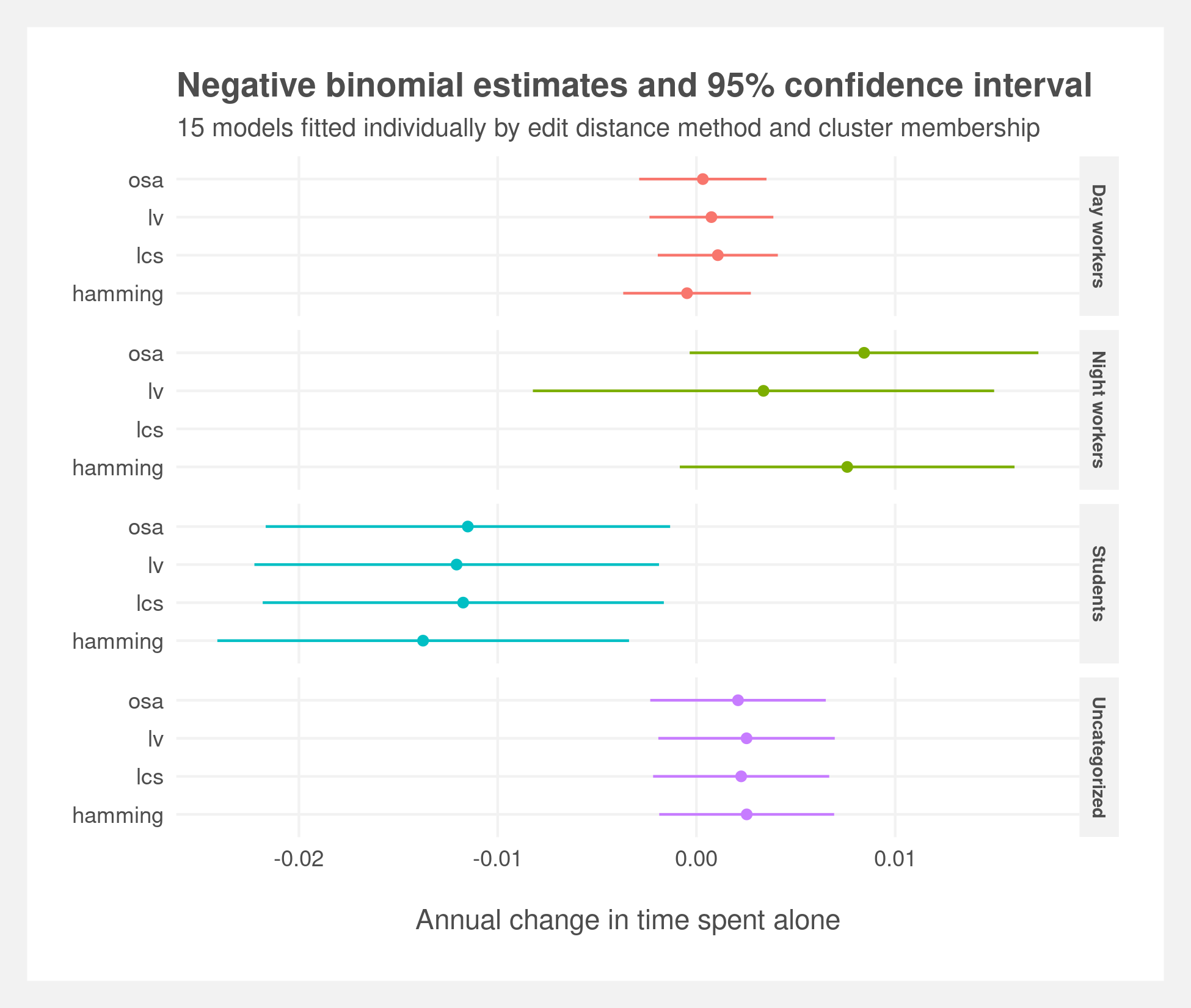
Modeling loneliness on sub-populations of Americans using sequence techniques and multi-level models
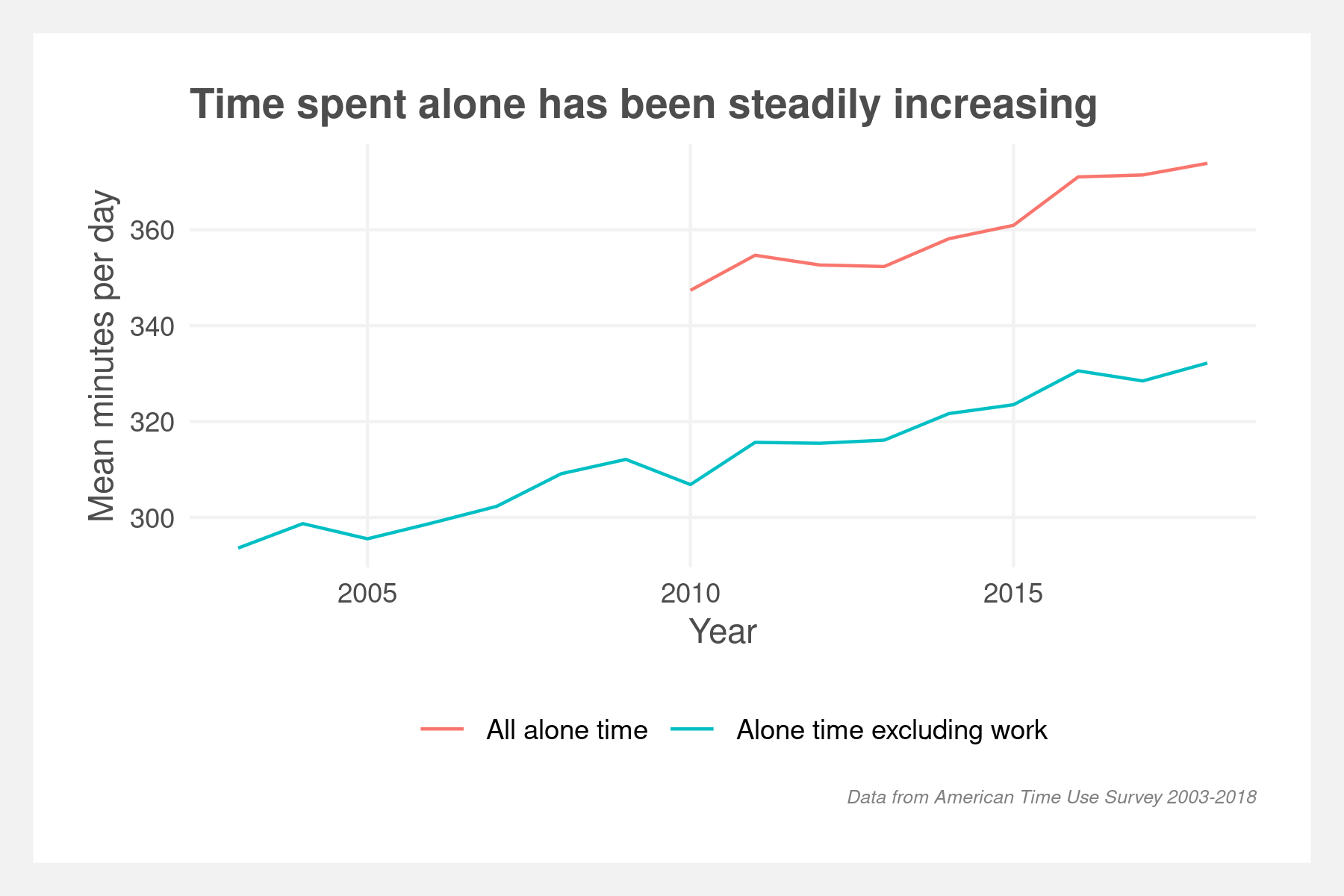
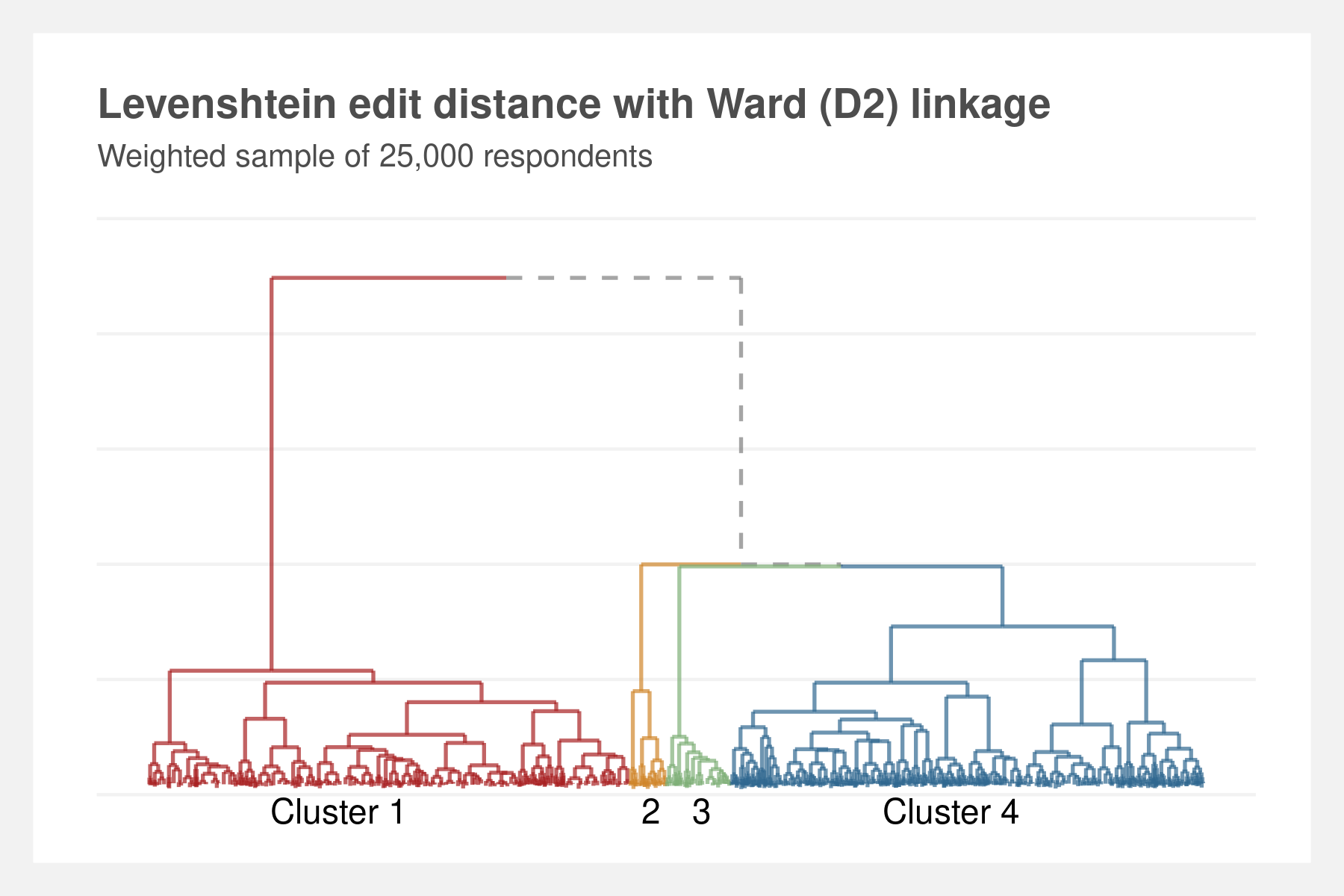
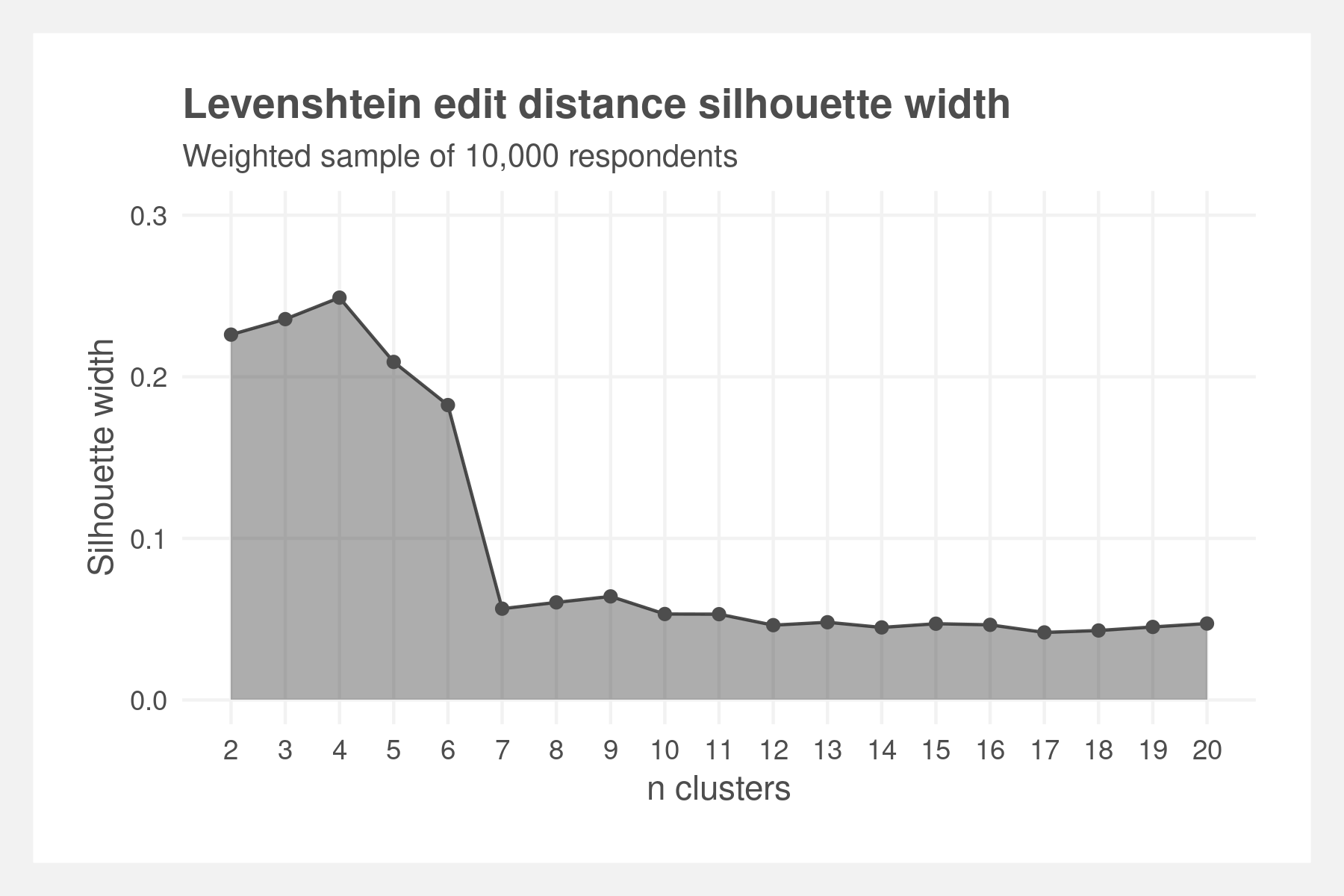
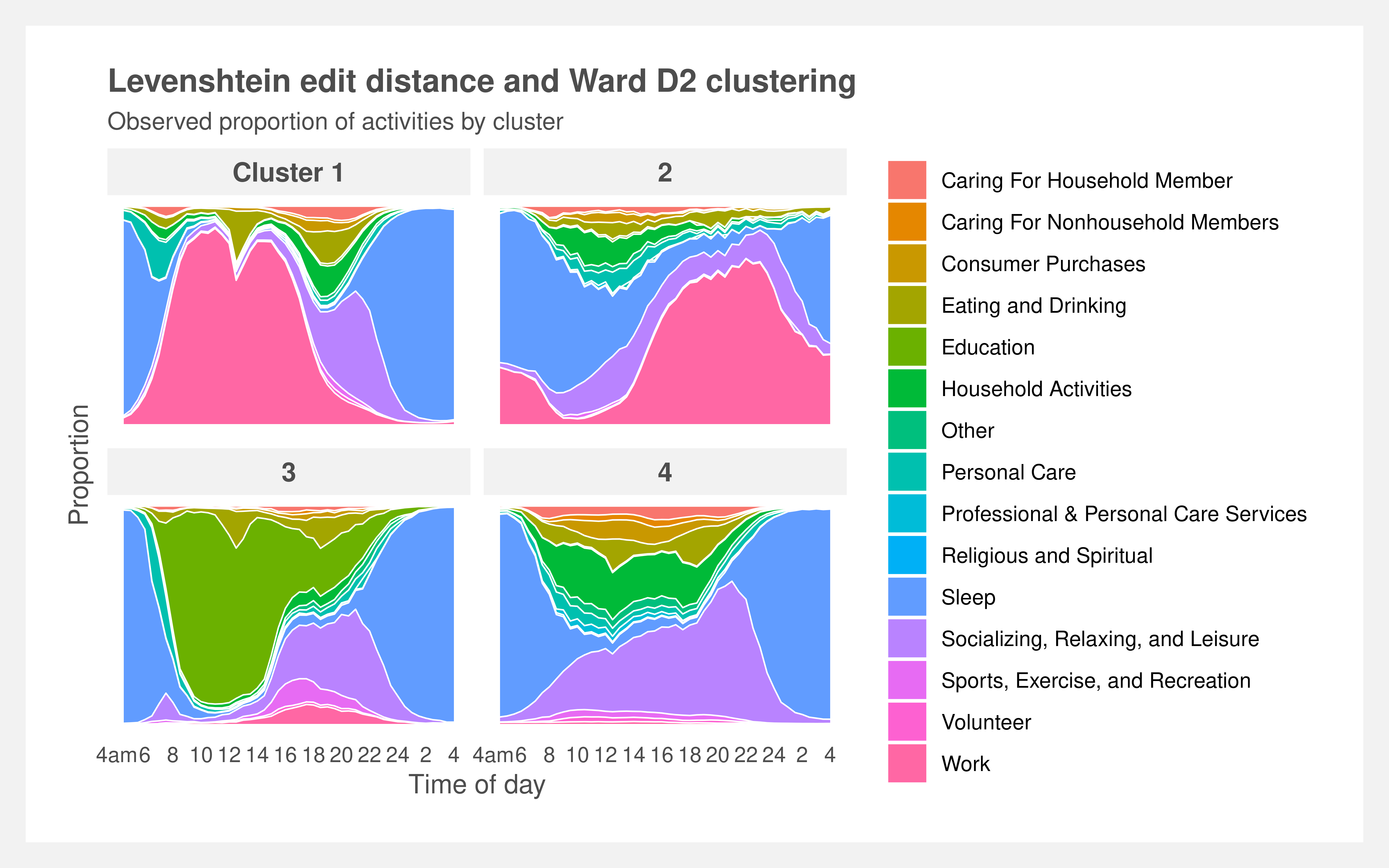
Finding differences in time spent alone among subpopulations of Americans. First, by clustering respondents' activities by applying sequence analysis techniques à la Abbot — string-editing techniques, dissimilarity matrices, and hierarchical clustering. Then using cluster membership and year as nested variables in multi-level models to predict time spent alone.
See also: ATUS repo