capstoneRun the docker container
docker run -p 4567:4567 -v $PWD:/capstone -v /tmp/log:/root/.ros/ --rm -it --name roskinetic capstoneIf you would like to create another connection to this container you can use command:
docker exec -i -t roskinetic bashIn container make and run styx
cd ros
catkin_make
source devel/setup.sh
roslaunch launch/styx.launchRun the simulator on host machine.
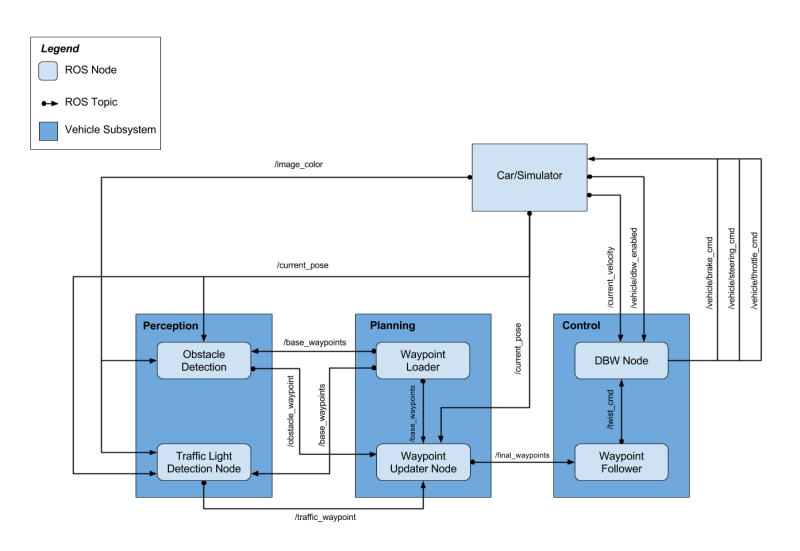
System components communication i based on ROS communication ideology. We have three main subsystems: perception, planing and control. Here is the system architecture diagram:
There are two versions of perception subsystem: the one used for simulator-generated data and the one used on site.
Perception subsystem used for simulator-generated data has a signle node:
- Traffic lights detection node - looks for traafic lights in images provided by camera.
The approach used in traffic lights detection node is based on OpenCV approach. Firstly, obtained image is converted to HSV color scheme. Then all pixels that are not red enough
are dropped. Pixels that are left are used as a mask on a grayscale image. Hough transform is then used to detect circles in this image. In case one o more circles are detected we publish
status that traffic lights are red. In case no circles are detected we use the same apporoch to detect yellow traffic lights (as yellow traffic lights are used in planning subsytem as
well). Green lights are not detected as it is of no significance for planning subsystem.
To determine which one of traffic lights is closest to our car and ahecd of it waypoints are used. We precompute a closest waypoint to each of traffic lights and are subscribed to current closest to the car waypoint. As waypoints are ordered we can determine which one of precomputed traffic lights waypoints is the closest to the car and ahead of it. We publish this waypoint number with traffic lights status for our car to determine at which waypoint it should stop in case of red (or yellow) traffic lights.
Description of perception subsystem used on site will be written later.
Planning subsystem has two nodes:
- Waypoint Loader - loads waypoints from the file for all track.
- Waypoint Updater - receives all waypoints and current car position and generate list with fixed number of next waypoints.
Also, waypoint updater takes into account if there are red or yellow traffic light ahead of car. It calculates distance to traffic light stop line and linear decrease speed from fixed distance to this line. As the result cars smoothly stops right before stop line if necessary.
We have reduced number of final waypoints from 200 to 50 as it makes CPU load less and free resources for other tasks.
The control subsystem has two nodes: Waypoint Follower and DBW Node. First node takes desired path waypoints as input and produce desired linear and angular velocities as input for the second node.
DBW Node takes desired velocities as input and outputs three control commands: throttle, brake and steering. It consists of 4 parts:
- DBW_node.py - ROS wrapper for subscribing, publishing and getting parameters
- twist_controller.py - main control logic
- yaw_controller.py - steering controller, converts target angular and linear velocities to steering command
- pid.py - PID controller, used for throttle/brake command
twist_controller uses pid controller for throttle/brake control and twist_controller for steering control. Next brake value converts from m/s^2 to N*m by multiplication of vehicle mass and wheel radius. Also, if desired speed is less that 0.1 m/s than brake value is set to minimum of 700 N*m to hold car on place.