- Official Ruby on Rails Documentation Ruby on Rails
- Ruby on Rails Packages Ruby Gems
- Create a new rails application
rails new application_name - Run Rails server
rails s - Default root route
- localhost:3000
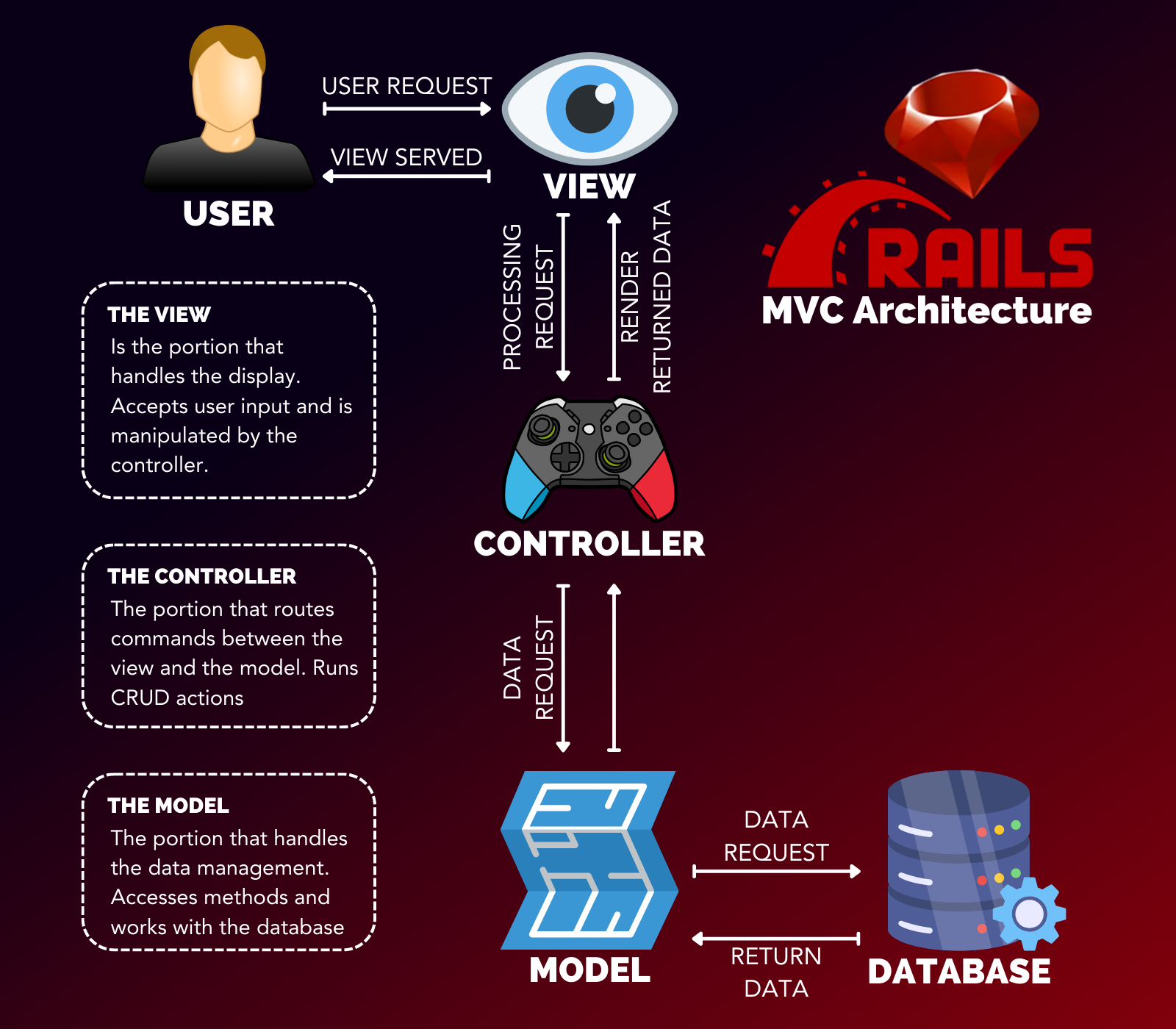
It is a separation of the presentation layer and the backend layer
- Presentation Layer (what the user sees when interacting with the application)
- Backend Layer (All of the logic code for operating the application)
- Resources within the application
- examples: posts, comments, users, listings, etc...
- Will generally access a database
- Sqlite is the default database with Rails
- Makes up the front-end or presentation layer of the application
- Shares data with controllers
- The app/views directory has a subdirectory for each controller
- Operates in standard web templates (HTML, CSS, JavaScript)
- Ruby is embedded into the HTML file as an extension "action_name.html.erb"
- Embedded Ruby is done with the HTML tag <%= ... %>
- The backend brains/logic of the application
- examples: users_controller, listings_controller, pages_controller
- Determines how user requests are handled and returned to the user via views
- .keep
- application.css (manifest file that is available to all application views)
- channel.rb
- connection.rb
- .keep
- application*controller.rb *(default functionality)_
- application_helper.rb
- controllers
- application.js
- index.js
- application.js
- application_jobs.rb
- application_mailers.rb
- .keep
- application_record.rb
-
application.html.erb
-
mailer.html.erb
-
mailer.text.erb
- bundle
- importmap
- rails
- rake
- setup
- development.rb
- production.rb
- test.rb
- assets.rb
- content_security_policy.rb
- filter_parameter_logging.rb
- inflections.rb
- permissions_policy.rb
-
en.yml
-
application.rb
-
boot.rb
-
cable.yml
-
environment.rb
-
importmap.rb
-
mastery.key
-
puma.rb
-
routes.rb
-
storage.yml
- .keep
- .keep
- Create (add rows)
- Read (display existing rows)
- Update (modify existing rows)
- Delete (remove existing rows)
- SQL (Structured Query Interface)
- Active Record
- ORM (Object Relational Mapper)
- Communicates between Rails Application and Database
- Translates Ruby Code into SQL queries
- Location: models > application_record.rb
- ApplicationRecord inherits functionality from ActiveRecord
- ORM (Object Relational Mapper)