WMNut is a program to monitor multiple UPS devices' statistics through the NUT (Network UPS Tools) framework on Linux and other systems.
It is a dockapp that is supported natively by X window managers such as Window Maker, AfterStep, BlackBox, FluxBox, and Enlightenment.
WMNut will run as a simple 64*64 pixels window in other Window Managers, or when using -w.
WMNut provides multiple UPS’s monitoring with:
-
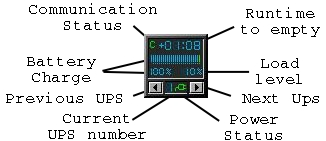
Status of power supply (battery or AC Power),
-
Communication status with UPS (Red/Green "C"),
-
Percentage of battery remaining (numeric and meter),
-
Load level percentage on output (numeric, if available),
-
Runtime to empty, i.e. time left to battery depletion (MM:SS),
-
High/Low/Critical battery status (Red/Yellow/Green colored meter and battery).
It is known to run on GNU/Linux, FreeBSD, OpenBSD and OpenIndiana (based on illumos/Solaris), but should also run on any other system supporting X11.
Like NUT, it may require C99 or newer compiler support.
WMNut requires the:
-
X Window client and Xpm libraries and development files.
-
For example on a Debian GNU/Linux system, you need to install the packages
libxext-devandlibxpm-dev.
-
-
NUT client library, version 2.8.0 or higher.
-
For example on a Debian GNU/Linux system, you need to install the package
libupsclient-dev(note that some stable distributions still ship older NUT v2.7.4 based packages!) -
WMNut may actually still work with 2.4.0 or higher — but at the expense of build warnings with data type mismatches and some needed tweaks of the
configure.acscript and possibly wmnut codebase itself. It may be easier to just take wmnut-0.67 or an older release then.
-
In order to compile WMNut using the Makefile, GNU make should be used.
|
Note
|
For FreeBSD, OpenBSD and OpenIndiana users, the default BSD make or
Sun dmake programs respectively in modern releases (2020’s) do also work
for the simple recipes used here; however in case of reported Makefile
syntax problems — remember to try using gmake instead!
|
1) Download WMNut source code (from GitHub) or archive (.tar.gz or .tar.bz2)
Either get an archive file from WMNut releases on GitHub or clone the git repository using:
$ git clone https://github.com/networkupstools/wmnut.git
2) Uncompress the archive (not needed for github source code)
$ tar -zxvf wmnut-X.YZ.tar.gz $ tar -jxvf wmnut-X.YZ.tar.bz2
3) Switch to WMNut source code directory
$ cd wmnut-X.YZ
If you are using the git source code, use:
$ cd wmnut
4) Prepare the source for building
|
Note
|
when using the git repository, be sure to first call: $ autoreconf -i It is also wrapped into a simple |
Just call the usual:
$ ./configure
|
Note
|
WMNut now uses NUT_LIBS="-L${HOME}/nut/clients/.libs -lupsclient" \
NUT_CFLAGS="-I${HOME}/nut/include -I${HOME}/nut/clients" \
./configure
# You would need to install that libdir or pass it with LD_LIBRARY_PATH
# to run the built program experimentally, e.g.:
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${HOME}/nut/clients/.libs ./src/wmnut -w
|
5) Now compile WMNut
$ make
Or (may be needed for *BSD and Solaris/illumos based systems):
$ gmake
6) And install it on your system
Use the following command, as root (or using sudo):
$ make install
Or simply copy the wmnut binary (and optionally its manual page) to the
right directories on your system.
7) Optionally, configure WMNut for your own use
WMNut will automatically connect to any local device(s).
So if you have remote system(s) that you want to monitor, edit and adapt your
wmnutrc file . Then copy it to your user home directory and/or to your system
/etc directory, using commands like:
$ cp wmnutrc /etc/wmnutrc
and/or:
$ cp wmnutrc ~/.wmnutrc
|
Note
|
|
8) Launch WMNut
$ wmnut &
You can also use wmnut -h for help, or man wmnut to access the manual page.
If no parameter is given, wmnut will try to access the UPS at "localhost"
address. Otherwise try wmnut -U upsname@hostname or edit your wmnutrc files.
Be sure to read the HINTS and TODO files too!
WMNut is Copyright © 2002 - 2020 by Arnaud Quette
WMNut is Copyright © 2021 - 2024 by the Network UPS Tools project and hosted at https://github.com/networkupstools/wmnut repository
wmnut is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
WMNut is based on wmapm originally written by Chris D. Faulhaber and
M.G. Henderson.
Huge thanks to:
-
Arnaud Quette for the majority of initial development and maintenance of the WMNut project since 2002.
-
Russell Kroll for having initiated and driven the NUT project (Network UPS Tools), until 2004. Note that Arnaud had also taken over NUT leadership since 2005 to 2020.
-
Bill Richter, Laszlo Hazy and David Butts for their support in beta test and improvement of WMNut,
-
Martijm Pieterse and Antoine Nulle for a great (and somewhat standardized) interface which Arnaud used as a template (
wmmon.appandwmgeneral), -
Luca Filipozzi for WMNut Debian package creation, later maintained by Arnaud, available at Debian website.
We are interested in having feedback about how WMNut runs on other platforms (BSD, Solaris, …) and searching for packagers on those platforms.
If you have nice suggestions, ideas, whatever, that are not on TODO list, feel free to post issues and pull requests at https://github.com/networkupstools/wmnut/releases
You can also try the NUT community support channels, as detailed at https://networkupstools.org/support.html
Yes, WMNut can monitor up to 9 UPSs since release 0.1. Take a look at HINTS
file and manual page for more details about using this feature.
I’m not running WindowMaker nor AfterStep. How can I run WMNut in windowed mode (i.e. not having transparent background !)?
Try running wmnut -w. See below for a screenshot.
I can’t compile WMNut ("undefined reference to ‘upslogx’", "upsfetch.h/o not found" or "upsclient.h/o not found") or WMNut doesn’t work!
There is always lots of improvements in both NUT and WMNut…
To solve your problem, you should upgrade to the most current release of NUT and WMNut, and the problem should disappear — it was solved in the past.