In this module, you will verify and confirm the prerequisites for ZTP, the Zero Touch Provisioning feature of IOS XE on the Catalyst 9300 switch. At the end of this module, you will issue the 'write erase' command, reload the switch, and watch as the ZTP process completes and the switch is configured programmatically and automatically.
What is ZTP? When a device that supports Zero-Touch Provisioning boots up, and does not find the startup configuration (during initial installation), the device enters the Zero-Touch Provisioning mode. The device searches for an IP from a DHCP server and bootstraps itself by enableing the Guest Shell. The device then obtains the IP address or URL of an HTTP/TFTP server, and downloads a Python script from an server to configure the device.
Connect to the Remote Desktop Environment and use MobaXterm to SSH into Ubuntu VM:
ZTP Python File: Review the ztp-simple.py file on the Ubuntu VM which is located at /var/www/html. This file uses the Python API to set the interface IP address, configure credentials and enables access to the device over the programmatic interfaces, as well as to configure some additional device features. From the Windows Jump Host desktop, onen a SSH session to the Ubuntu server and review the ztp-simple.py script:
auto@automation:~$ less /var/www/html/ztp-simple.py
Note : The Python script with the POD environment may differ slightly
print "\n\n *** Sample ZTP Day0 Python Script *** \n\n"
# Importing cli module
import cli
print "Configure vlan interface, gateway, aaa, and enable netconf-yang\n\n"
cli.configurep(["int gi1/0/24","no switchport", "ip address 10.1.1.5 255.255.255.0", "no shut", "end"])
cli.configurep(["username admin privilege 15 secret 0 Cisco123"])
cli.configurep(["interface Loopback0", "ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0", "end"])
cli.configurep(["aaa new-model", "aaa authentication login default local", "end"])
cli.configurep(["aaa authorization exec default local", "aaa session-id common", "end"])
cli.configurep(["ntp server 10.1.1.3", "netconf-yang", "end"])
cli.configurep(["line vty 0 15", "transport input all", "exec-timeout 0 0", "end"])
cli.configurep(["ip scp server enable", "end"])
cli.configurep(["hostname C9300", "end"])
cli.configurep(["telemetry ietf subscription 101","encoding encode-kvgpb","filter xpath /process-cpu-ios-xe-oper:cpu-usage/cpu-utilization/five-seconds","stream yang-push","update-policy periodic 500","receiver ip address 10.1.1.3 57500 protocol grpc-tcp","end"])
cli.configurep(["ip http secure-server", "restconf", "end"])
cli.configurep(["iox", "end"])
print "\n\n *** Executing show ip interface brief *** \n\n"
cli_command = "sh ip int brief"
cli.executep(cli_command)
print "\n\n *** ZTP Day0 Python Script Execution Complete *** \n\n"IP: The IP address on the Ubuntu VM is is 10.1.1.3 and can be confirmed with the following commands. It is important to know the IP as it is used for setting the DHCP option 67 - this is how the IOS XE devices know where to find the Python file to execute.
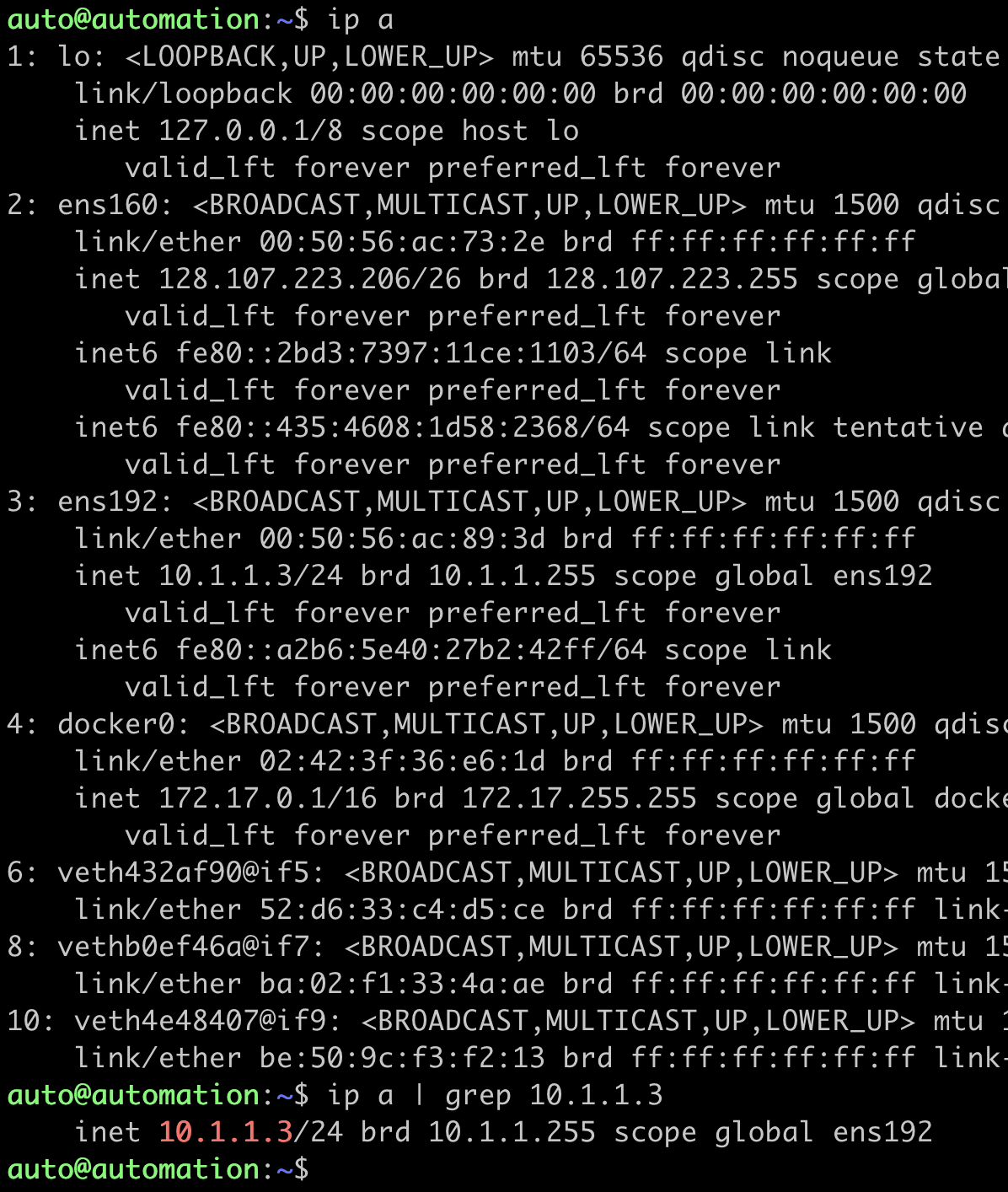
Check the interface IP assignments:
auto@automation:~$ ip a
auto@automation:~$ ip a | grep 10.1.1.3
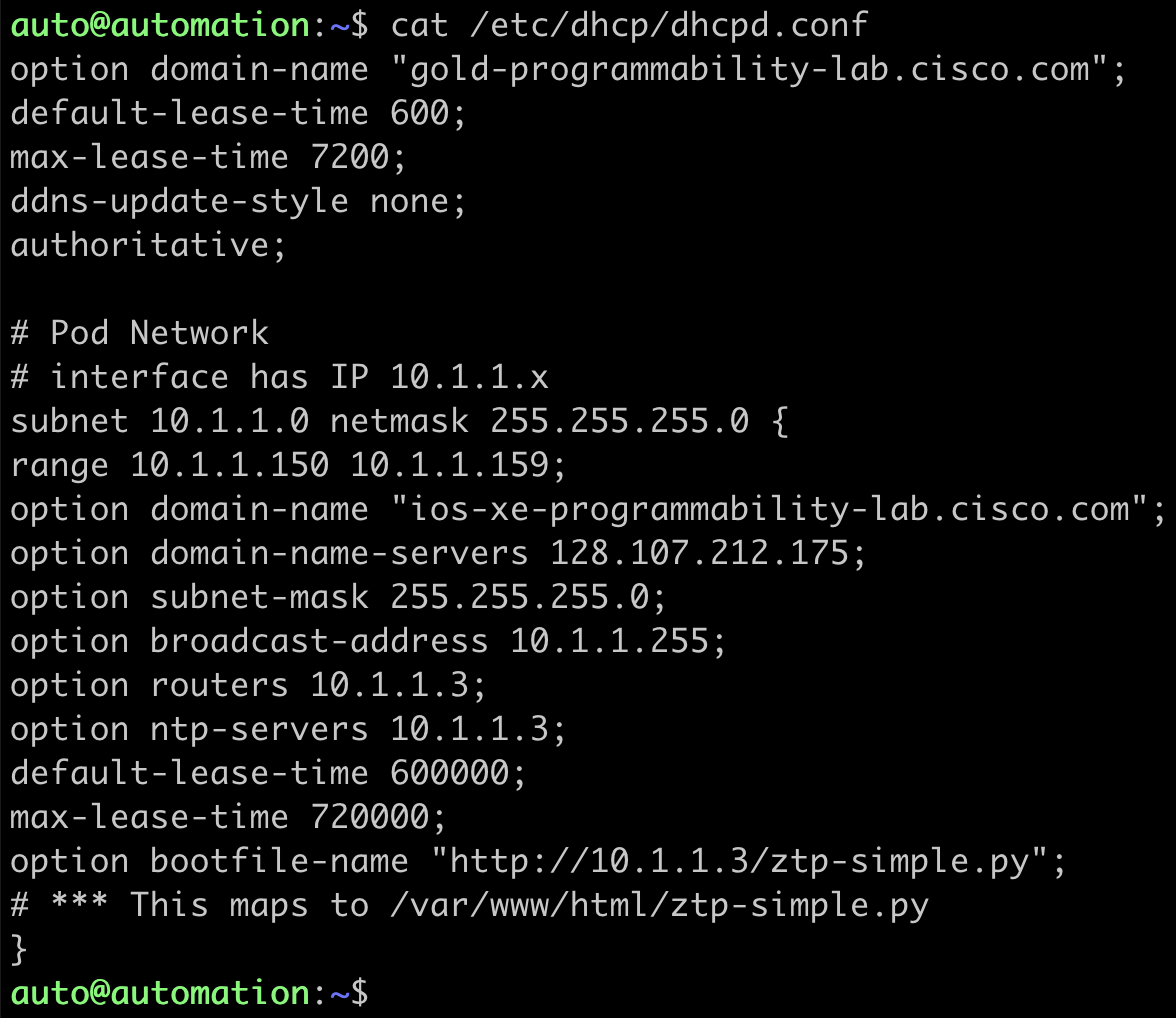
DHCP Server : ZTP works when the DHCP server replies to the IOS XE device with DHCP option 67 in the DHCP Response. The DHCP server's configuration file is called dhcpd.conf and it is located in the /etc/dhcp/ folder. It specifies the IP range to serve DHCP leases to, as well as the Python file that the device will download and executed as part of the option bootfile-name which is also known as option 67.
Examine the DHCP server configuration:
auto@automation:~$ cat /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
If any changes are made to the configure file it can be restarted with the commands below:
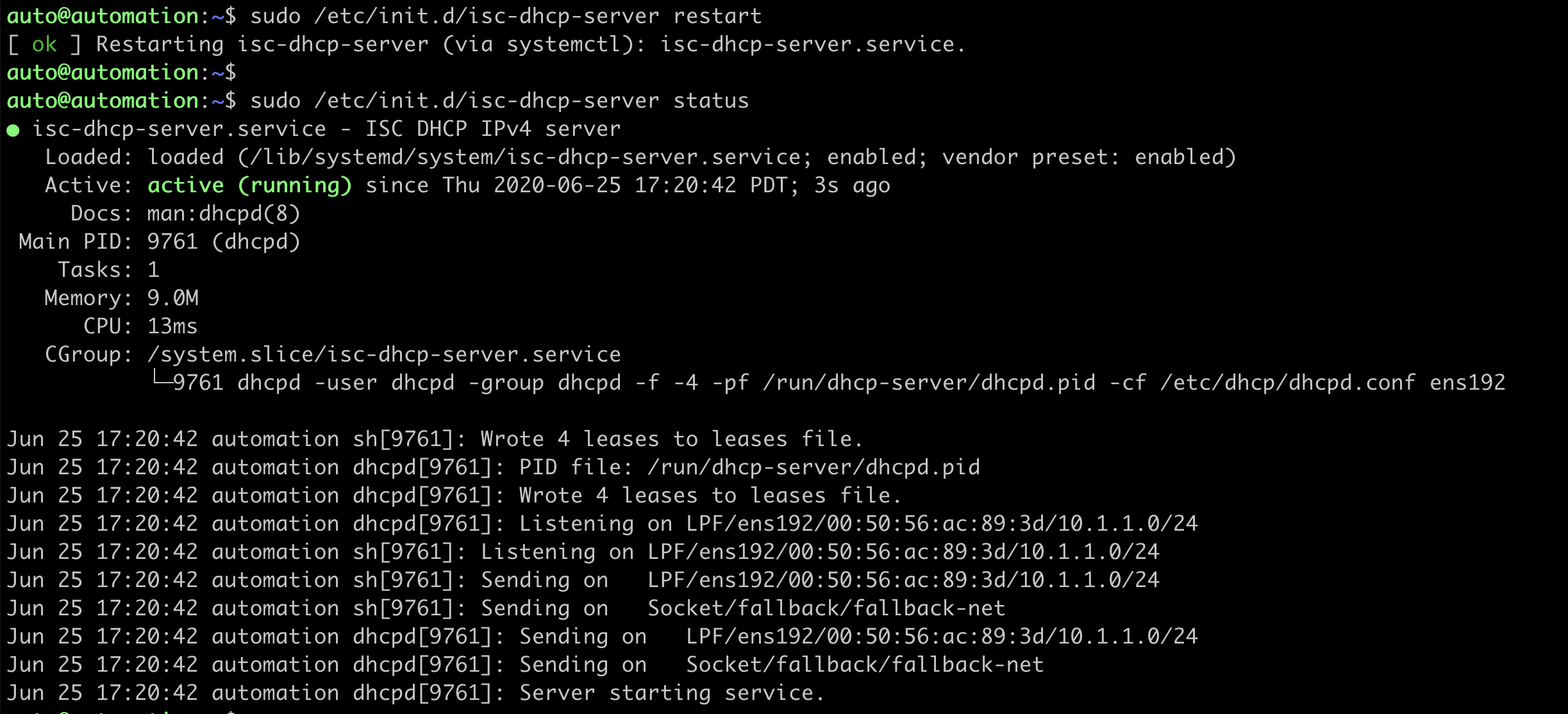
auto@automation:~$ sudo /etc/init.d/isc-dhcp-server restart
Check the status of the DHCP service to ensure it is running correctly
auto@automation:~$ sudo /etc/init.d/isc-dhcp-server status
Webserver : The Apache webserver is used to serve the Python file to the IOS XE device as part of the ZTP process. Either TFTP or HTTP can be used for the initial bootstrap configuration. In this example HTTP is used.
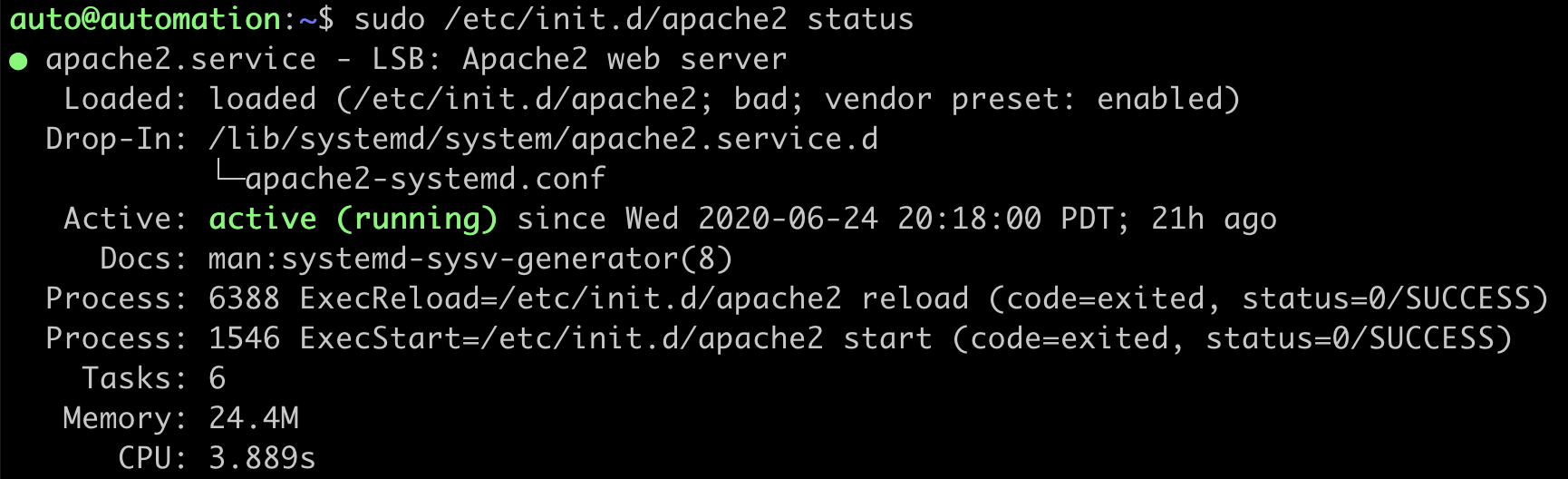
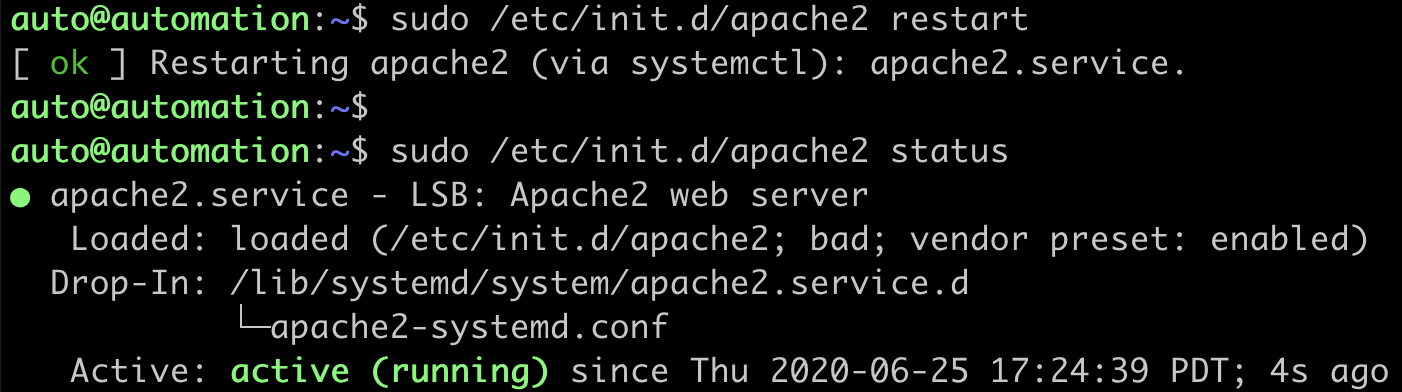
Check the status of the Apache webserver to ensure it is running:
auto@automation:~$ sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 status
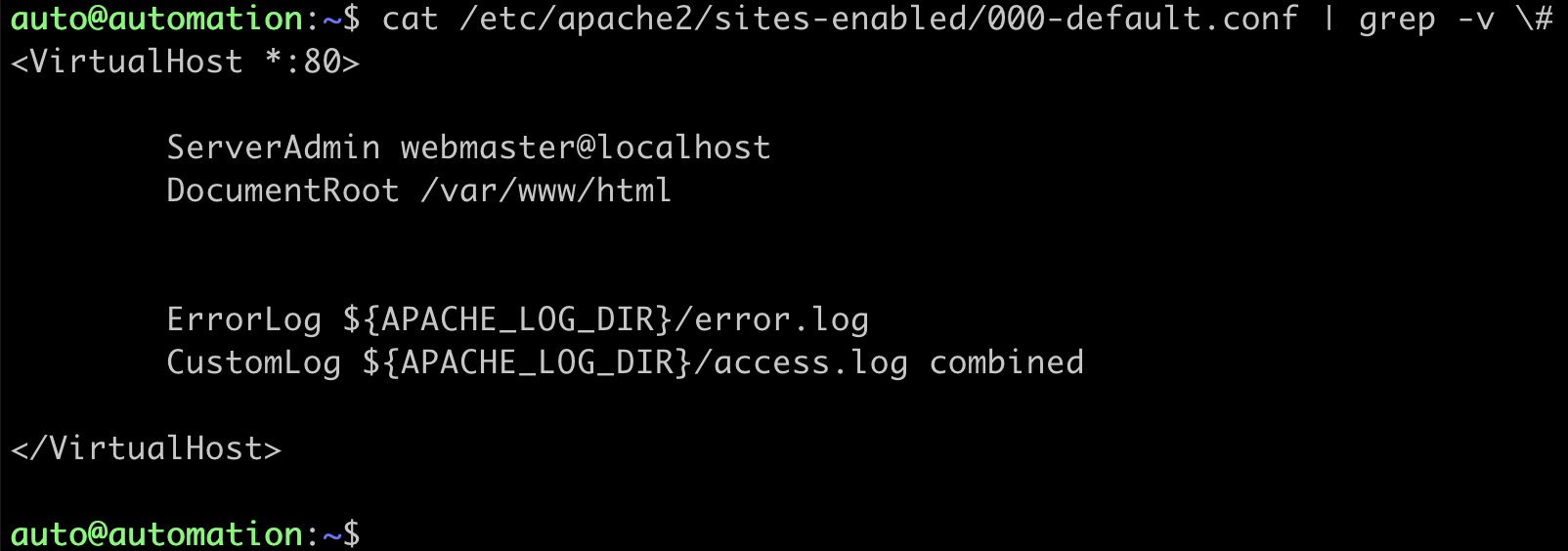
Check the configuration for the Apache webserver. This shows which folder the DocumentRoot is – this is the location where the Python files are stored:
*auto@automation:~$ cat /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf | grep -v #
If any changes are required to the Apache webserver configuration file, or if the service needs to be restart then run the following commands:
auto@automation:~$ sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
IOS XE Device: Now the prerequisites for ZTP are met and the device is ready to be reloaded once the previous configuration is removed – this is to ensure that the Day0 ZTP process is initialized once the switch boots. This emulates a new, un-configured device that is ready to provisioned.
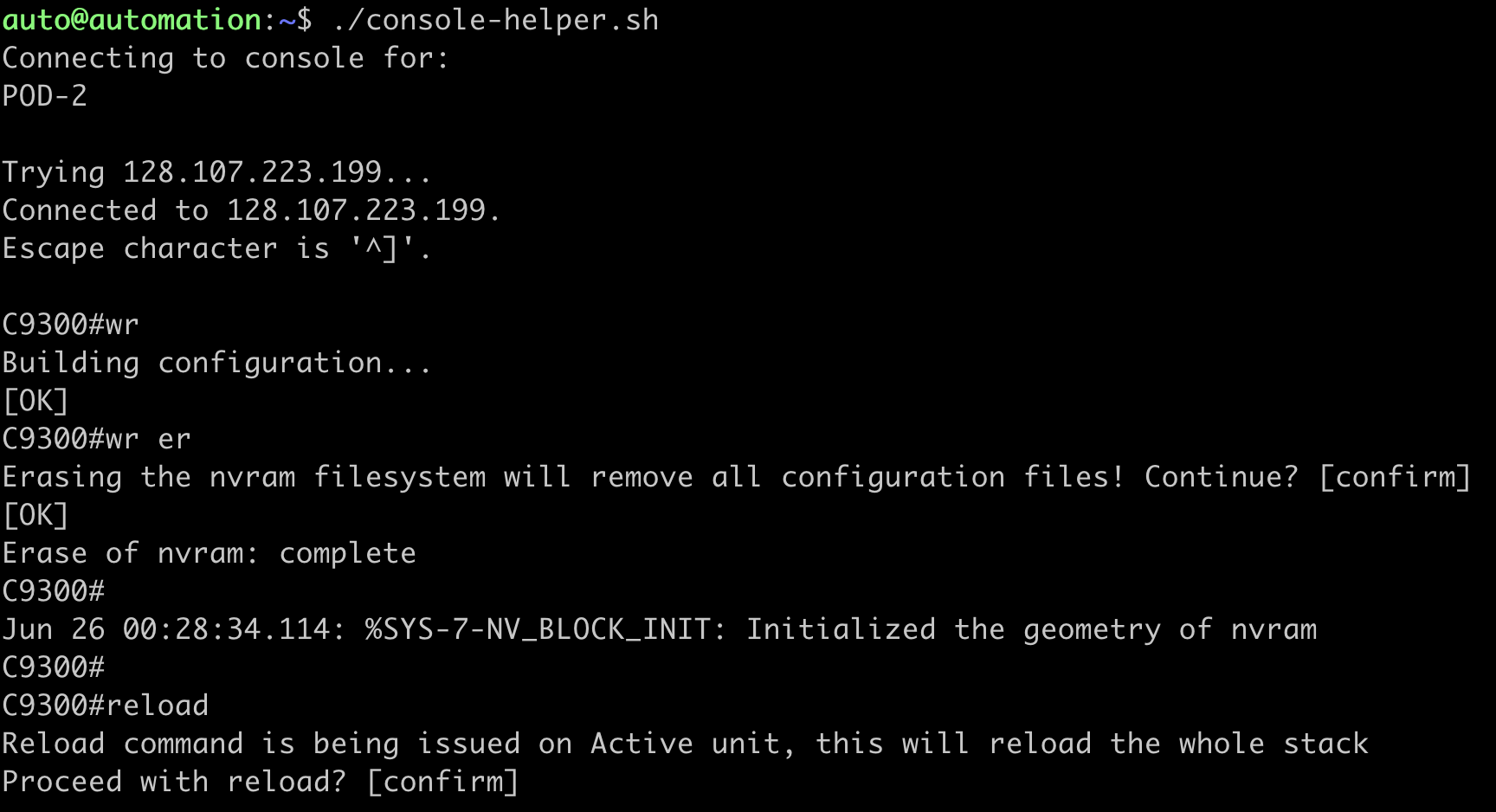
Conect to the Serial Console of the C9300 using MobaXterm's shortcut for "C9300 - Serial Console" or from the Ubuntu VM using the ~/console-helper.sh script - Both methods open a serial connection to the pod switch.
Once connected to the serial console the next step is to erase the configuration and reload the device
This process will take about 5 minutes to successfully complete. Once completed, ICMP pings from the device will begin responding.
C9300# wr
C9300# wr erase
C9300# reload
If prompted to save the configuration, enter no
Press enter to confirm reloading
The device will reload and once IOS XE boots up, the ZTP process will start. The device will obtain the ztp.py configuration file from the Ubuntu server that it receives in the DHCP response.
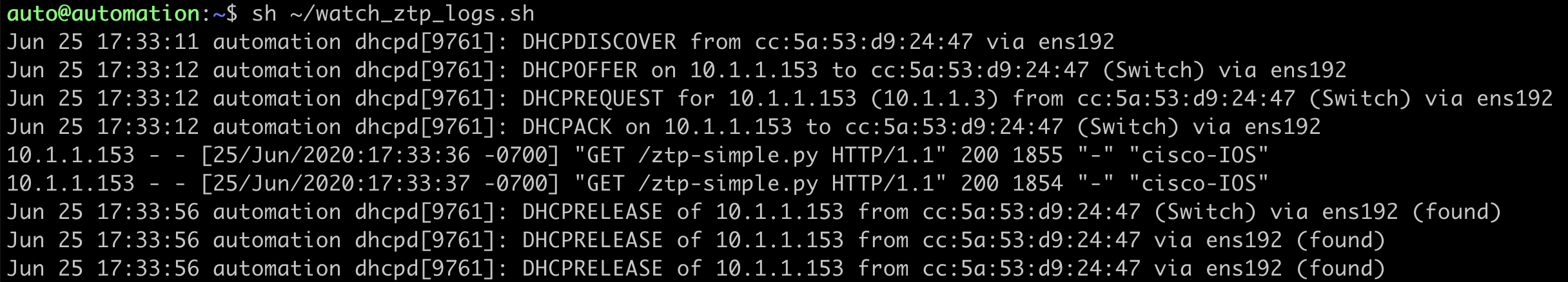
During this time, the DHCP and HTTP server logs can be followed, and progress can be tracked as the device boots completes the ZTP process. In this case, we see first the DHCP server providing the DHCPOFFER to the device, and next the GET requests to the HTTP server (from the device at IP 10.9.1.154) that accesses and executes the ztp-simply.py script:
auto@automation:~$ sh ~/watch_ztp_logs.sh
You may also start a ping to watch when the interface on the devices comes back online with the configuration applied. Start a ping to 10.1.1.5 which is the IP address specified in the ztp-simple.py file.
auto@automation:~$ ping 10.1.1.5
Once the ICMP ping replies start then the device has been successfully provisioned - You can now log back in using SSH or Telnet.
Example output from the serial console that shows successful ZTP and Python file execution:
The Cisco IOS XE Catalyst 9300 switch has now successfully completed the Zero Touch Provisioning process and is fully configured on the network. Because of the pre-configuration within the ztp-simple.py file, all use cases for the related IOS XE Programmability Lab have been enabled. Specifically, the switch has an IP, username/password, SSH access enabled, and the programmatic NETCONF and RESTCONF interfaces have also been configured and enabled.