Dijkstra's algorithm is an algorithm for finding the shortest paths between nodes in a graph. For more information, please refer to the wiki page(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dijkstra%27s_algorithm)
Tested on python 3.7+
git clone https://github.com/jlim262/dijkstra.git
cd dijkstra
python dijkstra.pyOutput
Graph data:
(a, b, 7)
(a, c, 9)
(a, f, 14)
(b, a, 7)
(b, c, 10)
(b, d, 15)
(c, a, 9)
(c, b, 10)
(c, d, 11)
(c, f, 2)
(f, a, 14)
(f, c, 2)
(f, e, 9)
(d, b, 15)
(d, c, 11)
(d, e, 6)
(e, d, 6)
(e, f, 9)
Dijkstra's shortest path
[Current Vertex] id: a(0), adjacent: ['b(inf, Visited:False)', 'c(inf, Visited:False)', 'f(inf, Visited:False)']
b(weight between:7) is updated (from: inf to 7)
c(weight between:9) is updated (from: inf to 9)
f(weight between:14) is updated (from: inf to 14)
[Current Vertex] id: b(7), adjacent: ['a(0, Visited:True)', 'c(9, Visited:False)', 'd(inf, Visited:False)']
a is already visited.
c(weight between:10) is not updated (still 9)
d(weight between:15) is updated (from: inf to 22)
[Current Vertex] id: c(9), adjacent: ['a(0, Visited:True)', 'b(7, Visited:True)', 'd(22, Visited:False)', 'f(14, Visited:False)']
a is already visited.
b is already visited.
d(weight between:11) is updated (from: 22 to 20)
f(weight between:2) is updated (from: 14 to 11)
[Current Vertex] id: f(11), adjacent: ['a(0, Visited:True)', 'c(9, Visited:True)', 'e(inf, Visited:False)']
a is already visited.
c is already visited.
e(weight between:9) is updated (from: inf to 20)
[Current Vertex] id: e(20), adjacent: ['d(20, Visited:False)', 'f(11, Visited:True)']
d(weight between:6) is not updated (still 20)
f is already visited.
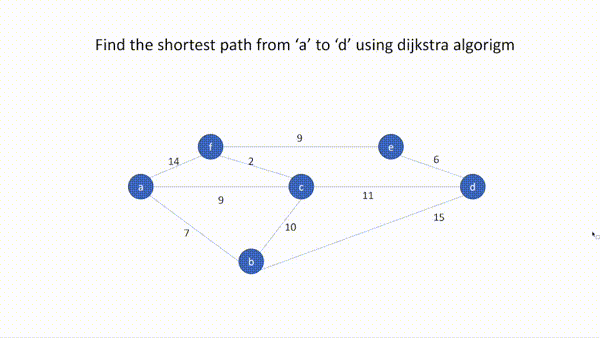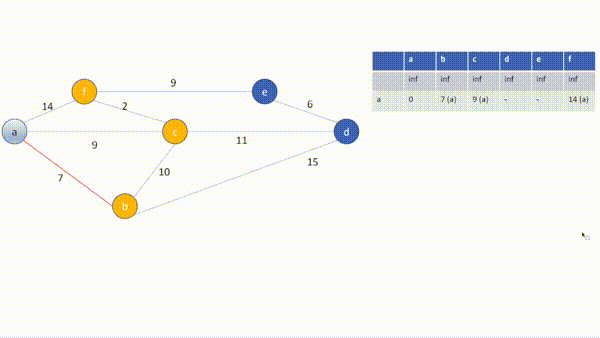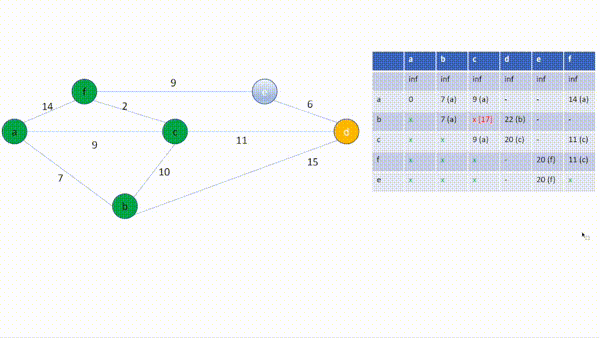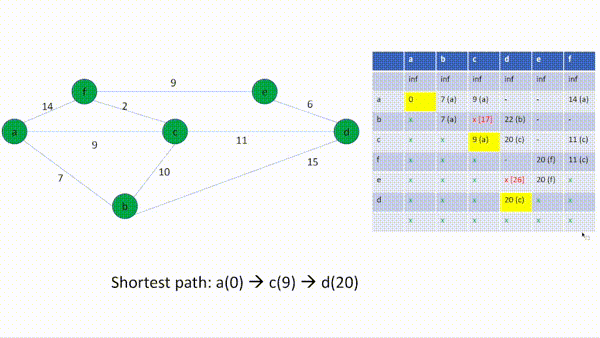
[Current Vertex] id: d(20), adjacent: ['b(7, Visited:True)', 'c(9, Visited:True)', 'e(20, Visited:True)']
b is already visited.
c is already visited.
e is already visited.
The shortest path: [(a,0), (c,9), (d,20)]
A vertex is the most basic part of a graph and it is also called a node. A vertex may also have additional information and we'll call it as payload.
An edge is another basic part of a graph, and it connects two vertices/ Edges may be one-way or two-way. If the edges in a graph are all one-way, the graph is a directed graph, or a digraph. The picture shown above is not a digraph.
Edges may be weighted to show that there is a cost to go from one vertex to another. For example in a graph of roads that connect one city to another, the weight on the edge might represent the distance between the two cities or traffic status.
A graph can be represented by G where G=(V,E). V is a set of vertices and E is a set of edges. Each edge is a tuple (v,w) where w,v in V. We can add a third component to the edge tuple to represent a weight. A subgraph s is a set of edges e and vertices v such that e in E and v in V. The picture above shows a simple weighted graph and we can represent this graph as the set of six vertices
V={a,b,c,d,e,f} and the set of nine edges:
E={(a,b,7),(a,c,9),(a,f,14),(b,d,15),(b,c,10),(c,d,11),(c,f,2),(d,e,6),(e,f,9)}
A path in a graph is a sequence of vertices that are connected by edges.
A cycle in a directed graph is a path that starts and ends at the same vertex. A graph with no cycles is called an acyclic graph or a DAG(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Directed_acyclic_graph).