In the repository, I demo the core idea of how JWT works. In the regular procedure of requests, clients connect to the server, the session is established on the server and its content is also saved by the session ID. On the other hand, the client side may have cookie. However such mechanism is expensive and less efficient especially on many requests.
JWT is one of solutions of the above. In addition, it also keeps the real stateless, like how the Restful API works. The general idea is like the below flow. The first step is the same to the regular. The client login a authentication server with the username and the password. The server would check the user information. If it is validated, the server would send back a JWT back to the client (authenticate and generate signature). After that, every operation the client sends to the server must carry the JSON Web Tokens instead of the regular mechanism of sessions and cookies.
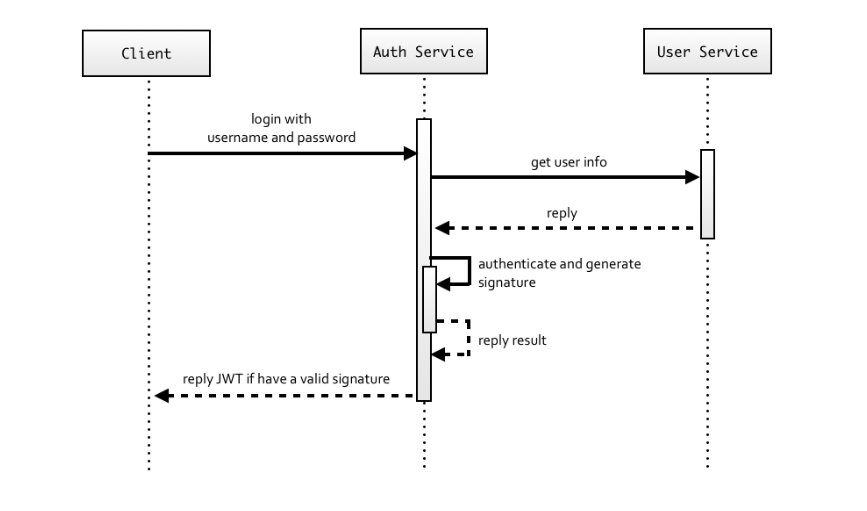 Refer to the link (2022).
Refer to the link (2022).
Next, let's have a look at the components of JWT.
Headerdefines the kind of algorithms generating the signature and token types.Payloaddefines the necessary information of the request, like the user name, operation, tmiestamp, etc.Signaturethe information of bothHeaderandPayloadto the hash code by using the private key. The format is likebase64(Header) + base64(Payload) + base64(Signature).
In the following, I demo how to generate the JSON Web Token on Python.
priKey = """-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----------END PRIVATE KEY-----"""
currentTime = int(datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%s"))
headers = json.dumps({"alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT"})
payload = json.dumps({"iss": "jiankaiwang",
"sub": "updating-db",
"aud": "db-server",
"exp": currentTime + 60*10,
"timestamp": currentTime})
unsignedToken = EncodeBase64(ToBytes(headers)) \
+ ToBytes('.') \
+ EncodeBase64(ToBytes(payload))
signature = CreateSHA256Sign(priKey, unsignedToken)
JWTTOKEN = unsignedToken.decode("utf-8") \
+ '.' \
+ signature.decode("utf-8")In the Payload, there are several standard fields you have to fill.
iss: issuer, the JWT publishersub: subject of JWTaud: audience of JWT, the JWT receiverexp: expiration timenbf: not before timeiat: issued at timejti: JWT ID
python3 -m virtualenv -p python3 env
source ./env/bin/activate
pip3 install --no-cache-dir ./environ/requirements.txt
python3 requests.pyThe result is like:
Headers:
{"alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT"}
Payload:
{"iss": "jiankaiwang", "sub": "updating-db", "aud": "db-server", "exp": 1651760527, "timestamp": 1651759927}
JWT:
eyJhbGciOiAiSFMyNTYiLCAidHlwIjogIkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiAiamlhbmthaXdhbmciLCAic3ViIjogInVwZGF0aW5nLWRiIiwgImF1ZCI6ICJkYi1zZXJ2ZXIiLCAiZXhwIjogMTY1MTc2MDUyNywgInRpbWVzdGFtcCI6IDE2NTE3NTk5Mjd9.aMXv8unaaUfL2NMxQduVYJ-nsHlLpLX4GsK0f6gE_5M
Next you can verify the JWT token by JWT.io.
Otherwise, you can verify the JWT by verify.py. You can replace the JWToken on the script.
if __name__ == '__main__':
priKey = """-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----------END PRIVATE KEY-----"""
JWToken = "(You can generate JWT from requests.py.)"
if len(JWToken) < 1:, then run the following commands.
python3 -m virtualenv -p python3 env
source ./env/bin/activate
pip3 install --no-cache-dir ./environ/requirements.txt
python3 verify.py