GitHub Checks allows you to quickly see the results of your CI tests from GitHub.
This is a simple, light-weight python implementation of the GitHub Checks API.
Once you have completed all the installation steps, here are a few examples of what your Checks implementation could look like:
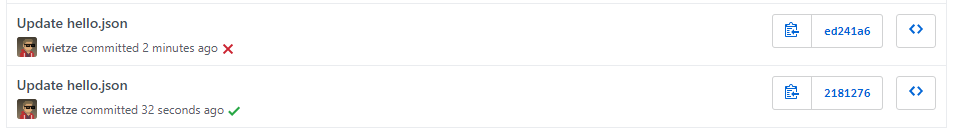
Automatically run Checks for new commits:
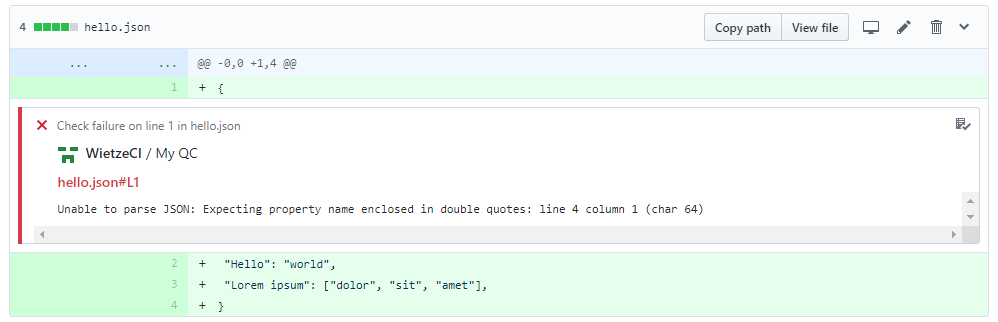
Annotate files with messages explaining why they failed tests:
Note that you need a self-hosted server that will run your CI logic.
In GitHub, do the following:
-
Click your profile in the right top corner, click Settings, click Developers Settings, click GitHub Apps and click New GitHub App.
-
Add a name and homepage URL (any URL will do). For User authorization callback URL and Webhook URL, use the server address you'll be using, with
/hookat the end of the address. -
Generate a strong, random secret and set it as Webhook secret (optional). While optional in GitHub, this project won't work without one.
-
Under Permissions, set the following:
Name Permission Checks Read & write Repository contents Read Repository metadata Read -
Under Subscribe to events, tick Check runs.
-
Click Create GitHub App.
-
If the creation was successful, you'll see an overview of your app. Copy the App ID as you'll need it for setting up the script.
-
Scroll to the bottom of the page to generate a private key. Save the file as
pk.pem, as you'll need it for setting up the script.
The server will run on port 443, using a simple Python 3 Flask server.
-
Install all dependencies by running the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txt
-
To create a locally signed SSL certificate, run the followingin the same folder as
server.py:openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -nodes -out cert.pem -keyout key.pem -days 365
-
Copy
pk.pem(see 'Creating a GitHub app' section) to the same folder asserver.py. -
Update
example.pyto set the correct App ID. If you're using GitHub Enterprise, also update thebase_apiparameter.
Run the server as follows:
GITHUB_WEBHOOK_SECRET={{your_secret_here}} sudo -E python3 server.py
Make sure you replace {{your_secret_here}} with your webhook secret set in GitHub (see 'Creating a GitHub app' section). You might want to consider changing port 443 to something else so that server.py doesn't have to run using sudo.