This project enables you to fetch liked tweets from Twitter (using Selenium), save it to JSON and Excel files, and perform initial data analysis and image captions.
This is part of the initial steps for a larger personal project involving Large Language Models (LLMs). Stay tuned for more updates!
Before running the code, ensure you have the following:
- Required Python libraries (listed in
requirements.txt) - Get your Twitter auth token (Not API key)
- Quick text instruction:
-
- Go to your already logged-in Twitter
F12(open dev tools) ->Application->Cookies->Twitter.com->auth_key
- or follow the video demo in FAQs section.
- GEMINI API key (*Optional, only needed if you want to try the image captions feature)
- Clone the repository (Recommend) or download the project files.
git clone https://github.com/jerlinn/X-Insight
- Install the requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Open the
config.pyfile and replace the placeholders with your actual API keys:
- Set
TWITTER_AUTH_TOKENto your Twitter API authentication token. - Set
GEMINI_API_KEYto your GEMINI API key. 🔑 Get your own key here.
To fetch data from Twitter and save it to JSON and Excel files, follow these steps:
- Open
twitter_data_ingestion.py. - Modify the
fetch_tweetsfunction call at the bottom of the script with your desired parameters:
- Set the URL of the Twitter page you want to fetch data from (e.g.,
https://twitter.com/ilyasut/likes). - Specify the start and end dates for the data range (in
YYYY-MM-DDformat).
-
Run the script by executing the following command (recommend run this in IDE directly):
python twitter_data_ingestion.py -
The script will fetch the data from Twitter, save it to a JSON file, and then export it to an Excel file.
To perform initial data analysis on the fetched data, follow these steps:
- Open the
twitter_data_initial_exploration.ipynbnotebook in Jupyter Notebook or JupyterLab. - Run the notebook cells sequentially to load the data from the JSON file and perform various data analysis tasks.
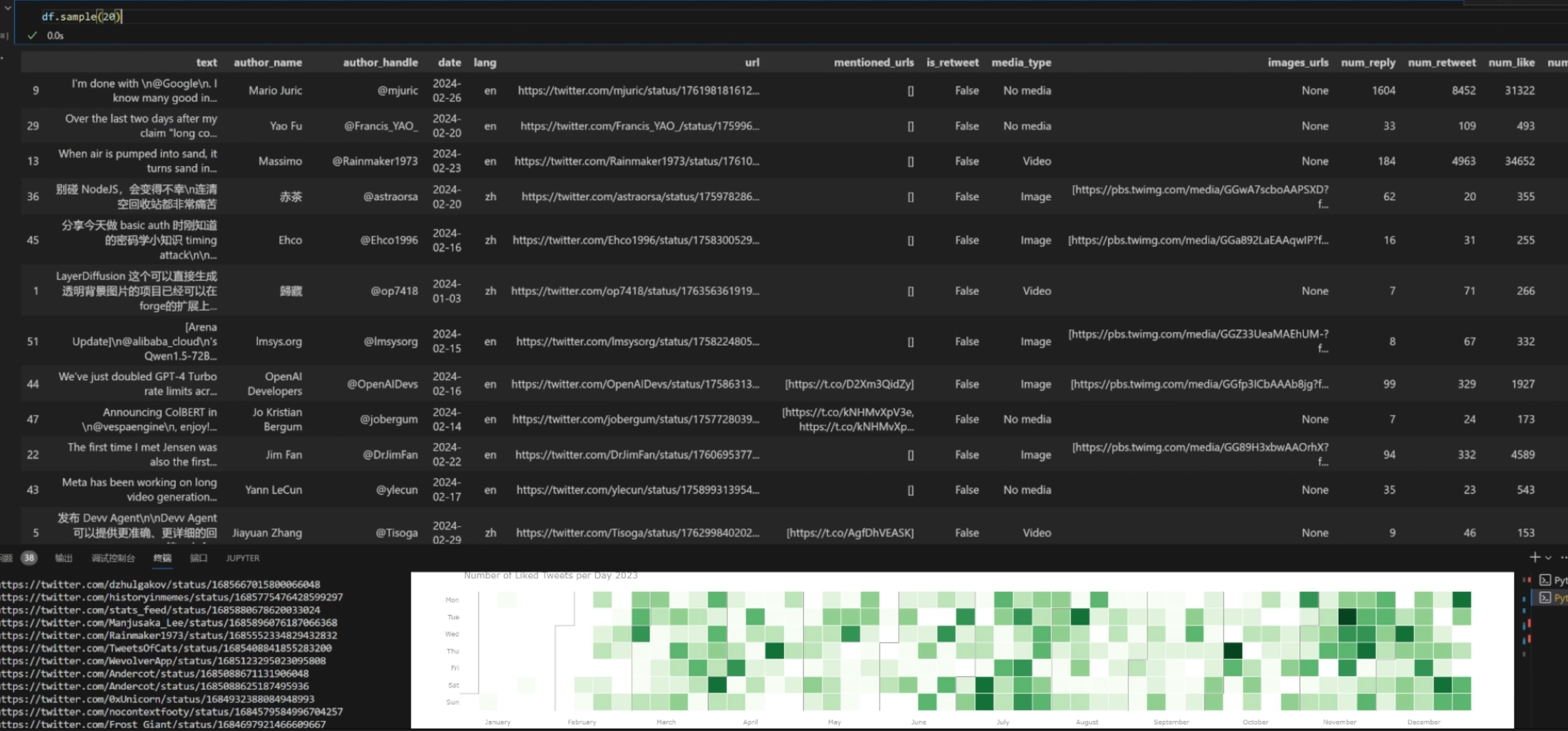
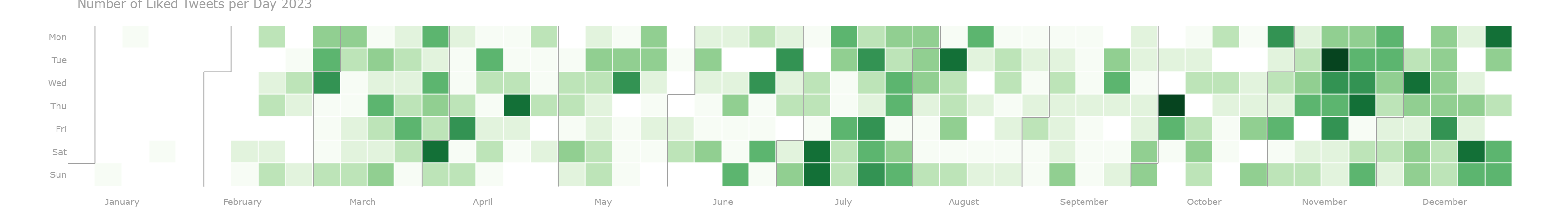
Some sample results:
- The notebook also demonstrates how to use the Gemini API & Replicate API with LlaVa V1.6 to generate image captions for tweet images (with tweet metadata).

The project includes sample output files for reference:
sample_output_json.json: A sample JSON file containing the fetched Twitter data.sample_exported_excel.xlsx: A sample Excel file exported from the JSON data.
Feel free to explore and modify the code to suit your specific data analysis requirements.
-
Will I get banned? Could this affect my account?
- Selenium is one of the safest scraping methods out there, but it's still best to be cautious when using it for personal projects.
- I've been using it for quite a while without any issues.
- (Though, if you've got a spare / alt account, I'd recommend using that one's auth token instead)
-
How do I find the auth token?
- Check out this for a step-by-step guide!
- Initial structure and parts of the Selenium code inspired by Twitter-Scrapper.
- The image captioning feature is powered by the OpenAI API. You should be able to achieve similar results using Gemini 1.0.
For any questions or issues, please open an issue in the repository.