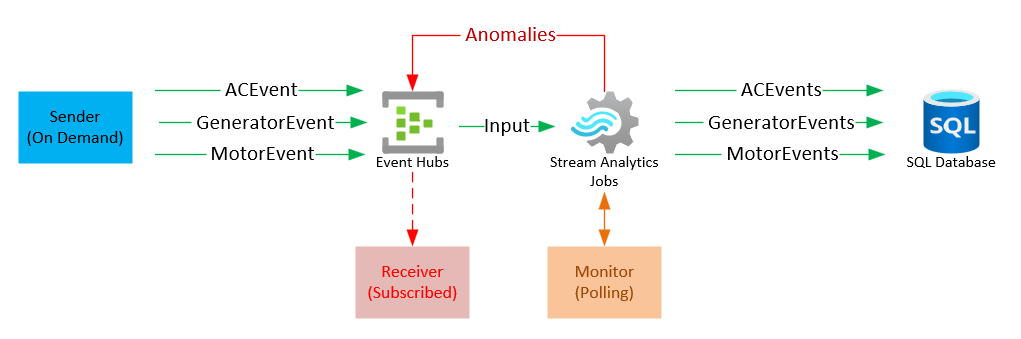
A customer is sending messages of different types to Event Hubs and wants to save these messages to Azure SQL tables without having to write custom code. He also wants to detect anomalies and process these anomalies as they are raised.
Azure Stream Analytics offers functionaltiy that allows messages to be read from Event Hubs, filter them, process them and save them to different destinations including Azure SQL tables and back to Event Hubs.
create table ACEvents
(
Id int not null primary key identity,
DeviceId varchar(10) not null,
Ts DateTime not null,
CoolantTemperature float not null,
AirFlow float not null,
AirTemperature float not null
)
create table GeneratorEvents
(
Id int not null primary key identity,
DeviceId varchar(10) not null,
Ts DateTime not null,
Hertz float not null,
Amps float not null,
Voltage float not null,
GasPercentage float not null
)
create table MotorEvents
(
Id int not null primary key identity,
DeviceId varchar(10) not null,
Ts DateTime not null,
Temperature float not null,
Revolutions float not null
)- Azure Hubs [hub-ecloud1-location1]
- Hub [hub-location1]
- Consumer group [hub_location1_cg]
- Hub [hub-location1]
Azure SQL Tables:
- ACEvents [hubdb-ACEvents]
- GeneratorEvents [hubdb-GeneratorEvents]
- MotorEvents [hubdb-MotorEvents]
- Anomalies Hub [anomalies-hub]
Note: One Stream Analytic jobs instance can process many jobs. The Stream Analytics query language can perform time based operations, aggregations, etc.
with [allData] as (
select * FROM [hub-ecloud1-location1]
),
anomalies AS (
SELECT a.ts,a.deviceId,'ACAnomality' as eventType, 'airFlow' as property, a.airflow as value
FROM allData a where a.type='ACEvent' and a.airFlow=0
UNION
SELECT a.ts,a.deviceId,'GeneratorAnomality' as eventType, 'voltage' as property, a.voltage as value
FROM allData a where a.type='GeneratorEvent' and a.voltage=0
UNION
SELECT a.ts,a.deviceId,'GeneratorAnomality' as eventType, 'gasPercentage' as property, a.voltage as value
FROM allData a where a.type='GeneratorEvent' and a.gasPercentage<20
UNION
SELECT a.ts,a.deviceId,'MotorAnomality' as eventType, 'revolutions' as property, a.revolutions as value
FROM allData a where a.type='MotorEvent' and a.revolutions=0
)
select
a.ts,a.deviceId,a.eventType,a.property,a.value
into
[anomalies-hub]
from anomalies a;
select a.deviceId,a.ts,a.coolantTemperature,a.airFlow,a.airTemperature
into [hubdb-ACEvents] from allData a
where type='ACEvent';
select a.deviceId,a.ts,a.hertz,a.amps,a.voltage,a.gasPercentage
into [hubdb-GeneratorEvents] from allData a
where type='GeneratorEvent';
select a.deviceId,a.ts,a.temperature,a.revolutions
into [hubdb-MotorEvents] from allData a
where type='MotorEvent';For the purposes of this demo, the code has been implemented in GO and the different executables share these structures in common:
type acEvent struct {
Ts time.Time `json:"ts"`
Type string `json:"type"`
DeviceID string `json:"deviceId"`
AirFlow float64 `json:"airflow"`
AirTemperature float64 `json:"airTemperature"`
CoolantTemperature float64 `json:"coolantTemperature"`
}
type generatorEvent struct {
Ts time.Time `json:"ts"`
Type string `json:"type"`
DeviceID string `json:"deviceId"`
Hertz float64 `json:"hertz"`
Amps float64 `json:"amps"`
Voltage float64 `json:"voltage"`
GasPercentage float64 `json:"gasPercentage"`
}
type motorEvent struct {
Ts time.Time `json:"ts"`
Type string `json:"type"`
DeviceID string `json:"deviceId"`
Temperature float64 `json:"temperature"`
Revolutions float64 `json:"revolutions"`
}
type EventsRequest struct {
Count int `json:"count"`
Delay int `json:"delay"`
Batch bool `json:"batch"`
}
type EventsResponse struct {
Message string `json:"message"`
Count int `json:"count"`
Delay int `json:"delay"`
Batch bool `json:"batch"`
}
type AnomalyEvent struct {
Ts time.Time `json:"ts"`
DeviceID string `json:"deviceId"`
EventType string `json:"eventType"`
Property string `json:"Property"`
Value float64 `json:"Value"`
}The sender application is an API server that can receive a message to emmit events via a POST event.
func GetRandomEvent() string {
anomaly := getRandom(1, 6)
eventType := getRandom(1, 4)
airTemperature := float64(getRandom(600, 800)) / 10.0
airFlow := float64(getRandom(30, 40)) / 10.0
coolantTemperature := float64(getRandom(200, 400)) / 10.0
gasPercentage := float64(getRandom(1, 1000)) / 10.0
voltage := float64(getRandom(2300, 2450)) / 10.0
motorTemp := float64(getRandom(1800, 2000)) / 10.0
motorRevolutions := float64(getRandom(2000, 5000)) / 10.0
hertz := float64(getRandom(580, 650)) / 10.0
amps := float64(getRandom(150, 250)) / 10.0
if anomaly == RaiseAnomaly {
voltage = 0
motorTemp = 0
motorRevolutions = 0
gasPercentage = 10
airFlow = 0
airTemperature = 90
}
var event Event
if eventType == AC_VENT {
event = NewACEvent(airFlow, airTemperature, coolantTemperature)
jsonBytes, _ := json.Marshal(event)
return string(jsonBytes)
} else if eventType == GENERATOR_EVENT {
event = NewGeneratorEvent(hertz, amps, voltage, gasPercentage)
jsonBytes, _ := json.Marshal(event)
return string(jsonBytes)
} else {
event = NewMotorEvent(motorTemp, motorRevolutions)
jsonBytes, _ := json.Marshal(event)
return string(jsonBytes)
}
}
func processInBatch(eventRequest common.EventsRequest) error {
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(),
time.Duration(30)*time.Second)
defer cancel()
hub, err := eventhub.NewHubFromConnectionString(connectionString)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err)
return err
}
if verbose {
logger.Debug(fmt.Sprintf("Sending %d messages in batch", eventRequest.Count))
}
var events []*eventhub.Event
for i := 1; i <= eventRequest.Count; i++ {
evt := common.GetRandomEvent()
events = append(events, eventhub.NewEventFromString(evt))
time.Sleep(1 * time.Millisecond)
}
hub.SendBatch(ctx, eventhub.NewEventBatchIterator(events...))
if verbose {
logger.Debug(fmt.Sprintf("Sent: %d messages in batch", eventRequest.Count))
}
wg.Done()
return nil
}The expected POST message can be:
{ "count": 50, "delay": 10, "batch": false}
or
{ "count": 100, "delay": 1, "batch": true}
The monitor application polls the SQL tables are reports the number of rows in the tables.
func getRowTotals() {
for {
acRows, _ := getRowCount("ACEvents")
genRows, _ := getRowCount("GeneratorEvents")
motorRows, _ := getRowCount("MotorEvents")
fmt.Println(styles.Bold(colors.Green("AC Events:")), acRows)
fmt.Println(styles.Bold(colors.Green("Generator Events:")), genRows)
fmt.Println(styles.Bold(colors.Green("Motor Events:")), motorRows)
time.Sleep(250 * time.Millisecond)
ansi.HideCursor()
fmt.Print(ansi.CursorUp(3))
ansi.ShowCursor()
}
wg.Done()
}The receiver application subscribes to the Anomaly hub and processes the messages as they are raised via a handler. The application is able to keep in state the last message received and avoids re-processing.
func main() {
// Azure Storage account information
storageAccountName := common.MustPassEvn("STORAGE_NAME")
storageAccountKey := common.MustPassEvn("STORAGE_KEY")
storageContainerName := common.MustPassEvn("STORAGE_CONTAINER")
// Azure Event Hub connection string
eventHubConnStr := common.MustPassEvn("EVENT_HUBS_STRING")
parsed, err := conn.ParsedConnectionFromStr(eventHubConnStr)
if err != nil {
// handle error
logger.Error(err)
os.Exit(1)
}
// create a new Azure Storage Leaser / Checkpointer
cred, err := azblob.NewSharedKeyCredential(storageAccountName, storageAccountKey)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err)
os.Exit(1)
}
leaserCheckpointer, err := storage.NewStorageLeaserCheckpointer(cred, storageAccountName, storageContainerName, azure.PublicCloud)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err)
os.Exit(1)
}
// SAS token provider for Azure Event Hubs
provider, err := sas.NewTokenProvider(sas.TokenProviderWithKey(parsed.KeyName, parsed.Key))
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err)
os.Exit(1)
}
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 20*time.Second)
defer cancel()
// create a new EPH processor
processor, err := eph.New(ctx, parsed.Namespace, parsed.HubName, provider, leaserCheckpointer, leaserCheckpointer)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// register a message handler -- many can be registered
handlerID, err := processor.RegisterHandler(ctx,
func(c context.Context, e *eventhub.Event) error {
var anomaly common.AnomalyEvent
err = json.Unmarshal(e.Data, &anomaly)
if err == nil {
fmt.Println(colors.Green("Device ID:"), anomaly.DeviceID)
fmt.Println(colors.Green("Type:"), anomaly.EventType)
fmt.Println(colors.Yellow("Property:"), anomaly.Property)
strValue := strconv.FormatFloat(anomaly.Value, 'f', 5, 64)
fmt.Println(colors.Yellow("Value:"), colors.Red(strValue))
}
return nil
})
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err)
os.Exit(1)
}
fmt.Printf("handler id: %q is running\n", handlerID)
// start handling messages from all of the partitions balancing across multiple consumers
err = processor.StartNonBlocking(ctx)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err)
os.Exit(1)
}
// Wait for a signal to quit:
logger.Info("Listening for events. Press CTRL+C to exit.")
signalChan := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(signalChan, os.Interrupt, os.Kill)
<-signalChan
logger.Debug("Terminating program & closing EPH Processor")
err = processor.Close(context.Background())
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err)
os.Exit(1)
}
}