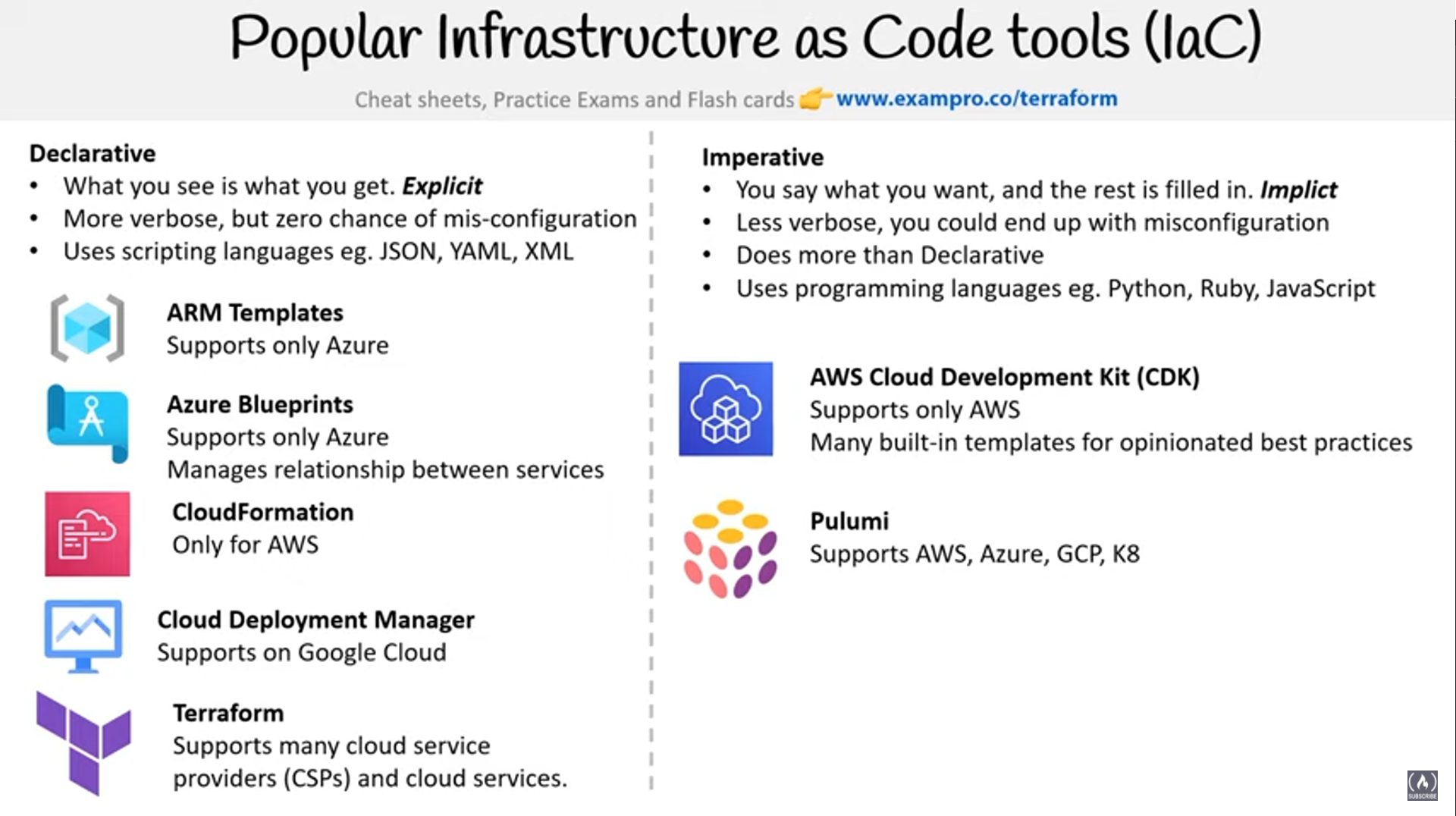
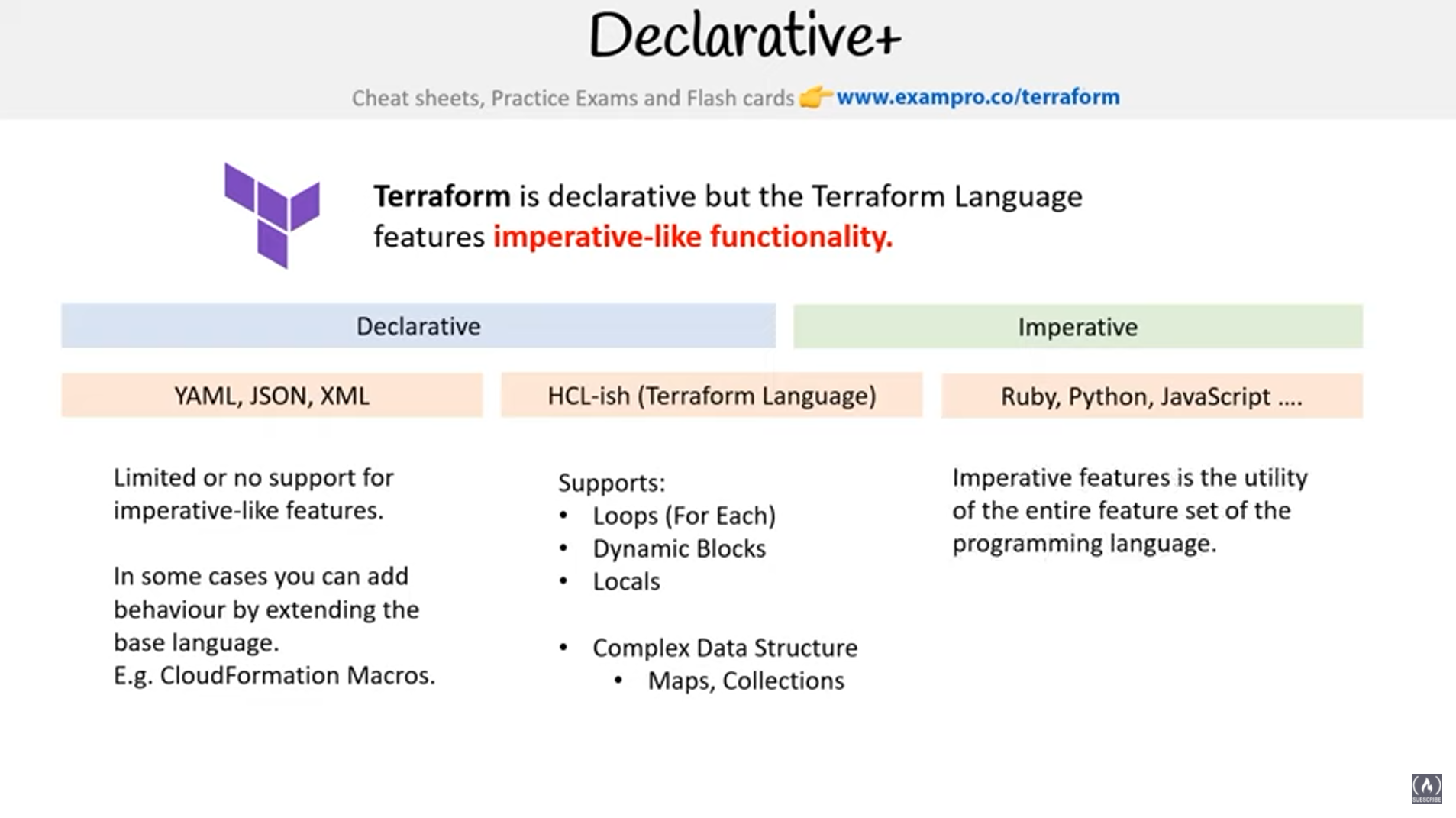
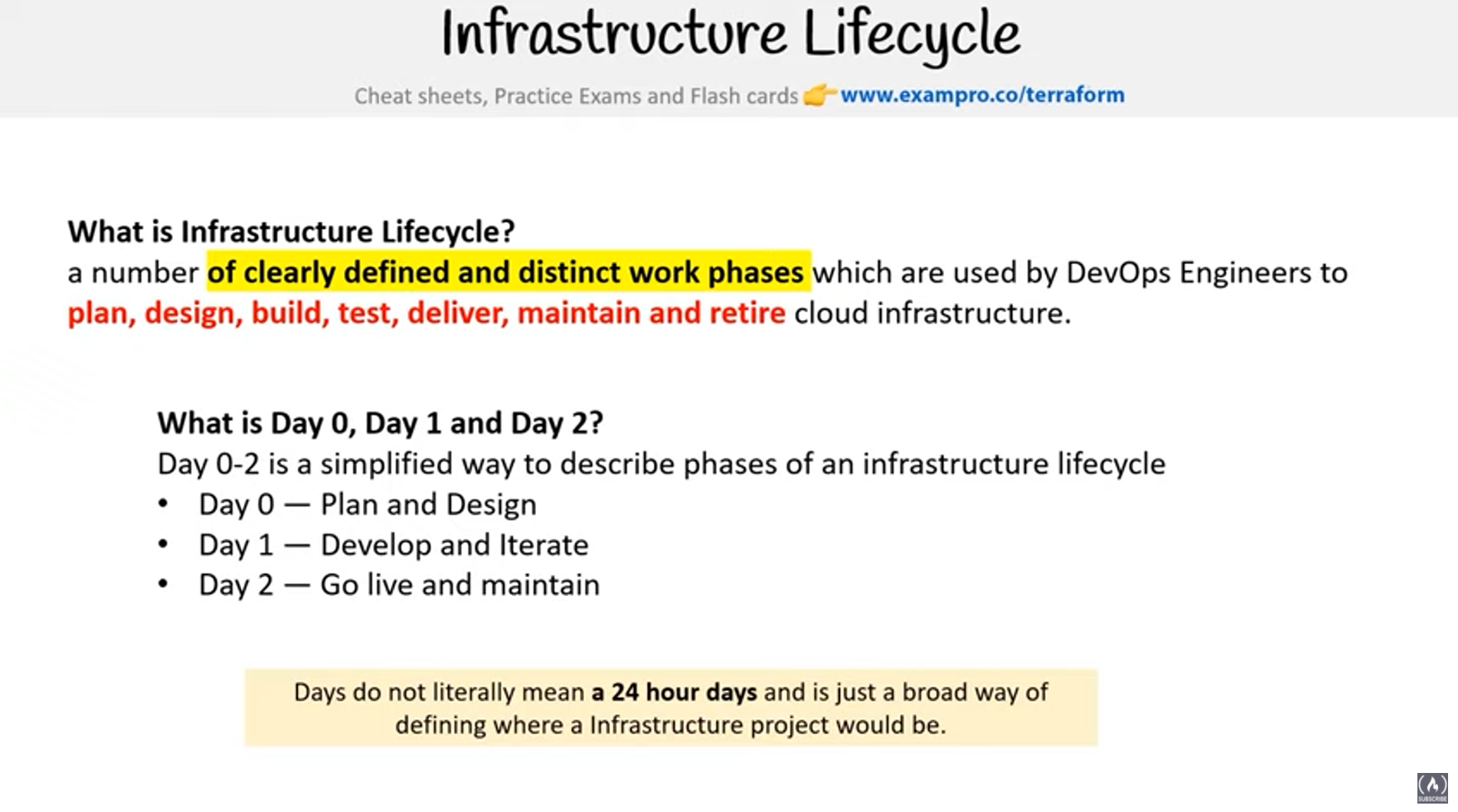
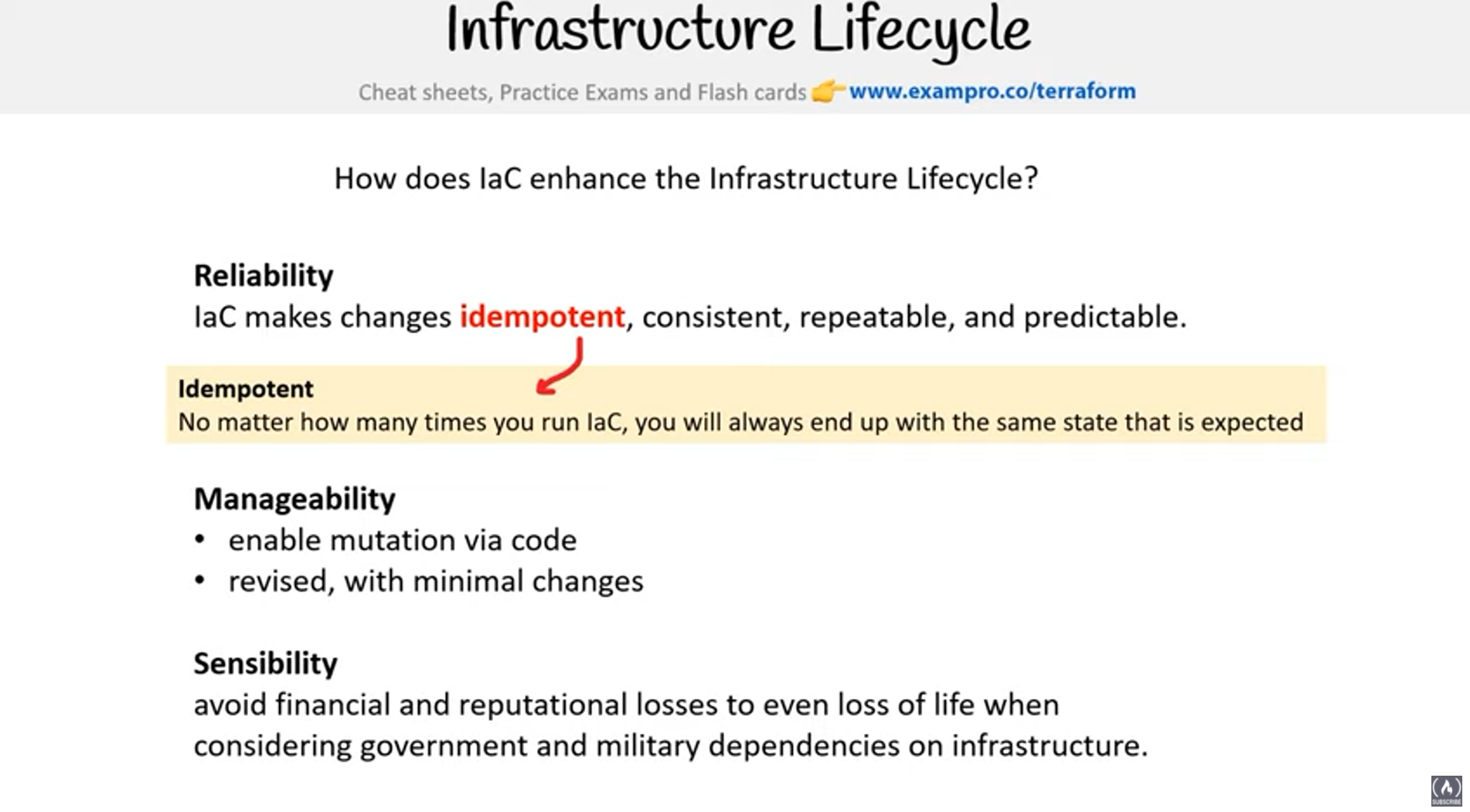
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool that is declarative and cloud agnostic
- Industry standard for IaC
- Understand IaC concepts
- Understand TF purpose (vs other IaC)
- Understand TF basics
- Use TF CLI (outside of core workflow)
- Interact with TF modules
- Navigate Terraform workflow
- Implement and maintain state
- Read, generate and modify configuration
- Understand TF cloud and Enterprise capabilities
- Passing grade is 700/1000 so circa 70% (may including scaling)
- 57 Questions, so can get 17 wrong, no penalty for wrong questions
- Format: Multiple Choice, Multiple Answer and Fill in the Blank (one word answer)
- Duration is 1 hour, so ~1 min per question
- Exam time is 60 mins, seat time is 90 mins (time allocated to exam incl reviewing instructions, showing online proctor your workspace, read NDA, provide feedback)
- Valid for 24 months
- Exam tends to be a little behind the stable version of TF (aka the version it is using)
-
If you can answer the following, you're very likely to pass n.b. it is dated
-
1 Understand infrastructure as code (IaC) concepts
- 1a Explain what IaC is
- 1b Describe advantages of IaC patterns
-
2 Understand Terraform's purpose (vs other IaC)
- 2a Explain multi-cloud and provider-agnostic benefits
- 2b Explain the benefits of state
-
3 Understand Terraform basics
- 3a Handle Terraform and provider installation and versioning
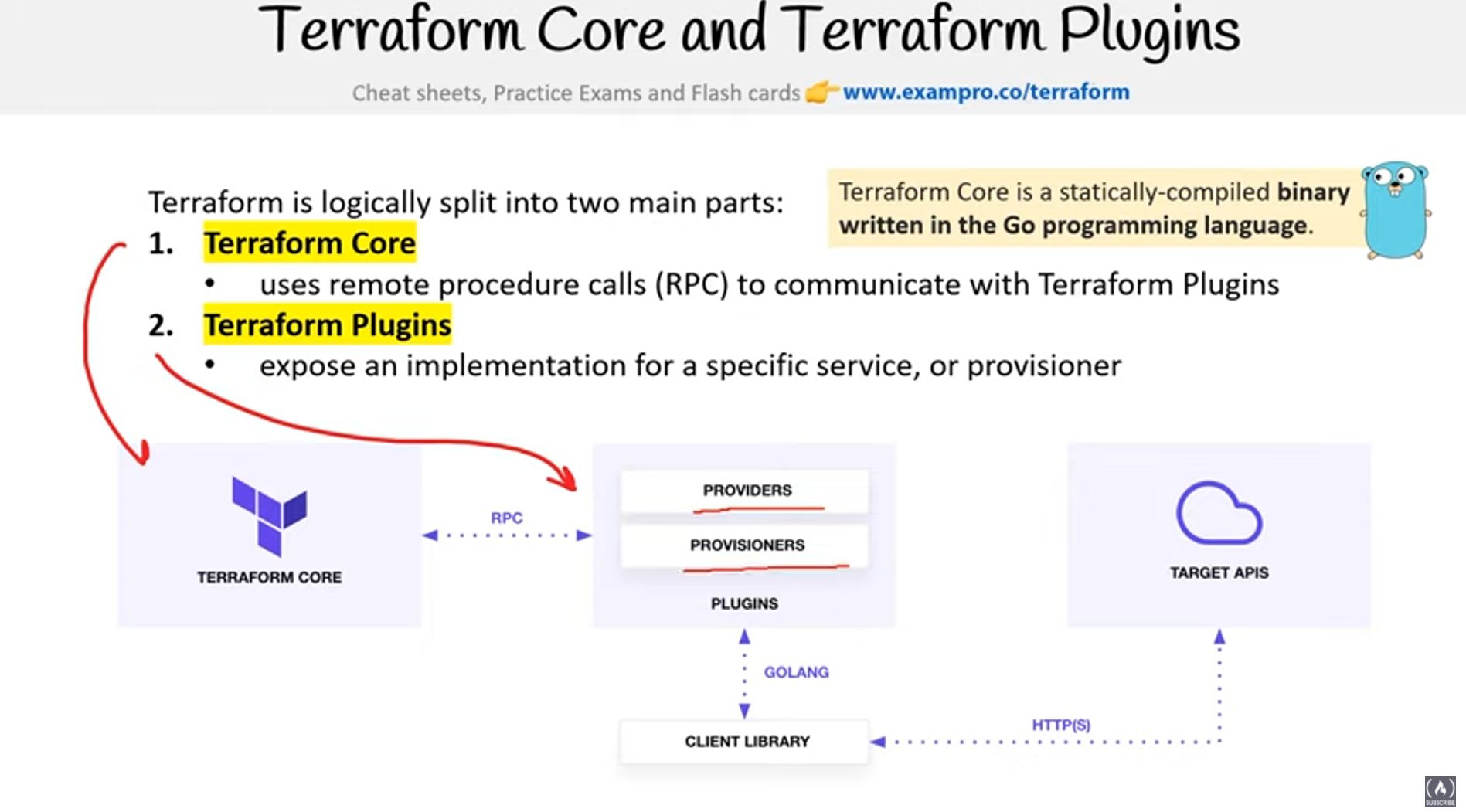
- 3b Describe plugin based architecture
- 3c Demonstrate using multiple providers
- 3d Describe how Terraform finds and fetches providers
- 3e Explain when to use and not use provisioners and when to use local-exec or remote-exec
-
4 Use the Terraform CLI (outside of core workflow)
- 4a Given a scenario: choose when to use terraform fmt to format code
- 4b Given a scenario: choose when to use terraform taint to taint Terraform resources
- 4c Given a scenario: choose when to use terraform import to import existing infrastructure into your Terraform state
- 4d Given a scenario: choose when to use terraform workspace to create workspaces
- 4e Given a scenario: choose when to use terraform state to view Terraform state
- 4f Given a scenario: choose when to enable verbose logging and what the outcome/value is
-
5 Interact with Terraform modules
- 5a Contrast module source options
- 5b Interact with module inputs and outputs
- 5c Describe variable scope within modules/child modules
- 5d Discover modules from the public Terraform Module Registry
- 5e Defining module version
-
6 Navigate Terraform workflow
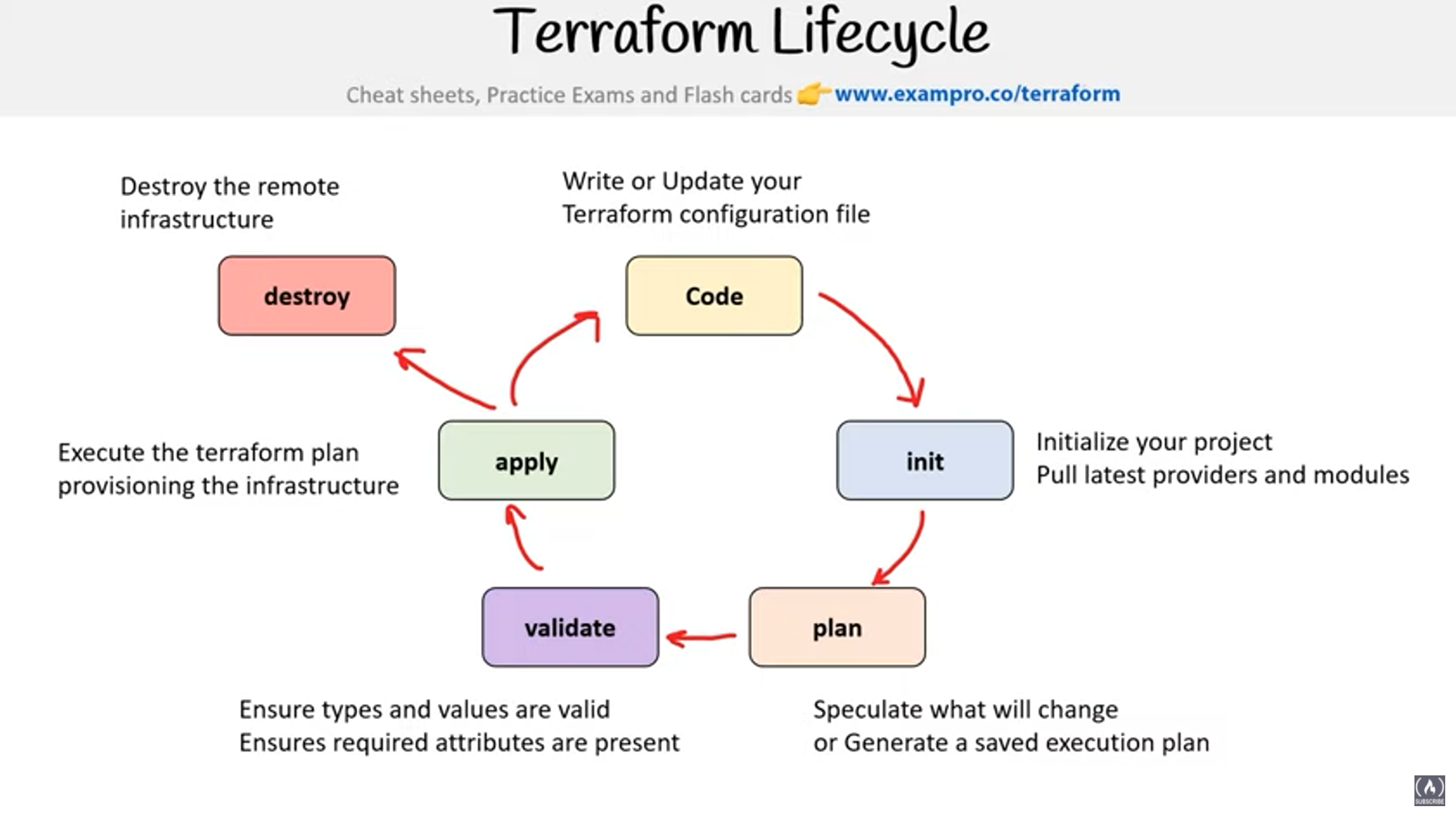
- 6a Describe Terraform workflow ( Write -> Plan -> Create )
- 6b Initialize a Terraform working directory (terraform init)
- 6c Validate a Terraform configuration (terraform validate)
- 6d Generate and review an execution plan for Terraform (terraform plan)
- 6e Execute changes to infrastructure with Terraform (terraform apply)
- 6f Destroy Terraform managed infrastructure (terraform destroy)
-
7 Implement and maintain state
- 7a Describe default local backend
- 7b Outline state locking
- 7c Handle backend authentication methods
- 7d Describe remote state storage mechanisms and supported standard backends
- 7e Describe effect of Terraform refresh on state
- 7f Describe backend block in configuration and best practices for partial configurations
- 7g Understand secret management in state files
-
8 Read, generate, and modify configuration
- 8a Demonstrate use of variables and outputs
- 8b Describe secure secret injection best practice
- 8c Understand the use of collection and structural types
- 8d Create and differentiate resource and data configuration
- 8e Use resource addressing and resource parameters to connect resources together
- 8f Use Terraform built-in functions to write configuration
- 8g Configure resource using a dynamic block
- 8h Describe built-in dependency management (order of execution based)
-
9 Understand Terraform Cloud and Enterprise capabilities
- 9a Describe the benefits of Sentinel, registry, and workspaces
- 9b Differentiate OSS and TFE workspaces
- 9c Summarize features of Terraform Cloud
- Easy to mis-configure through human error
- Hard to manage expected state of configuartion for compliance
- Hard to transfer configuration knowledge to others
- Write configuration script to automate creating, updating or destroying cloud infrastructure
- IaC in a blueprint of your infrastructure
- IaC allows you to easily share, version or inventory your cloud infrastructure
terraform init
terraform validate
terraform plan
terraform apply
terraform apply -auto-approve
terraform output
terraform refresh
terraform destroy
terraform plan -destroy