Is your printer secure? Check before someone else does...
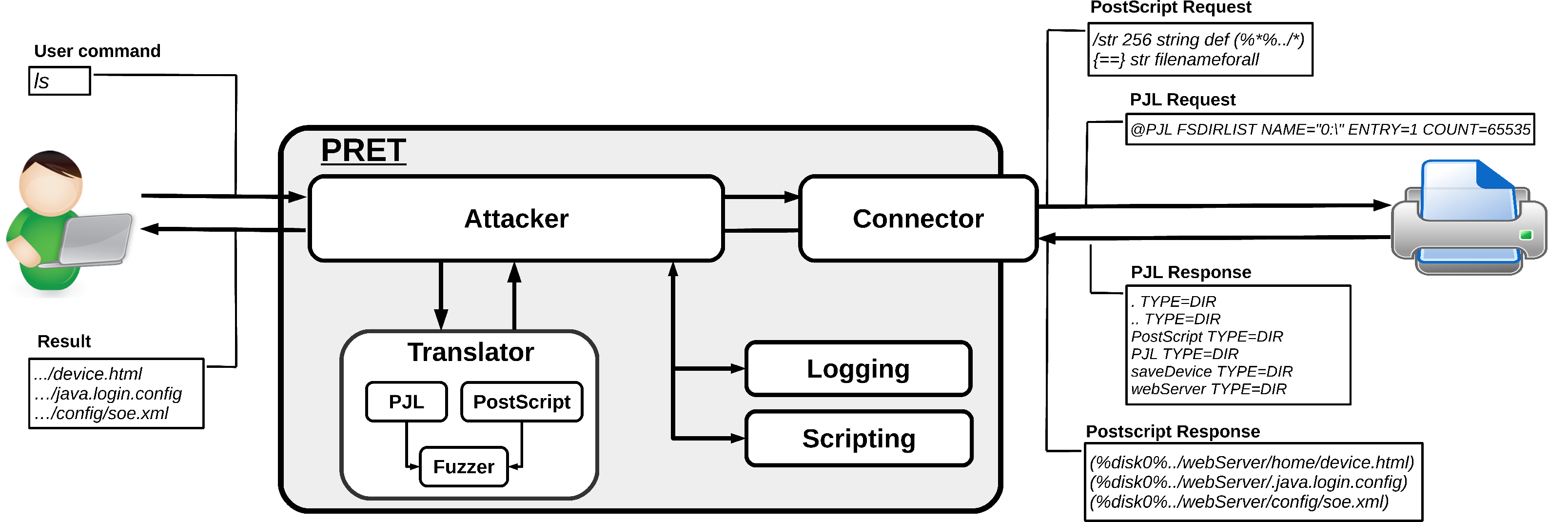
PRET is a new tool for printer security testing developed in the scope of a Master's Thesis at Ruhr University Bochum. It connects to a device via network or USB and exploits the features of a given printer language. Currently PostScript, PJL and PCL are supported which are spoken by most laser printers. This allows cool stuff like capturing or manipulating print jobs, accessing the printer's file system and memory or even causing physical damage to the device. All attacks are documented in detail in the Hacking Printers Wiki.
The main idea of PRET is to facilitate the communication between the end-user and the printer. Thus, after entering a UNIX-like command, PRET translates it to PostScript, PJL or PCL, sends it to the printer, evaluates the result and translates it back to a user-friendly format. PRET offers a whole bunch of commands useful for printer attacks and fuzzing.
PRET only requires a Python3 interpreter. For colored output and SNMP support however, third party modules need to be installed:
# python3 -m pip install colorama pysnmp
If running on a Windows console and Unicode characters are not displayed correctly, install the win_unicode_console module:
# python3 -m pip install win_unicode_console
For experimental, ‘driverless’ printing (see print command), ImageMagick and GhostScript need to be installed:
# apt-get install imagemagick ghostscript
usage: pret.py [-h] [-s] [-q] [-d] [-i file] [-o file] target {ps,pjl,pcl}
positional arguments:
target printer device or hostname
{ps,pjl,pcl} printing language to abuse
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-s, --safe verify if language is supported
-q, --quiet suppress warnings and chit-chat
-d, --debug enter debug mode (show traffic)
-i file, --load file load and run commands from file
-o file, --log file log raw data sent to the target
$ ./pret.py laserjet.lan ps
$ ./pret.py /dev/usb/lp0 pjl
PRET requires a valid target and a printer language as arguments. The target can either be the IP address/hostname of a network printer (with port 9100/tcp open) or a device like /dev/usb/lp0 for a local USB printer. To quickly discover all network printers in your subnet using SNMP broadcast, simply run PRET without arguments:
./pret.py
No target given, discovering local printers
address device uptime status
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
192.168.1.5 hp LaserJet 4250 10:21:49 Ready
192.168.1.11 HP LaserJet M3027 MFP 13 days Paper jam
192.168.1.27 Lexmark X792 153 days Ready
192.168.1.28 Brother MFC-7860DW 16:31:17 Sleep mode
The printer language to be abused must be one of ps, pjl or pcl. Not all languages are supported by every printer, so you may want to switch languages if you don't receive any feedback. Each printer language is mapped to a different set of PRET commands and has different capabilities to exploit.
--safe tries to check via IPP, HTTP and SNMP if the selected printing language (PS/PJL/PCL) is actually supported by the device before connecting. On non-networked printers (USB, parallel cable) this test will fail.
--quit suppresses printer model determination, intro message and some other chit-chat.
--debug shows the datastream actually sent to the device and the feedback received. Note that header data and other overhead is filtered. The see the whole traffic, use wireshark. Debugging can also be switched on/off within a PRET session using the debug command
--load filename reads and executes PRET commands from a text file. This is useful for automation. Command files can also be invoked later within a PRET session via the load command.
--log filename writes a copy of the raw datastream sent to the printer into a file. This can be useful to build a malicious print job file which can be deployed on another printer not directly reachable, for example by printing it from USB drive.
After connecting to a printer device, you will see the PRET shell and can execute various commands:
$ ./pret.py laserjet.lan pjl
________________
_/_______________/|
/___________/___//|| PRET | Printer Exploitation Toolkit v0.25
|=== |----| || by Jens Mueller <jens.a.mueller@rub.de>
| | ô| ||
|___________| ô| ||
| ||/.´---.|| | || 「 cause your device can be
|-||/_____\||-. | |´ more fun than paper jams 」
|_||=L==H==||_|__|/
(ASCII art by
Jan Foerster)
Connection to laserjet.lan established
Device: hp LaserJet 4250
Welcome to the pret shell. Type help or ? to list commands.
laserjet.lan:/> help
Available commands (type help <topic>):
=======================================
append debug edit free id ls open restart timeout
cat delete env fuzz info mirror printenv selftest touch
cd df exit get load mkdir put set traversal
chvol disable find help lock nvram pwd site unlock
close display format hold loop offline reset status version
laserjet.lan:/> ls ../../
- 834 .profile
d - bin
d - dev
d - etc
d - hp
d - hpmnt
- 1276 init
d - lib
d - pipe
d - tmp
laserjet.lan:/> exit
A list of generic PRET commands is given below:
help List available commands or get detailed help with 'help cmd'.
debug Enter debug mode. Use 'hex' for hexdump: debug [hex]
load Run commands from file: load cmd.txt
loop Run command for multiple arguments: loop <cmd> <arg1> <arg2> …
open Connect to remote device: open <target>
close Disconnect from device.
timeout Set connection timeout: timeout <seconds>
discover Discover local printer devices via SNMP.
print Print image file or raw text: print <file>|"text"
site Execute custom command on printer: site <command>
exit Exit the interpreter.
Generic file system operations with a PS/PJL/PCL specific implementation are:
┌───────────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Command │ PS │ PJL │ PCL │ Description │
├───────────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ ls │ ✓ │ ✓ │ ✓ │ List contents of remote directory. │
│ get │ ✓ │ ✓ │ ✓ │ Receive file: get <file> │
│ put │ ✓ │ ✓ │ ✓ │ Send file: put <local file> │
│ append │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ Append to file: append <file> <str> │
│ delete │ ✓ │ ✓ │ ✓ │ Delete remote file: delete <file> │
│ rename │ ✓ │ │ │ Rename remote file: rename <old> <new> │
│ find │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ Recursively list directory contents. │
│ mirror │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ Mirror remote filesystem to local dir. │
│ cat │ ✓ │ ✓ │ ✓ │ Output remote file to stdout. │
│ edit │ ✓ │ ✓ │ ✓ │ Edit remote files with vim. │
│ touch │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ Update file timestamps: touch <file> │
│ mkdir │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ Create remote directory: mkdir <path> │
├───────────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ cd │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ Change remote working directory. │
│ pwd │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ Show working directory on device. │
│ chvol │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ Change remote volume: chvol <volume> │
│ traversal │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ Set path traversal: traversal <path> │
├───────────┼─────┼─────┼─────┼────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ format │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ Initialize printer's file system. │
│ fuzz │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ File system fuzzing: fuzz <category> │
├─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─┴─ ─ ─┴─ ─ ─┴─ ─ ─┴─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ─ ┤
│ path - Explore fs structure with path traversal strategies. │
│ write - First put/append file, then check for its existence. │
│ blind - Read-only tests for existing files like /etc/passwd. │
├───────────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ df │ ✓ │ ✓ │ │ Show volume information. │
│ free │ ✓ │ ✓ │ ✓ │ Show available memory. │
└───────────┴─────┴─────┴─────┴────────────────────────────────────────┘
id Show device information.
version Show PostScript interpreter version.
devices Show available I/O devices.
uptime Show system uptime (might be random).
date Show printer's system date and time.
pagecount Show printer's page counter.
lock Set startjob and system parameters password.
unlock Unset startjob and system parameters password.
restart Restart PostScript interpreter.
reset Reset PostScript settings to factory defaults.
disable Disable printing functionality.
destroy Cause physical damage to printer's NVRAM.
hang Execute PostScript infinite loop.
overlay Put overlay eps file on all hardcopies: overlay <file.eps>
cross Put printer graffiti on all hardcopies: cross <font> <text>
replace Replace string in documents to be printed: replace <old> <new>
capture Capture further jobs to be printed on this device.
hold Enable job retention.
set Set key to value in topmost dictionary: set <key=value>
known List supported PostScript operators: known <operator>
search Search all dictionaries by key: search <key>
dicts Return a list of dictionaries and their permissions.
resource List or dump PostScript resource: resource <category> [dump]
dump Dump dictionary: dump <dict>
Dictionaries: - systemdict - statusdict - userdict
- globaldict - serverdict - errordict
- internaldict - currentsystemparams
- currentuserparams - currentpagedevice
config Change printer settings: config <setting>
duplex - Set duplex printing.
copies # - Set number of copies.
economode - Set economic mode.
negative - Set negative print.
mirror - Set mirror inversion.
Not all commands are supported by every printer. Especially Brother and Kyocera devices use their own PostScript clones – Br-Script and KPDL – instead of licensing original ‘Adobe PostScript’. Such flavours of the PostScript language may not be 100% compatible, especially concerning security sensitive features like capturing print jobs. Access to the file system is supported by most printers, however usually limited to a certain, sandboxed directory.
id Show device information.
status Enable status messages.
version Show firmware version or serial number (from 'info config').
pagecount Manipulate printer's page counter: pagecount <number>
printenv Show printer environment variable: printenv <VAR>
env Show environment variables (alias for 'info variables').
set Set printer environment variable: set <VAR=VALUE>
display Set printer's display message: display <message>
offline Take printer offline and display message: offline <message>
restart Restart printer.
reset Reset to factory defaults.
selftest Perform various printer self-tests.
disable Disable printing functionality.
destroy Cause physical damage to printer's NVRAM.
flood Flood user input, may reveal buffer overflows.
lock Lock control panel settings and disk write access.
unlock Unlock control panel settings and disk write access.
hold Enable job retention.
nvram NVRAM operations: nvram <operation>
nvram dump [all] - Dump (all) NVRAM to local file.
nvram read addr - Read single byte from address.
nvram write addr value - Write single byte to address.
info Show information: info <category>
info config - Provides configuration information.
info filesys - Returns PJL file system information.
info id - Provides the printer model number.
info memory - Identifies amount of memory available.
info pagecount - Returns the number of pages printed.
info status - Provides the current printer status.
info ustatus - Lists the unsolicited status variables.
info variables - Lists printer's environment variables.
Some commands are supported exclusively by HP printers, because other vendors have only implemented a subset of the PJL standard. This is especially true for PML based commands like restartor reset. Enabling long-term job retention via the hold command seems to be possible for some Epson devices only. NVRAM access via the nvram command is a proprietary feature of Brother printers. Limited access to the file system is supported by various HP, OKI, Konica, Xerox, Epson and Ricoh devices.
selftest Perform printer self-test.
info Show information: info <category>
info fonts - Show installed fonts.
info macros - Show installed macros.
info patterns - Show user-defined patterns.
info symbols - Show symbol sets.
info extended - Show extended fonts.
PCL is a very limited page description language without access to the file system. The get/put/ls commands therefore use a virtual file system based on PCL macros, implemented mostly for the hack value. This proof-of-concept shows that even a device which supports only minimalist languages like PCL can be used to store arbitrary files like copyright infringing material. Although such a file sharing service is not a security vulnerability per se, it might apply as ‘misuse of service’ depending on the corporate policy
pret.py- Executable main programcapabilities.py- Routines to check for printer language supportdiscovery.py- Routines to list printers using SNMP broadcastprinter.py- Generic code to describe a printing devicepostscript.py- PS specific code (inherits from class printer)pjl.py- PJL specific code (inherits from class printer)pcl.py- PCL specific code (inherits from class printer)helper.py- Help functions for output, logging, sockets, etc.codebook.py- Static table of PJL status/error codesfuzzer.py- Constants for file system fuzzingmibs/*- Printer specific SNMP MIBsdb/*- database of supported modelslpd/*- Scripts for LPD fuzzing
Given the features and various proprietary extensions in printing languages like PostScript and PJL, conducting a pentest on printers is not a trivial job. PRET can help to assist and verify known issues in the language. Once you have played around with the tool, you may want to perform a systematic printer security analysis. A good starting point is the Printer Security Testing Cheat Sheet.
Happy Hacking!