- Overview
- Installing and configuring the plugin
- Configuring JFrog CLI as a Tool
- Using JFrog CLI in your pipeline jobs
- Using HTTP/s proxy
- Jenkins Configuration as Code
- Examples
- Contributions
The Jenkins JFrog Plugin allows for easy integration between Jenkins and the JFrog Platform. This integration allows your build jobs to deploy artifacts and resolve dependencies to and from Artifactory, and then have them linked to the build job that created them. It also allows you to scan your artifacts and builds with JFrog Xray and distribute your software package to remote locations using JFrog Distribution. This is all achieved by the plugin by wrapping JFrog CLI. Any JFrog CLI command can be executed from within your Jenkins Pipeline job using the JFrog Plugin.
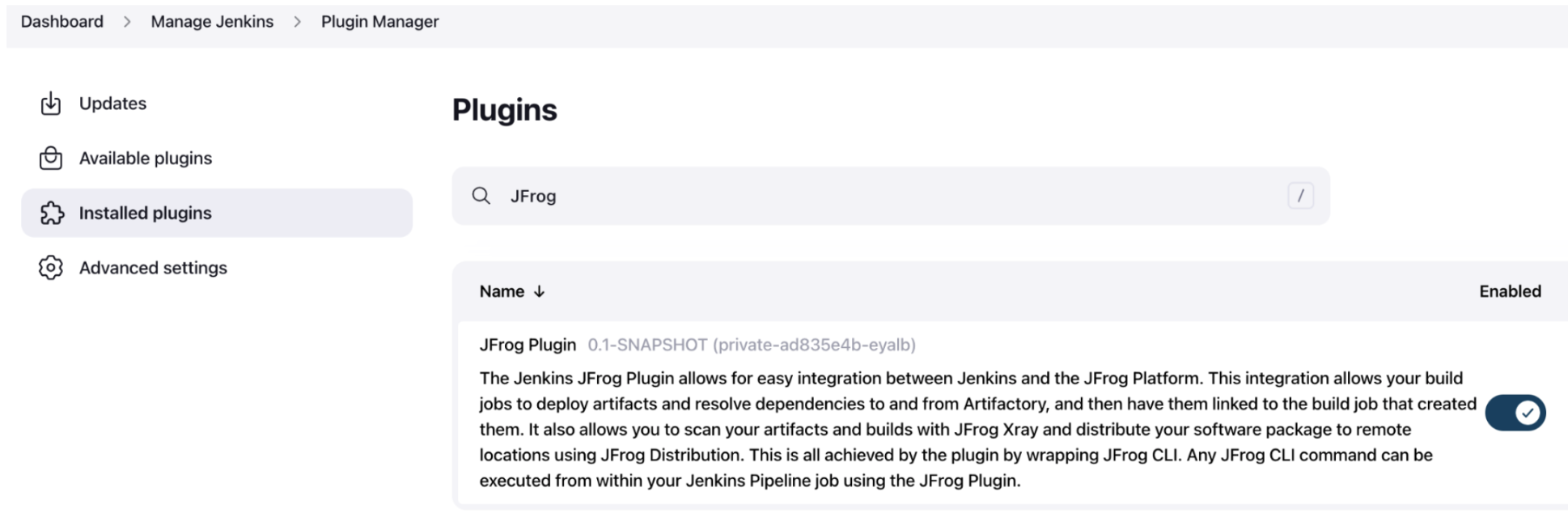
- Install the JFrog Plugin by going to
Manage Jenkins | Manage Plugins.
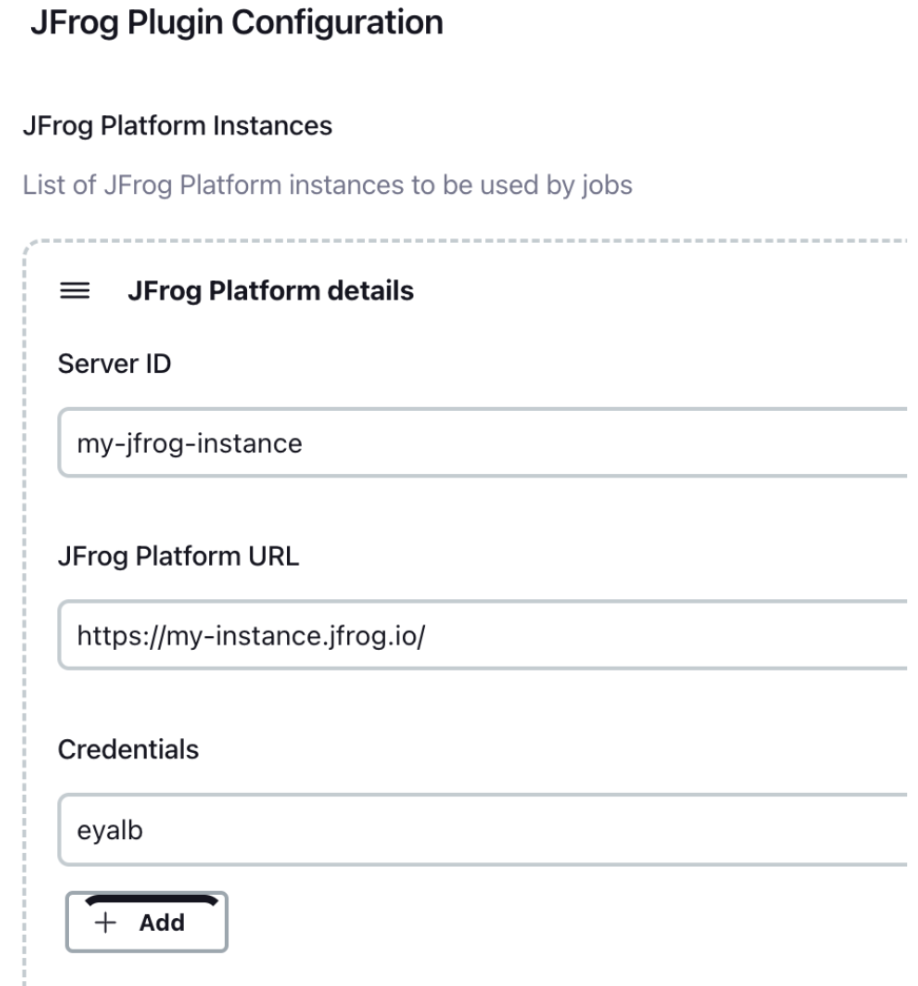
- Configure your JFrog Platform details by going to
Manage Jenkins | Configure System.
- Configure JFrog CLI as a tool in Jenkins as described in the Configuring JFrog CLI as a tool section.
To use JFrog CLI in your pipelines jobs, you should configure it as a tool in Jenkins by going to Manage Jenkins | Global Tool Configuration. You can use one of the following installation options:
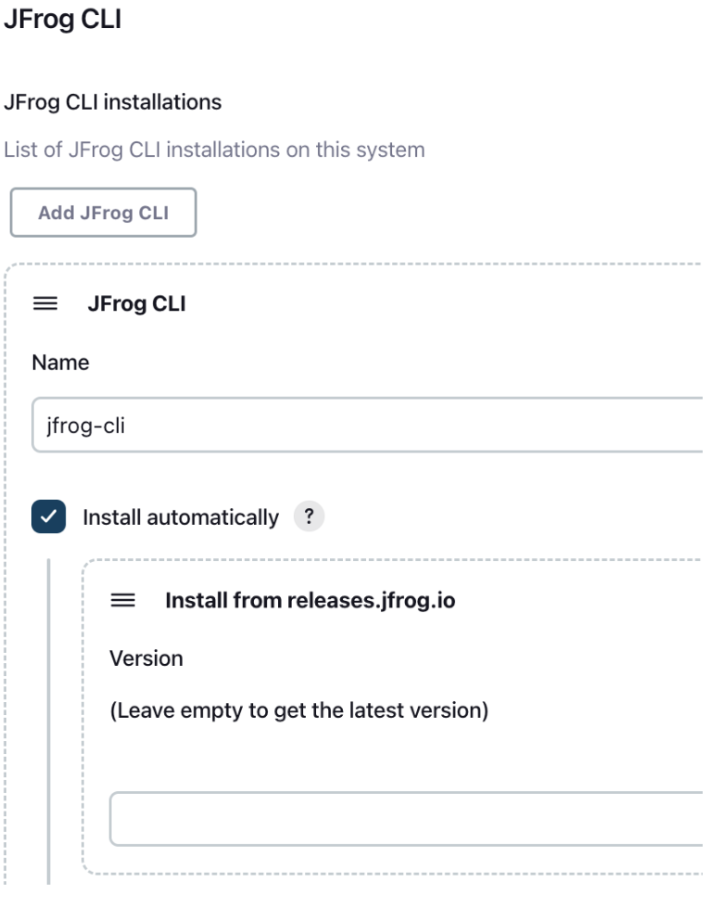
If your agent has access to the internet, you can set the installer to automatically download JFrog CLI from https://releases.jfrog.io as shown in the below screenshot.
If your agent cannot access the internet, you can set the installer to automatically download JFrog CLI from the JFrog instance you configured in Manage Jenkins | Configure System as shown in the below screenshot. To set this up, follow these steps:
-
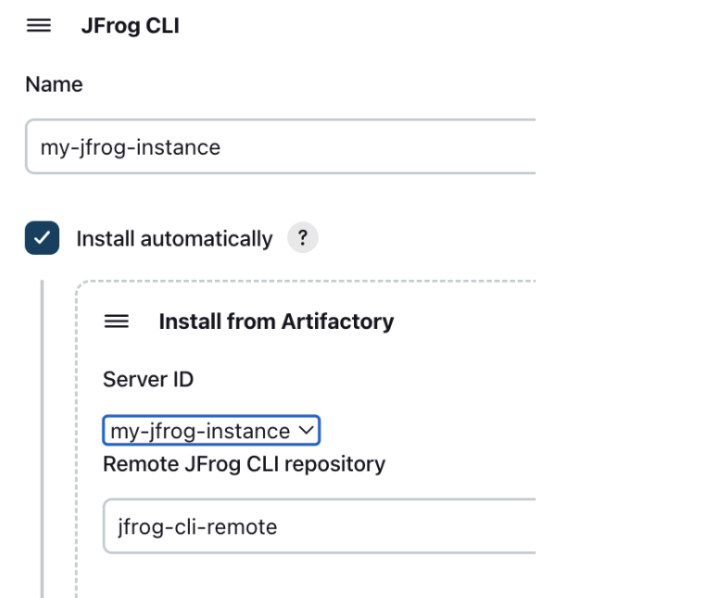
Create a generic remote repository in Artifactory for downloading JFrog CLI. You can name the repository jfrog-cli-remote. This is the name we'll be using here, but you can also choose a different name for the repository. Set the repository URL to https://releases.jfrog.io/artifactory/jfrog-cli/
-
In Manage Jenkins | Global Tool Configuration select the Install from Artifactory option as shown in the screenshot below.
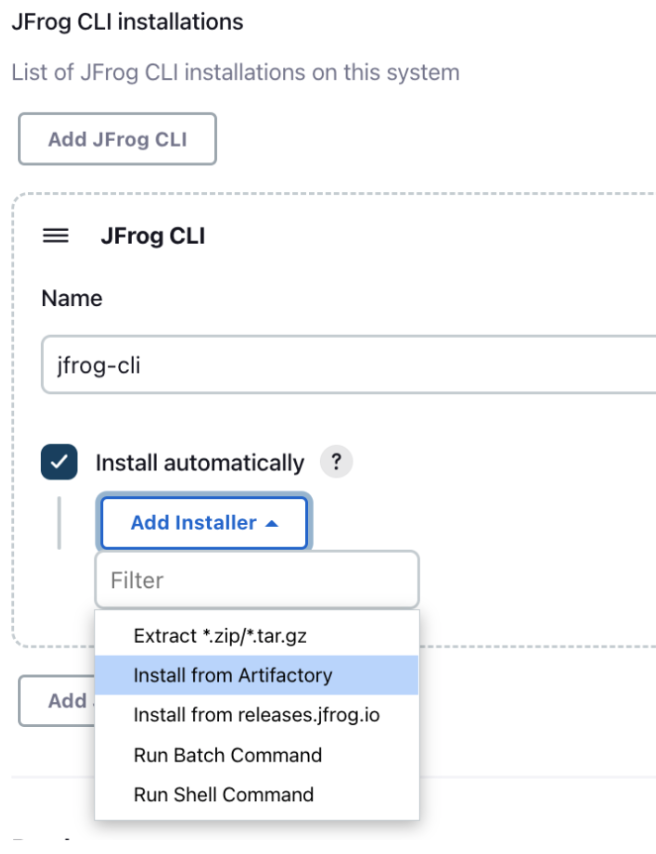
-
Set the Server ID of your JFrog instanced, which you configured in Manage Jenkins | Configure System. Also set jfrog-cli-remote as the name of the remote repository you created to download JFrog CLI from. If you used a different name for repository, set this name here.
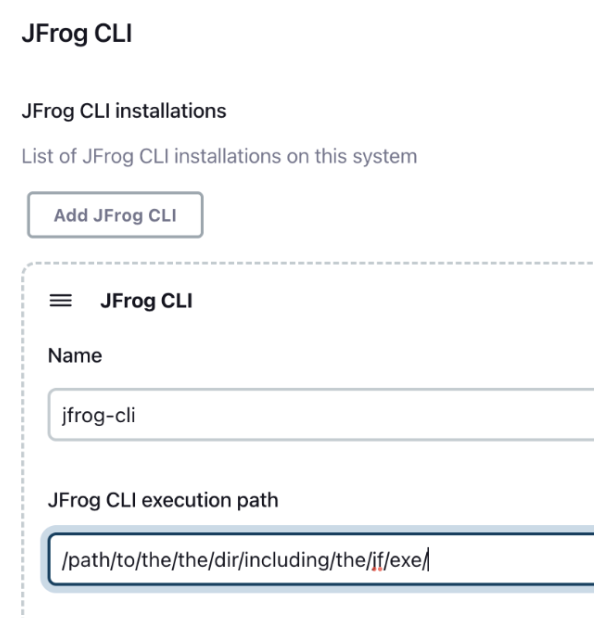
Install JFrog CLI manually on your build agent, and then set the path to the directory which includes the jf executable, as shown in the below screenshot.
To have your pipeline jobs run JFrog CLI commands, add the following to your pipeline script.
Step 1: Define JFrog CLI as a tool, by using the tool name you configured. For example, if you named the tool jfrog-cli, add the following to the script:
tools {
jfrog 'jfrog-cli'
}Scripted Pipeline
withEnv(["JFROG_BINARY_PATH=${tool 'jfrog-cli'}"]) {
// The 'jf' tool is available in this scope.
}Step 2: Use the jf step to execute any JFrog CLI command as follows:
// Upload all files in the target directory to the my-repo Artifactory repository.
jf 'rt u target/ my-repo/'IMPORTANT: Notice the single quotes wrapping the command right after the jf step definition.
If the JFrog CLI command has arguments with white-spaces, you can provide the arguments as a list as follows:
jf(['mvn', 'clean', 'install', '-Ddeploy.testProperty=Property with space'])When the above list syntax is used, the quotes required for the string syntax are replaced with quotes wrapping each item in the list as shown above. The above step is equivalent to the following shell command:
The list syntax also helps avoiding space and escaping problems, when some of those arguments use script variables.
The plugin automatically sets the following environment variables: JFROG_CLI_BUILD_NAME and JFROG_CLI_BUILD_NUMBER with Jenkins's job name and build number respectively. You therefore don't need to specify the build name and build number on any of the build related JFrog CLI commands. If you wish to change the default values, add the following code to your pipeline script:
environment {
JFROG_CLI_BUILD_NAME = "my-build-name"
JFROG_CLI_BUILD_NUMBER = "18"
}If you have multiple JFrog Platform instances configured, you can use the –-server-id command option with
the server ID you configured for the instance. For example:
jf 'rt u test-file my-repo –-server-id server-1'
jf 'rt u test-file my-repo –-server-id server-2'Build-info is the metadata of a build. It includes all the details about the build broken down into segments that include version history, artifacts, project modules, dependencies, and everything that was required to create the build. In short, it is a snapshot of the components used to build your application, collected by the build agent. See below how you publish the build-info from your pipeline jobs. This section should be placed inside the job after the execution of the JFrog CLI commands used for the build.
stage('Publish build info') {
steps {
jf 'rt build-publish'
}
}When the job publishes the build-info to Artifactory, you can access it by clicking on the build-info icon, next to the job run.
If you're using a JFrog platform that's situated behind an HTTP/S proxy, you should set up your proxy configuration
under Manage Jenkins > Manage Plugins > Advanced.
To exclude the JFrog platform from going through a configured proxy, provide your JFrog platform's host details in
the No Proxy Host section. This should be a list of comma-separated hosts.
Notice that the JFrog CLI is typically downloaded from releases.jfrog.io. You may need to add that to your list as well.
To configure this plugin on Jenkins Configuration as Code, add the following sections to the jenkins.yaml:
- Configure connection details to the JFrog platform
unclassified: jFrogPlatformBuilder: jfrogInstances: - serverId: "acme" url: "https://acme.jfrog.io" artifactoryUrl: "https://acme.jfrog.io/artifactory" distributionUrl: "https://acme.jfrog.io/distribution" xrayUrl: "https://acme.jfrog.io/xray" credentialsConfig: credentialsId: "acme-secret-recipe"
- Add JFrog CLI tool using one of the following methods:
-
Automatic installation from release.jfrog.io:
tool: jfrog: installations: - name: "jfrog-cli" properties: - installSource: installers: - "releasesInstaller"
-
Automatic installation from Artifactory:
tool: jfrog: installations: - name: "jfrog-cli" properties: - installSource: installers: - artifactoryInstaller: repository: "jfrog-cli-remote"
-
tool: jfrog: installations: - name: "jfrog-cli" home: "/path/to/jfrog/cli/dir/"
Uploading and downloading generic files
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
jfrog 'jfrog-cli'
}
stages {
stage('Testing') {
steps {
// Show the installed version of JFrog CLI.
jf '-v'
// Show the configured JFrog Platform instances.
jf 'c show'
// Ping Artifactory.
jf 'rt ping'
// Create a file and upload it to a repository named 'my-repo' in Artifactory
sh 'touch test-file'
jf 'rt u test-file my-repo/'
// Publish the build-info to Artifactory.
jf 'rt bp'
// Download the test-file
jf 'rt dl my-repo/test-file'
}
}
}
}Docker
- Populate 'DOCKER_REG_URL' with the Artifactory Docker registry, for example - 'acme.jfrog.io'.
- Use an agent with a running Docker daemon.
- To build the Docker image, install the "Docker Pipeline" on Jenkins.
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
jfrog 'jfrog-cli'
}
environment {
DOCKER_IMAGE_NAME = "$DOCKER_REG_URL/docker-local/hello-frog:1.0.0"
}
stages {
stage('Clone') {
steps {
git branch: 'master', url: "https://github.com/jfrog/project-examples.git"
}
}
stage('Build Docker image') {
steps {
script {
docker.build("$DOCKER_IMAGE_NAME", 'docker-oci-examples/docker-example')
}
}
}
stage('Scan and push image') {
steps {
dir('docker-oci-examples/docker-example/') {
// Scan Docker image for vulnerabilities
jf 'docker scan $DOCKER_IMAGE_NAME'
// Push image to Artifactory
jf 'docker push $DOCKER_IMAGE_NAME'
}
}
}
stage('Publish build info') {
steps {
jf 'rt build-publish'
}
}
}
}Maven
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
jfrog 'jfrog-cli'
}
stages {
stage('Clone') {
steps {
git branch: 'master', url: "https://github.com/jfrog/project-examples.git"
}
}
stage('Exec Maven commands') {
steps {
dir('maven-examples/maven-example') {
// Configure Maven project's repositories
jf 'mvn-config --repo-resolve-releases libs-release --repo-resolve-snapshots libs-snapshots --repo-deploy-releases libs-release-local --repo-deploy-snapshots libs-snapshot-local'
// Install and publish project
jf 'mvn clean install'
}
}
}
stage('Publish build info') {
steps {
jf 'rt build-publish'
}
}
}
}Gradle
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
jfrog 'jfrog-cli'
}
stages {
stage('Clone') {
steps {
git branch: 'master', url: "https://github.com/jfrog/project-examples.git"
}
}
stage('Exec Gradle commands') {
steps {
dir('gradle-examples/gradle-example-ci-server') {
// Configure Gradle project's repositories
jf 'gradle-config --repo-resolve libs-release --repo-deploy libs-release-local'
// Install and publish project
jf 'gradle clean artifactoryPublish'
}
}
}
stage('Publish build info') {
steps {
jf 'rt build-publish'
}
}
}
}npm
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
jfrog 'jfrog-cli'
}
stages {
stage('Clone') {
steps {
git branch: 'master', url: "https://github.com/jfrog/project-examples.git"
}
}
stage('Exec npm commands') {
steps {
dir('npm-example') {
// Configure npm project's repositories
jf 'npm-config --repo-resolve npm-remote --repo-deploy npm-local'
// Install dependencies
jf 'npm install'
// Pack and deploy the npm package
jf 'npm publish'
}
}
}
stage('Publish build info') {
steps {
jf 'rt build-publish'
}
}
}
}Go
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
jfrog 'jfrog-cli'
}
stages {
stage('Clone') {
steps {
git branch: 'master', url: "https://github.com/jfrog/project-examples.git"
}
}
stage('Exec Go commands') {
steps {
dir('golang-example/hello/') {
// Configure Go project's repositories
jf 'go-config --repo-resolve go-remote --repo-deploy go-local'
// Build the project with go and resolve the project dependencies from Artifactory
jf 'go build'
// Publish version v1.0.0 of the package to the go-local repository in Artifactory
jf 'go-publish v1.0.0'
}
}
}
stage('Publish build info') {
steps {
jf 'rt build-publish'
}
}
}
}These examples demonstrate only a fraction of the capabilities of JFrog CLI. Please refer to the JFrog CLI documentation for additional information.
We welcome pull requests from the community. To help us improve this project, please read our Contribution guide.