This repository contains the assets for the Amazon Sagemaker and Apache Airflow integration sample described in an upcoming AWS blogpost.
This repository shows a sample example to build, manage and orchestrate large-data, Spark-based ML workflows using Amazon Sagemaker and Apache Airflow. We use a publicly-available Abalone dataset to demonstrate the flow, but the same flow would work for any large dataset as well. More details on this dataset can be found at UCI data repository. The ML pipeline shows how to do data ETL pre-processing with PySpark code on SageMaker Processing, train an XGBoost model on this data, implement an inference pipeline container (Spark ETL + XGBoost), and use it for both real-time inference as well as batch inference.
The repository contains
- AWS CloudFormation Template to launch the AWS services required to create the components
- Airflow DAG Python Script that integrates and orchestrates all the ML tasks in a ML workflow for building a recommender system.
- Airflow Python operators for SageMaker Processing and Inference Pipeline
- SageMaker Processing PySpark script
- A companion Jupyter Notebook.
.
├── README.md About the repository
├── cfn AWS CloudFormation Templates
│ └── airflow-ec2.yaml CloudFormation for installing Airflow instance backed by RDS
├── notebooks Jupyter Notebooks
│ └── end-to-end-pipeline.ipynb
└── src Source code for Airflow DAG definition
├── config.py Config file to configure SageMaker jobs and other ML tasks
├── dag_ml_pipeline.py Airflow DAG definition for ML workflow
└── ml_pipeline Python module used in Airflow DAG for data preparation
├── __init__.py
├── smprocpreprocess.py PySpark ETL job script
└── sm_proc_job.py Airflow Python Operator for SageMaker Processing
└── inference_pipeline_ep.py Airflow Python Operator for SageMaker Inference Pipeline endpoint
└── prepare.py Airflow Python Operator for start-up code
└── schema_utils.py JSON schema definition for abalone dataset
The workflow performs the following tasks
- Data Pre-processing: Extract and pre-process data from S3 to prepare the training data using SageMaker Processing PySpark script running on several ML EC2 instances. The same script also serializes the ETL pipeline using MLeap for subsequent use as data pre-processing stage of inference pipeline. The job will be launched using Airflow Python operator sm_proc_job.
- Training the Model: Train the SageMaker's built-in Gradient Boosted Decision Tree model with the training data and generate model artifacts. The training job will be launched by the Airflow SageMaker operator
SageMakerTrainingOperator. - Compile Inference Pipeline: Containerize MLeap Spark ETL data preprocessing artifact and XGBoost model (both stored in S3 bucket), combine them into an inference pipeline and deploy this pipeline onto a SageMaker real-time endpoint. This job will be launched by the Airflow Python operator
inference_pipeline_ep. - Batch inference: Using the Inference Pipeline created in previuos step, get off-line, non-realtime inferences on the test dataset stored in Amazon S3 using Airflow SageMaker operator
SageMakerTransformOperator.
We will set up a simple Airflow architecture with scheduler, worker and web server running on the same instance. Typically, you will not use this setup for production workloads. We will use AWS CloudFormation to launch the AWS services required to create the components in the blog post. The stack includes the following
- Amazon EC2 instance to set up the Airflow components
- Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) Postgres instance to host Airflow metadata database
- Amazon S3 bucket to store the Sagemaker model artifacts, outputs and Airflow DAG with ML workflow. Template will prompt for the S3 bucket name
- AWS IAM roles and EC2 Security Groups to allow Airflow components interact with the metadata database, S3 bucket and Amazon SageMaker
The prerequisite for running this CloudFormation script is to set up an Amazon EC2 Key Pair to log in to manage Airflow such as any troubleshooting or adding custom operators etc. You also need to create a password for RDS database - it can be any alphanumeric sequence.
It may take up to 15 minutes for the CloudFormation stack to create the resources. After the resource creation is completed, you should be able to login to Airflow Web UI. The Airflow web server should be running on port 8080 by default. To open the Airflow Web UI, open any browser and type in the http://ec2-public-dns-name:8080. The public DNS Name of the EC2 instance can be found on the Outputs tab of CloudFormation stack on AWS console.
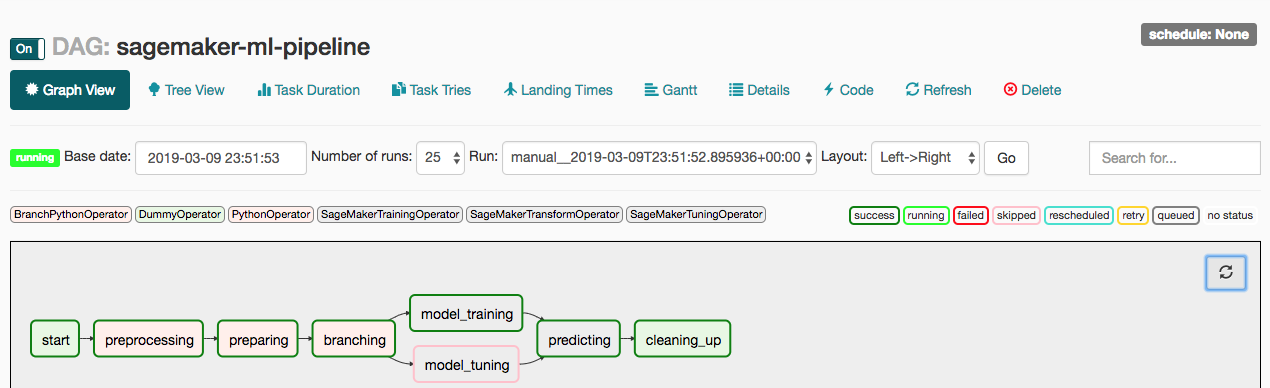
Airflow DAG integrates all the ML tasks in a ML workflow. Airflow DAG is a python script where you express individual tasks as Airflow operators, set task dependencies and associate the tasks to the DAG to run either on demand or scheduled interval. The Airflow DAG script is divided into following sections
- Set DAG with parameters such as schedule_interval to run the workflow at scheduled time
- Set up training, tuning and inference configurations for each operators using Sagemaker Python SDK for Airflow operators.
- Create individual tasks as Airflow operators defining trigger rules and associating them with the DAG object. Refer previous section for defining the individual tasks
- Specify task dependencies
You can find the Airflow DAG code here in the repo.
The final step is to clean up. To avoid unnecessary charges,
- You should destroy all of the resources created by the CloudFormation stack in Airflow set up by deleting the stack after you’re done experimenting with it. You can follow the steps here to delete the stack.
- You have to manually delete the S3 bucket created because AWS CloudFormation cannot delete non-empty S3 bucket.
- You have to manually delete SageMaker endpoint that was created as part of "Compile Inference Pipeline" step above, as well as XGBoost and Spark models.
- Refer to SageMaker SDK documentation and Airflow documentation for additional details on the Airflow SageMaker operators.
- Refer to SageMaker documentation to learn more about Gradient Boosted Decision Tree algorithm used in the blog post.
- Refer to SageMaker documentation to learn more about SageMaker Processing service.
- Refer to SageMaker documentation to learn more about SageMaker inference pipelines.
This sample code is made available under a modified MIT license. See the LICENSE file.