Configuration of magnolia modules is stored in JCR database, if the configuration contains sensible data - passwords, api keys etc. - it can be a lack of security.
To solve the above issue, sensible data should be stored in a Secret Manager as Vault
- Integration with Secrets manager: Hashicorp Vault, AWS Secrets manager (to be done) and Google Secret manager (to be done).
- Population of secrets in configuration of modules.
Maven module that implements the integration with Secrets managers and loads module configuration.
Magnolia bundle to check the module with-secrets.
Example of magnolia module using the module with-secrets to get secrets from a Secret Manager.
Add dependency with the module with-secrets
<dependency>
<groupId>com.formentor</groupId>
<artifactId>with-secrets</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>Extends the module class with ModuleConfigSecrets
public class ExampleWithSecrets extends ModuleConfigSecrets {
private String vendorApiKey;
@Inject
public ExampleWithSecrets(WithSecrets withSecrets, SecretsStorageFactory secretsStorageFactory, PreConfiguredBeanUtils beanUtils, MagnoliaConfigurationProperties magnoliaConfigurationProperties) {
super(withSecrets, secretsStorageFactory, beanUtils, magnoliaConfigurationProperties);
}
}See example-with-secrets
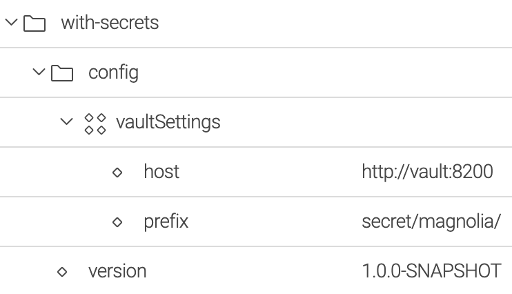
Secrets can be stored in Vault, AWS Secrets Manager and Google Secret Manager, and depending on the origin the configuration will be different.
Vault is a product from Hashicorp to store and manage secrets.
- Set variable VAULT_TOKEN with the token in Vault.
export VAULT_TOKEN=myroothost with the address of the Vault server
prefix prefix or path of the modules of magnolia in Vault. The prefix is added to the module name to get the configuration.
The implementation of the integration with AWS Secrets Manager has to bee done.
The implementation of the integration with Google Secret Manager has to bee done.
The project provides a docker-compose that starts a Vault Server and a Magnolia instance with the module example-with-secrets whose configuration is stored in Vault.
# Build the project
$ mvn clean package
# Launch the services
$ docker compose up -d
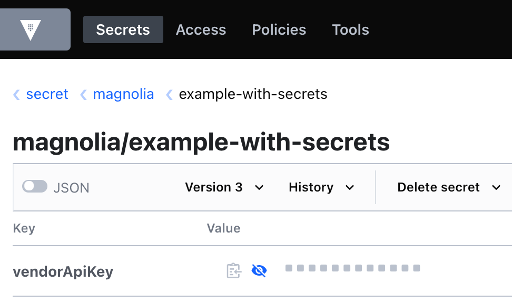
2. Add the secret "vendorApiKey" for the module example-with-secrets in Vault
a) Using Vault cli
# Adds "vendorApiKey" with the value "i-am-a-secret"
docker exec -ti magnolia-with-secrets-bundle_vault_1 sh -c "vault kv put secret/magnolia/example-with-secrets vendorApiKey=i-am-a-secret"b) Using Vault ui
http://localhost:8200/ui using token "myroot"
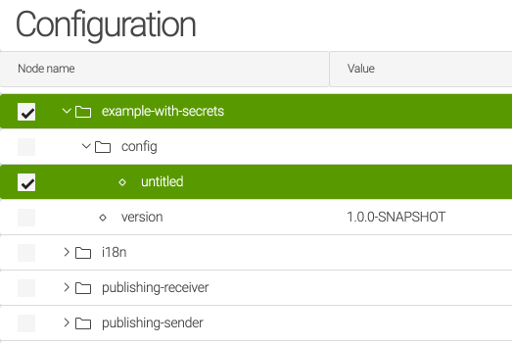
Restart the module example-with-secrets to load the new configuration from Vault.
a) Restarting the container of Magnolia
$ docker stop magnolia-with-secrets-bundle_magnolia_1
$ docker start magnolia-with-secrets-bundle_magnolia_1b) Changing the configuration of the module
Magnolia is exposed in http://locahost:8080/.magnolia
You can create a dummy property to trigger the starting of example-with-secrets
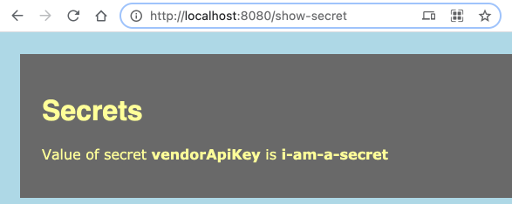
The page show-secret of Magnolia shows the value of the property "vendorApiKey" of the module example-with-secrets.
As you will see the value matches the entry "vendorApiKey" of the secret "secret/magnolia/example-with-secret" in Vault
Implements the integration with the Secret manager implementing the interface SecretsStorage and implement the method readModuleConfig()
import java.util.HashMap;
public class SecretsStorageImpl implements SecretsStorage {
@Override
public Map<String, String> readModuleConfig(String module) {
return new HashMap<>();
}
}Creates a method in the factory of secret managers to instantiate the secret manager
public class SecretsStorageFactory {
/**
* Returns an instance of SecretsStorage implemented for the secret manager
* @param config
* @param magnoliaConfigurationProperties
* @return
*/
public SecretsStorage getSecretsStorageAWS(SecretSettings config, MagnoliaConfigurationProperties magnoliaConfigurationProperties) {
return new SecretsStorageImpl();
}
}