Simple server monitoring for your GPU cluster.
Periodically calls nvidia-smi through SSH and parses it into a website.
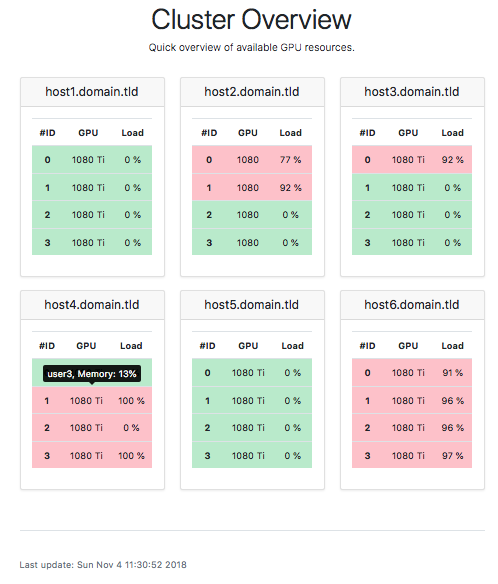
The generated website highlights the available GPUs in green and shows the
GPU load.
Occupied GPUs are marked in red. By hovering the entry with your mouse,
it will show you the users which have processes on the machine and how much
GPU memory is consumed.
You need to satisfy some Python dependencies. Start by creating a conda environment with Python3.6.
conda create -n web-gpu-monitor python=3.6
Then, activate the environment with conda activate web-gpu-monitor and install the dependencies with
pip install -r requirements.txt
First step is to create a config.ini where your credentials and hostnames are specified.
An exemplary ini-file could look like this:
[common]
user = yourusername
hosts = host1.domain.tld,host2.domain.tld
key_filename=path_to_keySave this as config.ini in the root of this repository.
Now you can run python fetch_data.py -c config.ini to fetch data from
your specified hosts. The result is then saved in load_data.csv.
Call python render_website.py to create a HTML site out of it.
The result is stored in index.html.
To make the monitoring service available in a website, you will first have to configure an HTTP server. We recommend nginx (simply run sudo apt install nginx followed by sudo systemctl enable nginx and sudo systemctl start nginx). Then, you should put the index.html file and the assets directory somewhere under /var/www.
In our case, we have put it under /var/www/gpu-monitor, and updated the config file at /etc/nginx/sites-available/mlkd accordingly by inserting the following lines:
location ^~ /gpu-monitor {
alias /var/www/mlkd/gpu-monitor;
try_files $uri $uri.html $uri/ =404;
index index.html;
}In our case, the name of the config file is mlkd because of some other stuff we're hosting, but usually you can use the default config file or a new custom one.
To keep the files under the /var/www/gpu-monitor directory updated, we created soft links from there to the place where they are generated, i.e.:
ln -sf /home/ubuntu/web-gpu-monitor/index.html /var/www/gpu-monitor/index.html
ln -sf /home/ubuntu/web-gpu-monitor/assets /var/www/gpu-monitor/assetsThere were other ways to achieve this, such as regularly copying the files, but this was probably the simplest.
The execution of these scripts can be done using a cronjob. For code at /home/ubuntu/web-gpu-monitor, and a conda environment with Python at /home/ubuntu/.conda/envs/web-gpu-monitor/bin/python and to run it every 5 minutes, run crontab -e to edit the crontab, and insert the lines below:
*/5 * * * * cd /home/ubuntu/web-gpu-monitor/ && /home/ubuntu/.conda/envs/web-gpu-monitor/bin/python /home/ubuntu/web-gpu-monitor/fetch_data.py -c config.ini && /home/ubuntu/.conda/envs/web-gpu-monitor/bin/python /home/ubuntu/web-gpu-monitor/render_website.pyNote: you need to make sure the user running the script has write access to the
You will need a user that can access all machines and call nvidia-smi. In our cluster, that user is gpu_monitor.