For Chinese README, please refer to 中文说明.
HiveMQ-TDengine-Extension is a HiveMQ extension that can parse and store messages published to a specific topic in the TDengine time series database.
- Support TDengine 2.0 RESTful API and JDBC API for data storage.
- Support HiveMQ v4 and comply with HiveMQ extension development specifications.
- Support Docker deployment environment.
- The source code is open source under the Apache License.
This article simulates the environment data collection scenario of the Internet of Things. It is assumed that there are environmental data collection points for certain data. All collected point data are transmitted to the collection platform (MQTT Publish) through the MQTT protocol. The theme is designed as follows:
application/sensor_data
The data format sent by the sensor is JSON, and the data includes data such as timestamp, temperature, voltage, name, and device ID.
{
"ts": 1519833600000,
"temperature": 32.1,
"voltage": 321,
"name": "d02",
"devid": 2
}Now it needs real-time storage to view the data at any subsequent time, and put forward the requirement: each device reports data at a frequency of once every 5 seconds, and the database needs to store each piece of data for subsequent retrospective analysis.
The test environment used in this article can be built using Docker. Docker needs to be installed and deployed first. For Docker installation, please refer to: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/.
Resources and tutorial reference:
-
HiveMQ CE Community Edition: https://www.hivemq.com/
-
TDengine: https://www.taosdata.com/cn/
-
JDK11: https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/javase-jdk11-downloads.html
-
Maven: http://maven.apache.org/
Here is how to build a local docker image and run the steps:
git clone http://github.com/john-bigz/hivemq-tdengine-extension
Compiling HiveMQ-TDengine-Extension requires JDK11 and Maven3.6.x, please install it yourself. Use the following compilation and packaging to get tdengine-extension-1.0.0-distribution.zip
mvn clean package
After successful compilation, you will get the package file: target/tdengine-extension-1.0.0-distribution.zip. In the terminal window, go to the target subdirectory under the directory where the tdengine-extension code is located, and unzip tdengine-extension-1.0.0-distribution.zip:
unzip tdengine-extension-1.0.0-distribution.zip
Since you are going to redeploy TDengine to the local container, you need to download the TDengine installation package to the directory where the hivemq-tdengine-extension code is located:
wget -O ./TDengine-server-2.x-latest-Linux-x64.tar.gz https://www.taosdata.com/download/download-gettingStarted.php\?pkg\=tdengine_tar
Build the docker image with the following command:
docker build -t taosdata-hivemq-extension.
Deploy and run in a docker container, and map the service port in the container to the outside:
docker run --name hivemq-ce -d -p 1883:1883 -v /etc/taos:/etc/taos -p 6030:6030 -p 6035:6035 -p 6041:6041 -p 6030-6040:6030-6040 /udp taosdata-hivemq-extension
Check whether the container instance started successfully:
$ docker ps -a
- The test needs to use the MQTT publish/subscribe tool, the following is the command to install mosquitto-clients under ubuntu:
sudo apt install mosquitto-clients
- Publish a test message to the MQTT service, the subject is application/sensor_data, and the content is a string in JSON format:
mosquitto_pub -h 127.0.0.1 -p 1883 -t'application/sensor_data' -m'{"ts": 1519833600000, "temperature": 32.1, "voltage": 321, "name": "d02", "devid": 2}'
- Check whether the test message has been stored in the database table through TDengine's RESTful Connector interface, where the Basic authentication string "cm9vdDp0YW9zZGF0YQ==" is the Base64 encoding of "root:taosdata", see TDengine RESTful Connector:
curl -H'Authorization: Basic cm9vdDp0YW9zZGF0YQ==' -d'select * from hivemqdb.sensor_data' 127.0.0.1:6041/rest/sql
{"status":"succ","head":["ts","temperature","voltage","name","devid"],"data":[["2018-03-01 00:00 :00.000",32.10000,321,"d02",2]],"rows":1}%
If you can find a data record similar to the above from the data table hivqmedb.sensor_data, it means that the service test has passed.
Automatic testing according to HiveMQ extension. See: https://www.hivemq.com/docs/hivemq/4.3/extensions/testing-extension.html for details, Here are the basic test steps:
- Import HiveMQ-TDengine-Extension into Ideal or Eclipse.
- Use Junit5 to execute
TDengineInterceptorITfor automated unit testing. - The unit test uses {hivemq-testcontainer}[HiveMQ Testcontainer] to automatically package, deploy and run HiveMQ-TDengine-Extension in a HiveMQ docker container.
- The unit test will create a {hivemq-mqtt-client}[HiveMQ MQTT Client], publish a test message to the topic application/sensor_data, and then use the RESTful interface to retrieve the newly written record and verify that the record is correct.
Directory: HiveMQ/extension/tdengine-extension/
# Mode selection: jdbc or http
mode=jdbc
# msg_coder: base64 or json
msg_coder=json
# mqtt_topic: only available when msg_coder is json
mqtt_topic=application/sensor_data
# Create TDEngine database SQL statement
sql.create_database=create database if not exists hivemqdb;
# Create TDEngine data table SQL statement
sql.create_table=create table if not exists hivemqdb.sensor_data (ts timestamp, temperature float, voltage int, name binary(32)) TAGS (devid int);
# Insert TDEngine data table SQL statement
sql.insert_table=insert into hivemqdb.sensor_data_${payload.devid} using hivemqdb.sensor_data TAGS (${payload.devid}) VALUES (${payload.ts}, ${payload.temperature}, ${payload.voltage} ,'${payload.name}');
# JDBC related configuration parameters
jdbc.driverClass=com.taosdata.jdbc.TSDBDriver
jdbc.url=jdbc:TAOS://127.0.0.1:6030/log
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=taosdata
jdbc.pool.init=1
jdbc.pool.minIdle=3
jdbc.pool.maxActive=20
jdbc.testSql=select server_status();
# HTTP related configuration parameters
http.url=http://127.0.0.1:6041/rest/sql/
http.token=root:taosdata
HiveMQ-TDengine-Extension supports two data storage modes: JDBC and HTTP. The JDBC mode calls the native JDBC interface provided by TDengine to write data into the database table, and the HTTP mode calls TDengine's RESTful Connector interface.
When HiveMQ CE starts to load tdengine-extension, tdengine-extension will automatically perform TDengine database table initialization operations: execute new database SQL and new data table SQL respectively.
| Parameter name | Parameter description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| sql.create_database | Create database SQL statement | create database if not exists hivemqdb; |
| sql.create_table | Create data table SQL statement | create table if not exists hivemqdb.sensor_data (ts timestamp, temperature float, voltage int, name binary(32)) TAGS (devid int); |
| sql.insert_table | Insert SQL statement | insert into hivemqdb.sensor_data_${payload.devid} using hivemqdb.sensor_data TAGS (${payload.devid}) VALUES (${payload.ts}, ${payload.temperature}, ${payload.voltage}, '${payload.name}'); |
When mode=jdbc, JDBC mode is enabled. In JDBC mode, when HiveMQ CE starts to automatically load tdengine-extension, it first establishes a jdbc connection pool (depending on Druid), so you need to configure the following jdbc Related parameters:
| Parameter name | Parameter description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| jdbc.driverClass | TDengine's JDBC driver | com.taosdata.jdbc.TSDBDriver |
| jdbc.url | JDBC URL | jdbc:TAOS://127.0.0.1:6030/log |
| jdbc.username | JDBC username | root |
| jdbc.password | JDBC password | taosdata |
| jdbc.pool.init | Initial number of JDBC connection pool connections | 1 |
| jdbc.pool.minIdle | Minimum number of JDBC connection pool connections | 1 |
| jdbc.pool.maxActive | Maximum number of JDBC connection pool connections | 20 |
| jdbc.testSql | JDBC connection pool keeps testing SQL | select server_status(); |
When mode=http, enable HTTP mode. In HTTP mode, tdengine-extension calls httpclient to send RESTful requests to TDEngine, and the following http related parameters need to be configured:
| Parameter name | Parameter description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| http.url | TDengine RESTful interface URL | http://127.0.0.1:6041/rest/sql/ |
| http.token | TDengine RESTful interface authentication information | root:taosdata |
For TDengine RESTful interface certification information, please refer to the TDengine website RESTful-Connector .
The following script simulates a scenario where 10,000 devices reported a piece of simulated data every 5 seconds and sent it to HiveMQ in the past 24 hours.
-
Total data volume: 24 * 3600/5 * 10000 = 172 million
-
News TPS: 2000
After installing Node.js and modifying the configuration parameters as needed, you can start it with the following command:
1 npm install mqtt mockjs --save --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
2 node mock.js
Attachment: The simulated data is generated and sent to the HiveMQ code, please adjust the relevant parameters according to the actual test environment
// mock.js
const mqtt = require('mqtt')
const Mock = require('mockjs')
const EMQX_SERVER ='mqtt://localhost:1883'
const CLIENT_NUM = 10000
const STEP = 5000 // Analog acquisition time interval ms
const AWAIT = 5000 // Sleep time after each transmission to prevent the message rate from being too fast ms
const CLIENT_POOL = []
const BEGIN_TIMESTAMP = 1519833600000;
startMock()
function sleep(timer = 100) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve, timer)
})
}
async function startMock() {
const now = Date.now()
for (let i = 0; i <CLIENT_NUM; i++) {
const client = await createClient(`mock_client_${i}`)
CLIENT_POOL.push(client)
}
let count = 0
// last 24h every 5s
const last = 24 * 3600 * 1000
for (let n = now-last; n <= now; n += STEP) {
for (const client of CLIENT_POOL) {
ts = BEGIN_TIMESTAMP + count
const mockData = generateMockData()
const data = {
...mockData,
id: client.clientId,
name:'D01',
ts,
}
client.publish('application/sensor_data', JSON.stringify(data))
count++
}
const dateStr = new Date(n).toLocaleTimeString()
console.log(`${dateStr} send success.`)
await sleep(AWAIT)
}
console.log(`Done, use ${(Date.now()-now) / 1000}s, published ${count}`)
}
/**
* Init a virtual mqtt client
* @param {string} clientId ClientID
*/
function createClient(clientId) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const client = mqtt.connect(EMQX_SERVER, {
clientId,
})
client.on('connect', () => {
console.log(`client ${clientId} connected`)
resolve(client)
})
client.on('reconnect', () => {
console.log('reconnect')
})
client.on('error', (e) => {
console.error(e)
reject(e)
})
})
}
/**
* Generate mock data
*/
function generateMockData() {
return {
"temperature": parseFloat(Mock.Random.float(22, 100).toFixed(2)),
"voltage": parseFloat(Mock.Random.float(12, 86).toFixed(2)),
"devid": Mock.Random.integer(0, 20),
}
}The following is the result of querying TDengine after the simulation data test is completed:
taos> select count(*) from sensor_data;
count(*) |
========================
172810020 |
Query OK, 1 row(s) in set (0.521210s)
The following problems may be encountered in the process of running mock.js to simulate a large amount of data. The corresponding solutions are provided below.
By default, the Linux system limits the number of open files. If the "Too many open files" error occurs when the above simulation scenario test is enabled, the relevant configuration parameters need to be modified (take Ubuntu 18.04 as an example):
- Modify the following lines in /etc/security/limits.conf:
* soft nofile 65535
* hard nofile 65535
- Modify the configuration items in /etc/systemd/user.conf and /etc/systemd/system.conf as the following line:
DefaultLimitNOFILE=65535
- After the files in these three places are changed, the system must be restarted to take effect.
ERROR-failed in onInboundPublish
java.sql.SQLException: TDengine Error: Invalid table ID
at com.taosdata.jdbc.TSDBJNIConnector.executeQuery(TSDBJNIConnector.java:131)
at com.taosdata.jdbc.TSDBStatement.execute(TSDBStatement.java:153)
at com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidPooledStatement.execute(DruidPooledStatement.java:633)
at com.hivemq.extensions.tdengine.TDenginePublishInterceptor.lambda$onInboundPublish$0(TDenginePublishInterceptor.java:107)
at com.hivemq.extensions.services.executor.WrappedRunnable.run(WrappedRunnable.java:55)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter.call(Executors.java:515)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:264)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor$ScheduledFutureTask.run(ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.java:304)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1128)
at java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:628)
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:834)
If an error similar to the above occurs during the test, you need to create the corresponding table before running the test, for example:
# create super table
create table if not exists hivemqdb.sensor_data (ts timestamp, temperature float, voltage int, name binary(32)) TAGS (devid int);
# create normal tables
create table if not exists sensor_data_0 using sensor_data tags(0);
create table if not exists sensor_data_1 using sensor_data tags(1);
create table if not exists sensor_data_2 using sensor_data tags(2);
create table if not exists sensor_data_3 using sensor_data tags(3);
create table if not exists sensor_data_4 using sensor_data tags(4);
create table if not exists sensor_data_5 using sensor_data tags(5);
create table if not exists sensor_data_6 using sensor_data tags(6);
create table if not exists sensor_data_7 using sensor_data tags(7);
create table if not exists sensor_data_8 using sensor_data tags(8);
create table if not exists sensor_data_9 using sensor_data tags(9);
create table if not exists sensor_data_10 using sensor_data tags(10);
create table if not exists sensor_data_11 using sensor_data tags(11);
create table if not exists sensor_data_12 using sensor_data tags(12);
create table if not exists sensor_data_13 using sensor_data tags(13);
create table if not exists sensor_data_14 using sensor_data tags(14);
create table if not exists sensor_data_15 using sensor_data tags(15);
create table if not exists sensor_data_16 using sensor_data tags(16);
create table if not exists sensor_data_17 using sensor_data tags(17);
create table if not exists sensor_data_18 using sensor_data tags(18);
create table if not exists sensor_data_19 using sensor_data tags(19);
create table if not exists sensor_data_20 using sensor_data tags(20);
For detailed TDengine SQL syntax description, please refer to TDengine website: data modeling.
Use mqttloader to test, save the published subject and content in the TDengine table, where the message content is encoded in Base64.
# mode: jdbc or http
mode=jdbc
# msg_coder: base64 or json
msg_coder=base64
# mqtt_topic: only available when msg_coder is json
mqtt_topic=application/sensor_data
sql.create_database=create database if not exists hivemqdb;
sql.create_table=create table if not exists hivemqdb.sensor_data (ts timestamp, topic nchar(1024), payload nchar(1024) );
sql.insert_table=insert into hivemqdb.sensor_data VALUES (now, '${topic}', '${payload}');
#JDBC settings
jdbc.driverClass=com.taosdata.jdbc.TSDBDriver
jdbc.url=jdbc:TAOS://127.0.0.1:6030/log
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=taosdata
jdbc.pool.init=1
jdbc.pool.minIdle=3
jdbc.pool.maxActive=20
jdbc.testSql=select server_status();
#HTTP settings
http.url=http://127.0.0.1:6041/rest/sql/
http.token=root:taosdata
$ bin/mqttloader -b tcp://127.0.0.1:1883 -p 10 -s 10 -m 1000 -t application/sensor_data
-----Publisher-----
Maximum throughput[msg/s]: 9478
Average throughput[msg/s]: 5000.00
Number of published messages: 10000
Per second throughput[msg/s]: 9478, 522
-----Subscriber-----
Maximum throughput[msg/s]: 42517
Average throughput[msg/s]: 12500.00
Number of received messages: 100000
Per second throughput[msg/s]: 694, 1247, 879, 1305, 12229, 30946, 42517, 10183
Maximum latency[ms]: 6806
Average latency[ms]: 5367.31
The code structure of HiveMQ-TDengine-Extension is relatively simple. The application business processing code is included in the src/main directory, which is mainly divided into three parts:
| Module name | Module description |
|---|---|
| TDengineConfiguration.java | Read the configuration file taosdata.properties and check its validity. |
| TDengineExtensionMain.java | Initialize and install the HiveMQ message interceptor. |
| TDenginePulishInterceptor.java | Intercept MQTT messages and transfer the message content to TDengine. |
In addition, the unit test code is included in the src/test directory, which is mainly divided into two parts:
| Module name | Module description |
|---|---|
| TDengineExtensionMainTest.java | Contains unit tests for TDengineExtensionMain. |
| TDengineInterceptoIT.java | Contains unit tests for TDenginePulishInterceptor and meets HiveMQ's extension test requirements. |
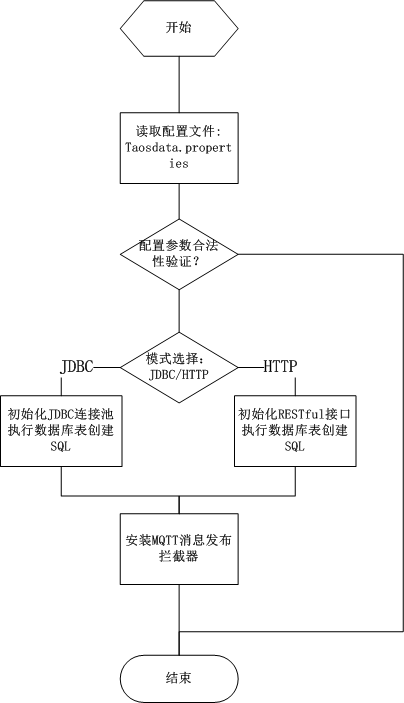
TDengineExtensionMain.java
-
- Initialize extension, read the configuration file taosdata.properties.
-
- If the jdbc mode is configured, initialize the JDBC connection pool (Druid), and use the JDBC API to execute the configured new database table SQL statement.
-
- If the http mode is configured, initialize the HTTP connection pool (HttpClient), and use the RESTful API to execute the configured new database table SQL statement.
-
- Install the MQTT publish interception filter, and the initialization process is complete.
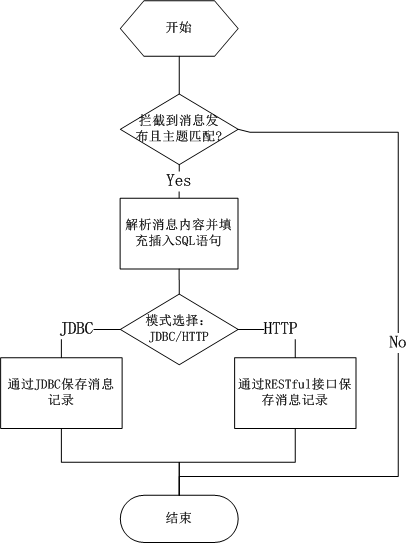
TDenginePulishInterceptor.java
-
- Intercept an MQTT Publish, check topic and payload.
-
- If the check is passed, the payload will be parsed in JSON format to get the inserted SQL statement.
-
- If jdbc mode is configured, call JDBC API to execute SQL insert record.
-
- If http mode is configured, call RESTful API to execute SQL insert record.
.