bragg-detect is python library to detect Bragg peaks in 3D X-ray/neutron images.
To install bragg-detect:
pip install https://github.com/stfc-sciml/bragg-detect/archive/refs/heads/main.zipbragg-detect only has one user API:
def detect_bragg_peaks(data,
# slicing
large_peak_size, detect_block_size=5,
detect_block_overlap=2, verify_block_size=10,
# 2d blobs by LoG
min_sigma=None, max_sigma=None, num_sigma=5,
threshold=.2, overlap=.5, log_scale=False,
# 3d peak selection
strategy_3d='individual', n_components_bgm=5,
n_init_bgm=1,
# others
workers=1, verbose=True):
"""
Detect Bragg peaks.
:param data: the 3D data as a numpy.ndarray or a tuple
(filename, dsetname) to specify a HDF5 dataset storing the 3D data;
when using multiple works, use (filename, dsetname) for both better
performance and less memory consumption
:param large_peak_size: approximate size of the large peaks in data,
array-like in the form of (size_x, size_y, size_z);
:param detect_block_size: size of the detection blocks relative to
`large_peak_size`; default is 5
:param detect_block_overlap: overlap of the detection blocks
relative to `large_peak_size`; default is 2
:param verify_block_size: size of the verification blocks relative
to `large_peak_size`; default is 10
:param min_sigma: min_sigma for blob_log() of scikit-image;
default is None, or large_peak_size // 4
:param max_sigma: max_sigma for blob_log() of scikit-image;
default is None, or large_peak_size
:param num_sigma: num_sigma for blob_log() of scikit-image;
default is 5
:param threshold: threshold for blob_log() of scikit-image;
default is 0.2
:param overlap: overlap for blob_log() of scikit-image;
default is 0.5
:param log_scale: log_scale for blob_log() of scikit-image;
default is False
:param strategy_3d: strategy for 3d morphological analysis; can be
`individual` or `bgm_clustering`; default is `individual`
:param n_components_bgm: n_components for BayesianGaussianMixture() of
scikit-learn, used only for `bgm_clustering` strategy; default is 5
:param n_init_bgm: n_init for BayesianGaussianMixture() of
scikit-learn, used only for `bgm_clustering` strategy; default is 1
:param workers: number of workers; default is 1
:param verbose: verbose info during running; default is True
:return: detected Bragg peaks
"""See example/example.py to learn the usage.
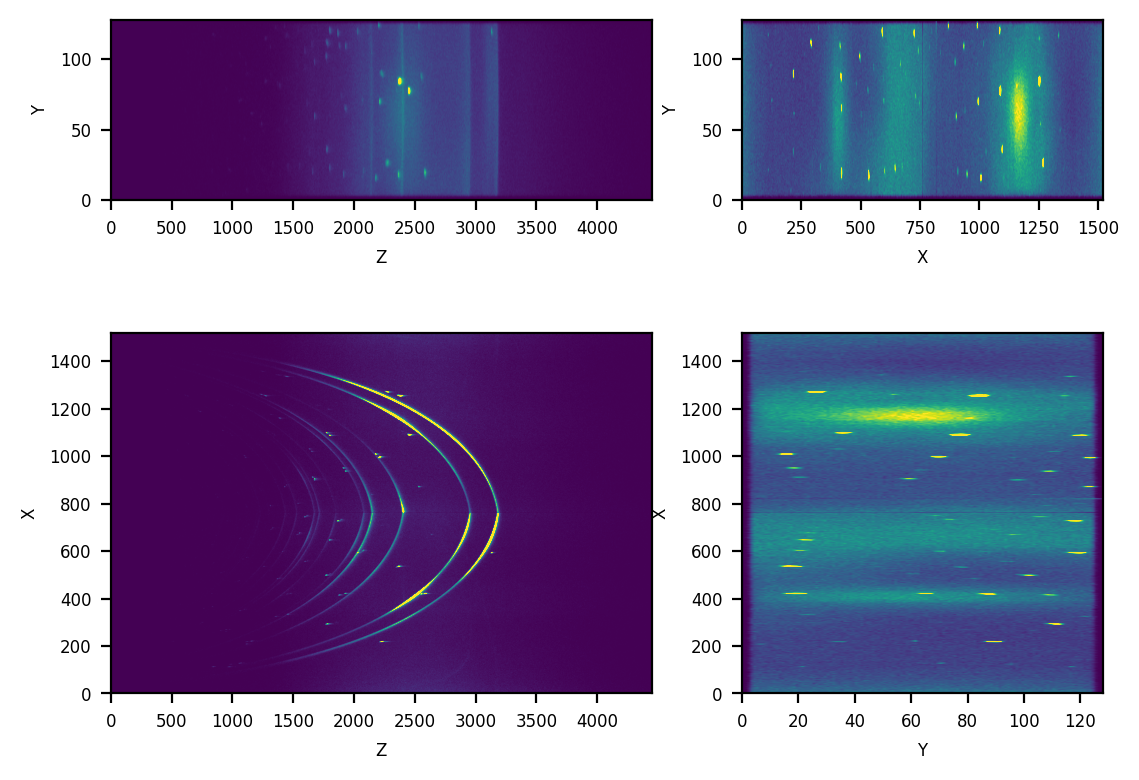
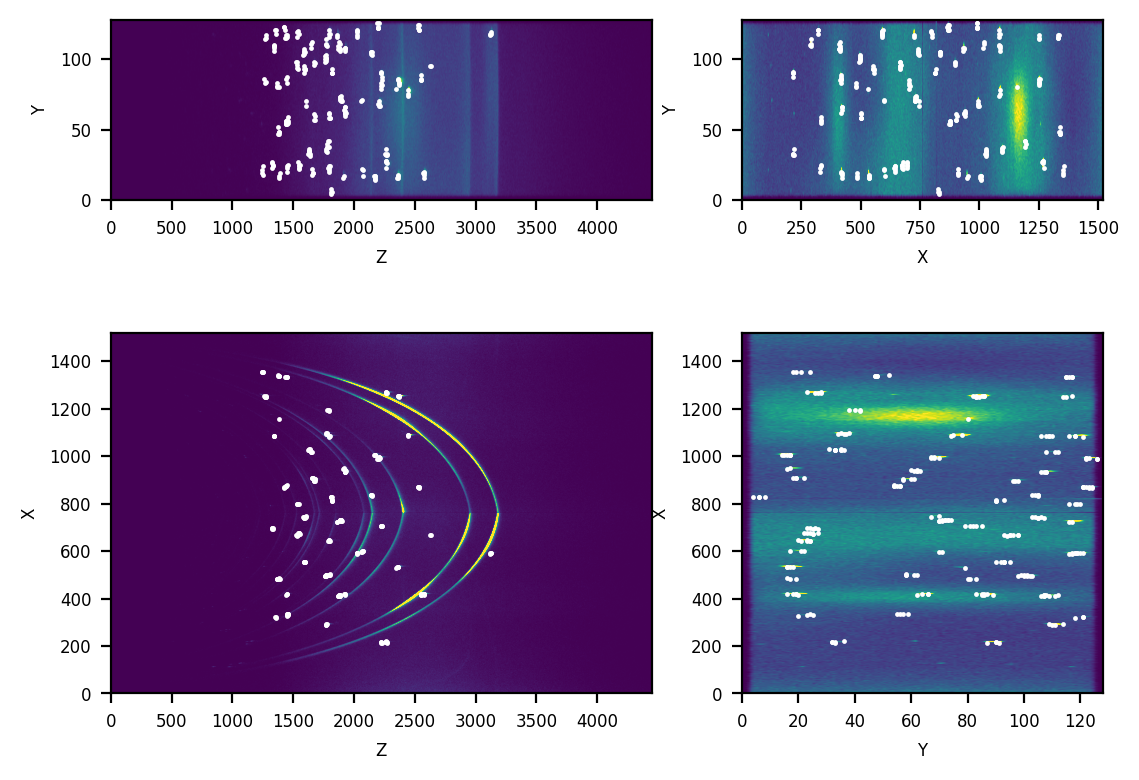
The 3D data has a shape of (1520, 128, 4451). The following two figures
show respectively the input 3D data and the detected Bragg peaks.
Kuangdai Leng1, Pascal Manuel2, Jeyan Thiyagalingam1
1 Scientific Computing Department, STFC, UK
2 ISIS Neutron and Muon Source, STFC, UK
We thank Samuel Jackson1 and Anders Markvardsen2 for their investigations in an earlier project that have facilitated our understanding of the problem.
This work was supported by the ISIS Neutron and Muon Source (ISIS) of the Science and Technology Facilities Council through the ISIS-ML funding, and by Wave I of the UKRI Strategic Priorities Fund under the EPSRC grant (EP/T001569/1), particularly the AI for Science theme in that grant and the Alan Turing Institute. We gratefully acknowledge their support.