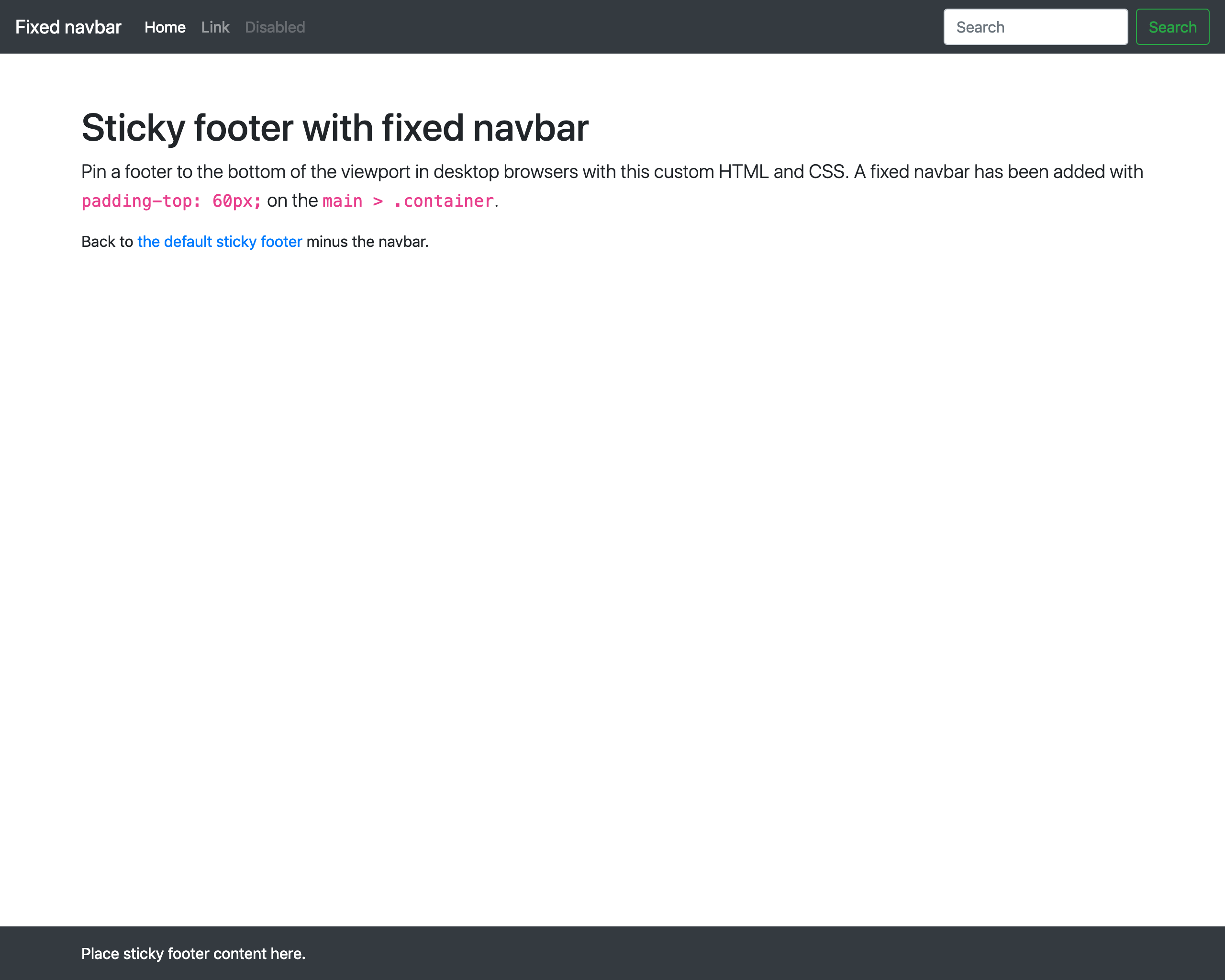
A simple example that shows how to create a sticky footer with React and Bootstrap. This examples is based on create-react-app, but this can be used in any React project.
See commits with "Add sticky footer" as the message for full changesets.
- Add Bootstrap
npm install bootstrap- Reference bootstrap. (Quick and dirty way is to add reference in index.js.)
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css'- Update html, body, and root div classes in public/index.html
<!-- h-100 -->
<html lang="en" class="h-100">
...
<!-- h-100 -->
<body class="h-100">
...
<!-- d-flex flex-column h-100 -->
<div id="root" class="d-flex flex-column h-100"></div>
</body>
</html>- Create App.css and add the following
main > .container {
padding: 60px 15px 0;
}- Add reference to App.css in App.js
import './App.css'- Add boilerplate to App.js. This is copied directly from Bootstrap's example here with only minor changes*. The important thing is to ensure the header, main, and footer tags are wrapped in a React Fragment. I'm using the short syntax:
<></>.
* Minor Changes to Bootstrap Example
- Converted HTML to JSX. (This is the only critical change.)
- Tweaked footer classes with
bg-darkandtext-whiteto make it more visible - Change
href='#'references tohref='/'to fix lint rules.
This project was bootstrapped with Create React App.
In the project directory, you can run:
Runs the app in the development mode.
Open http://localhost:3000 to view it in the browser.
The page will reload if you make edits.
You will also see any lint errors in the console.
Launches the test runner in the interactive watch mode.
See the section about running tests for more information.
Builds the app for production to the build folder.
It correctly bundles React in production mode and optimizes the build for the best performance.
The build is minified and the filenames include the hashes.
Your app is ready to be deployed!
See the section about deployment for more information.
Note: this is a one-way operation. Once you eject, you can’t go back!
If you aren’t satisfied with the build tool and configuration choices, you can eject at any time. This command will remove the single build dependency from your project.
Instead, it will copy all the configuration files and the transitive dependencies (Webpack, Babel, ESLint, etc) right into your project so you have full control over them. All of the commands except eject will still work, but they will point to the copied scripts so you can tweak them. At this point you’re on your own.
You don’t have to ever use eject. The curated feature set is suitable for small and middle deployments, and you shouldn’t feel obligated to use this feature. However we understand that this tool wouldn’t be useful if you couldn’t customize it when you are ready for it.
You can learn more in the Create React App documentation.
To learn React, check out the React documentation.
This section has moved here: https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/code-splitting
This section has moved here: https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/analyzing-the-bundle-size
This section has moved here: https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/making-a-progressive-web-app
This section has moved here: https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/advanced-configuration
This section has moved here: https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/deployment
This section has moved here: https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/troubleshooting#npm-run-build-fails-to-minify