NOTE: in a follow-up work, we have parallelized the DRL part of the training. The code and container are also made available. If you want to use our code as a starting point for your own work, we strongly recommend to consider starting with the parallel code, rather than the code in this repository. The parallel code is simply more modern, and overall better. It is available at: https://github.com/jerabaul29/Cylinder2DFlowControlDRLParallel .
NOTE: cloning this repository may take quite a bit of time, because the full singularity container is committed through git-lfs in the container folder. The upside is that this makes all the code here "fully reproducible forever", the downside is that cloning takes time: be patient :) .
This repository performs Flow Control of the 2D Kármán Vortex Street with Deep Reinforcement Learning. The simulations are done with FEniCS, while the Reinforcement Learning is performed with the help of the library TensorForce. You will need Fenics, Tensorflow, Tensorforce and Gmsh available on your system in order to be able to run the code, and all in the right versions (see later down to get our container).
A question? Open an issue. An improvement? Make a push request.
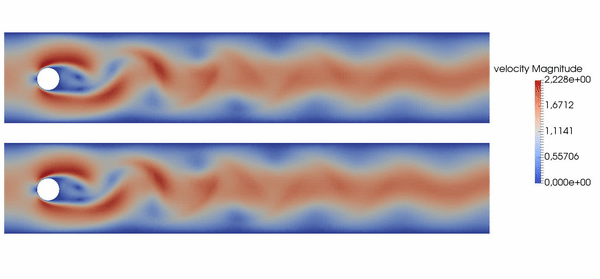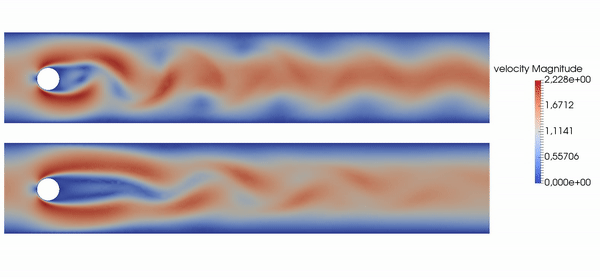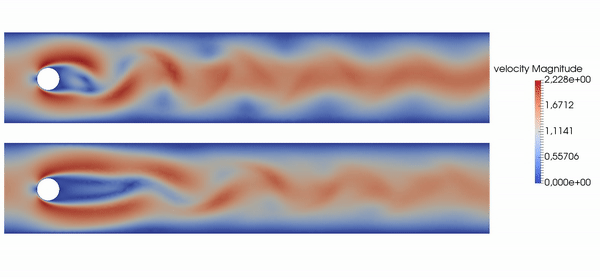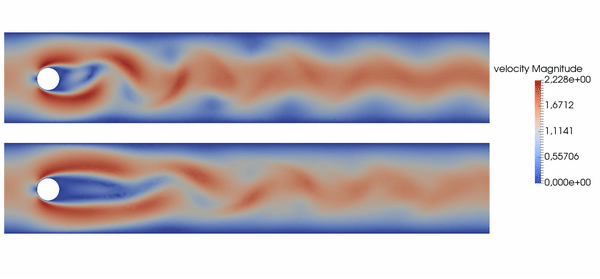
Basically, this repository allows you to produce results like the following, where top is baseline, bottom is controlled flow:
We are working on parallelization of the DRL algorithm through the use of several environments. See our preprint here:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1906.10382.pdf
and the repository with the parallel learning code here:
https://github.com/jerabaul29/Cylinder2DFlowControlDRLParallel
The DRL control can be coupled with a variety of CFD codes, and this was recently released by Li and Zhang, Reinforcement-learning-based control of confined cylinder wakes with stability analyses, in the case of Nek5000. Their code is available at: https://github.com/npuljc/RL_control_Nek5000 . That may also be a good further materials :) .
The code is in the Cylinder2DFlowControlWithRL subfolder. Inside it, you will find :
-
Python scripts, that are unchanged from one simulation to another, and are also unchanged from one learning to another.
- Env2DCylinder.py. This is the environment seen by the RL agent. It is the main class of the repo.
- flow_solver.py
- generate_msh.py
- jet_bcs.py
- msh_convert.py
- probes.py
-
Simulation folders, that contain information relative to the learning process. For each set of parameter you would like to test, you will have to create one folder. You can change a lot of parameters by modifying the environment itself or the learning session. 4 python scripts and up to 4 folders are in each of these Simulation folders :
- env.py is the script setting the environment parameters. Here you can modify, for example, the position of the probes, reward function used, etc.
- make_mesh.py allows you to remake the mesh if the geometry changed, and to re-compute a base state.
- perform_learning.py is the script for performing learning.
- single_runner.py allows you to test a model by evaluating a model using no randomness. You will also eventually see some subfolders :
- mesh, if mesh has been successfully created.
- results, containing some flow data in vtu files (so, look at these with for example paraview).
- saved_models, if you either launched a training session or tested some control on a single episode.
- best_model, if you launched a training session.
In addition, there is a folder about LearningMaterial that should be useful for people with no background in DRL / PPO. Following the links and looking at the videos should be enough to get you started in the field.
This code corresponds to the articles:
- https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.07664.pdf
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1808.10754.pdf
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-fluid-mechanics/article/artificial-neural-networks-trained-through-deep-reinforcement-learning-discover-control-strategies-for-active-flow-control/D5B80D809DFFD73760989A07F5E11039
If you use our code in your research, please consider citing our papers:
Rabault, J., Kuchta, M., Jensen, A., Reglade, U., Cerardi, N., 2018. Artificial Neural Networks trained through Deep Reinforcement Learning discover control strategies for active flow control. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.07664.
Rabault, J., Reglade, U., Cerardi, N., Kuchta, M. and Jensen, A., 2018. Deep Reinforcement Learning achieves flow control of the 2D Karman Vortex Street. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.10754.
Rabault, J., Kuchta, M., Jensen, A., Réglade, U., & Cerardi, N. (2019). Artificial neural networks trained through deep reinforcement learning discover control strategies for active flow control. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 865, 281-302. doi:10.1017/jfm.2019.62
In addition, some slides of a lecture about this work are available on my website:
Note that, in the first article (and the JFM article), we adopt a renormalization where the diameter of the cylinder is 1. In both the second article and the code, the renormalization is a bit different and follows what is done in the Turek benchmark. This simply means that lengths and times are scaled a factor 10 between the simulations / second article and the first one
I was recently invited to give a guest lecture about DRL for flow control at AFMS; the recording is available at: https://youtu.be/irNheFmWZTo .
You can find the corresponding slides at: https://github.com/jerabaul29/2023_slides_DeepReinforcementLearning_ActiveFlowControl_AFMS/blob/main/slides_2023_03_01_RABAULT_DRL_active_flow_control.pdf .
I present two methods here: install everything by hand in the right versions, or use a singularity container for virtualization and reproducibility. The singularity container is the recommended solution, that has been tested at many institutions and reproducibility has been confirmed and validated. Several users who tried to install things by hand contacted me because they had problem to reproduce the software stack: this is not the recommended solution and I will not help with debugging problems you encounter in this case.
Before launching any script, check that you have installed (tested on Ubuntu 16.04) :
- Tensorflow (tested with tensorflow 1.8.0)
- TensorForce (tested with tensorforce 0.4.2, commit from the tensorforce repo: 5f770fd)
- Gmsh (versions 3.+ but not 4.+, tested with 3.0.6; you can use the gmsh binary for linux 64 bits provided alongside this readme)
- Fenics (2017.1.0 or 2017.2.0)
For this, you can either install these modules on your computer yourself (respecting the version / commit, otherwise some things may break), or use the singularity image we provide (recommended). Some of the steps below assume that you are working on a Linux machine, but you can adapt to a windows / Mac.
If you want to use our singularity container (recommended, credits to Terje Kvernes, UiO / IT of the Department of Mathematics for setting up this infrastructure):
- Download and install singularity (see for example the tutorial here http://www.sdsc.edu/support/user_guides/tutorials/singularity.html , or the singularity documentation).
- Download our singularity container parts from the repo, available in the
containerfolder of hte present repo: https://github.com/jerabaul29/Cylinder2DFlowControlDRL/tree/master/container . The previous solution that relied on the folk.uio.no personal websites has been end-of-lifed and discontinued. - The container was committed using git-lfs in several segments, to make sure that the size limit is not over-run. To put the segments from the container folder together. A note here: while git-lfs should allow to download sucessfully all segments upon cloning the repository, it seems that there is a problem, either with github serving the git-lfs files, or with git checking out the large files. So to get all the fragments, you may have to use the github web GUI, i.e. to 1) go to the right folder (
https://github.com/jerabaul29/Cylinder2DFlowControlDRL/tree/master/container) 2) for each fragment there, to click on the filename and use the download button to start downloading directly from your browser. Once this is done, you can assemble by:
> cat fenics-and-more.img_part.?? > fenics-and-more.img
> sha256sum fenics-and-more.img
e6e3c6b24d4edb93022d1156aba1a458367242d0ba1f249508bd2669f87ee4b8 fenics-and-more.img
Remember to check the checksum to make sure that the image was correctly assembled.
- Download from their website ( http://gmsh.info/ ) and unpack Gmsh, in the right version.
- Now you should be able to load your singularity container inside which you can work in command line as a normal UNIX and run our scripts (of course, you will nedd to adapt the SET_YOUR_PATH stuff to your local paths; note that the gmsh path can only be DOWNSTREAM of the root path for your home if you use the -H option):
singularity shell SET_YOUR_PATH/fenics-and-more.img -c "export DISPLAY=:0.0 && export PATH="SET_YOUR_PATH/gmsh-git-Linux64/bin:$PATH" && /bin/bash"
Note that if you want to execute on an external media, you can type a command as following, but you will also need a copy of gmsh on the corresponding media (as the -H acts as a mounting point, so your usual home will not be available anymore):
singularity shell -H SET_YOUR_BASE_PATH SET_YOUR_PATH/fenics-and-more.img -c "export DISPLAY=:0.0 && export PATH="SET_YOUR_BASE_PATH/gmsh-git-Linux64/bin:$PATH" && /bin/bash"
This singularity image contains tensorflow, tensorforce, fenics, and a Python install with the packages you need to run our scripts. If you want to mesh, you have to make sure that the path export to your gmsh is valid (the path export works only from folders visible to singularity, i.e. under the SET_YOUR_BASE_PATH in the tree). If you have problems with the gmsh calls, you may also hard code the paths to gmsh in the calls lines 35 and 52 in Cylinder2DFlowControlWithRL/generate_msh.py, putting the path to the gmsh in your cloned repo. If you do this, remember to make gmsh executable first (chmod +x gmsh).
Go in Cylinder2DFlowControlWithRL/baseline_flow. Just launch single_runner.py to look at the baseline flow. During the computation, the graphical interface shows the state of the flow, and the data is saved in baseline_flow/results for the vtu files, and in baseline_flow/saved_models for the csv files.
Go in Cylinder2DFlowControlWithRL/ANN_controlled_flow_singlerun. This folder contains a copy of one of our best model. The velocity field shown in our article stems from this model. You can run this model by launching single_runner.py.
Go in Cylinder2DFlowControlWithRL/ANN_controlled_flow_learning. You will see that this folder contains less elements than ANN_controlled_flow_singlerun. Indeed, we made a copy and deleted the results from the learning session. You can try to launch a session, it will have the same parameters as ANN_controlled_flow_singlerun, and you can compare the model you obtain with ours.
To start a learning, launch perform_learning.py. This will create three directories: results, saved_models, and best_model.
results contains the .vtu outputs for the pressure, velocity, and the recirculation area for the last epoch.
saved_models contains the last stat of the ANN, as well as output.csv, the history of the training, debug.csv, the history of the console debug. Please note that if the training is interrupted, it will automatically restart from it's last save.
Finally, best_model contains the save of the best neural network encountered during the training phase.
In some situation, you will have to recreate the mesh. If you change the geometry of the simulation, for instance if you change the jets positions, you will have to do so.
For this, go in empty_simulation and run make_mesh.py. This script will create a directory mesh that contains all the needed files to start the training. This includes the mesh, as well as the converged pressure and velocity fields. If the directory already exists, it will be automatically overwritten.
By default, the graphical debug is launched, but to run this script on a distant computer, it's preferable to turn it off. Just go ahead and edit make_mesh.py:
import env
env.resume_env(plot=False, remesh=True) #plot to 500 if a graphical debug neededOnce this is finished, you have a new folder containing the mesh and converged pressure and velocity fields, and you are ready to perform more learning.
We are going to see how to configure and launch a simple simulation where the jets form an angle of 5 degree with the vertical. First, we highly recommend you to run the simulations in a copy of the GitHub directory, in order to not pollute the Git with simulation results. Make a copy of the repo, and within this new folder an empty_simulation within Cylinder2DFlowControlWithRL. Rename it with an appropriate name. Here, we will call it angle5.
Now, we are going to edit env.py. This file contains all the parameters relative to the simulation. In our case we will simply set jet_angle to 5 degrees:
jet_angle = 5Here is a non exhaustive list of all the parameters that can be changed and their effect:
nb_actuations: The number of controls performed during an epoch.simulation_duration: The duration in seconds of the simulation (an epoch).dt: The time step in second of the simulation- Note that this parameter might need to be adjust to respect CFL condition.
- The number of actuations must not exceed the duration of the simulation divided by dt.
jet_angle: angle of the jets, can be positive or negative.'coarse_size': The refinement of the mesh far from the cylinder.'cylinder_size': The refinement of the mesh far cloth to the cylinder.reward_function: The type of reward function to train the NN, can be:'plain_drag''drag''drag_plain_lift''recirculation_area'
Now, just run make_mesh.py. This script will create a directory mesh that will contains all the needed files to start the training. This includes the mesh, as well as the converged pressure and velocity fields. If the directory already exists, it will be automatically overwritten.
By default, the graphical debug is launched, but to run this script on a distant computer, it's preferable to turn it off. Just go ahead and edit make_mesh.py:
import env
env.resume_env(plot=False, remesh=True) #plot to 500 if a graphical debug neededYou have a number of parameters you can adjust regarding the mesh. These are summarized in the geometry_params dictionary of the env.py file of each simulation. You can control the shape of the cylinder and simulation box, the position and number of the jets, the mesh refinement, etc. You can also set up different input velocity profiles through the profile function of the same file.
To launch the training, just run perform_learning.py. This will create three directories: results, saved_models, and best_model. The first one contains the .vtu outputs for the pressure, velocity, and the recirculation area for the last epoch.
saved_models contains the last stat of the NN, as well as output.csv, the history of the training, debug.csv, the history of the console debug. Please note that if the training is interrupted, it will automatically restart from it's last save.
Finally, best_model contains the save of the best neural network encountered during the training phase.
- The code is for some bad legacy reasons written in a 'dimensional' form. All results in the JFM paper are by contrast non dimensional. This can be confusing. For a detailed discussion of the non-dimensionalization process, see the discussion on this issue: #3 . Note that if you want to change the Reynolds number, you may need to adapt the renormalization coefficients: #6 .
-
There is a small erratum in one of the dumping routine, that is not fixed because of backwards compatibility of some of our plotting routines. Namely, files of the kind debug.csv have columns in a different order than indicated by the header; the real order is [Name;Episode;Step;RecircArea;Drag;lift]).
-
There is a memory leak in the specific matplotlib version included in the container... This means that, if you let your code run with plotting, the RAM of your computer will saturate after a while. To avoid this, only use matplotlib showing when you want to visually inspect training. When you want to perform 'heavy' training, disable plotting by setting the plot named argument to False in your perform_learning.py
-
In the JFM paper
-
Eqn. defining Q_ref (just after Eqn. 2.6, in the text):
rhoshould not be needed in non-dimensional form. Anyways,rhois 1, so this makes not difference. -
Eqn. B3: there is a typo, this should be
/R, not/R^2. This is purely a typo and is of course correctly implemented in the code (i.e., the code is correct).
-