Red Hat Dependency Analytics (RHDA) plugin gives you awareness to security concerns within your software supply chain while you build your application.
NOTE:
The Red Hat Dependency Analytics plugin is an online service hosted and maintained by Red Hat.
Dependency Analytics only accesses your manifest files to analyze your application dependencies before displaying the
vulnerability report.
IMPORTANT:
Currently, Dependency Analytics only supports projects that use Maven (mvn), Node (npm), Golang (go mod),
Python (pip) and Gradle (gradle) ecosystems, and base images in Dockerfile.
In future releases, Red Hat plans to support other programming languages.
Prerequisites
- For Maven projects, analyzing a
pom.xmlfile, you must have themvnbinary in your IDE'sPATHenvironment. - For Node projects, analyzing a
package.jsonfile, you must have thenpmandnodebinaries in your IDE'sPATHenvironment. - For Golang projects, analyzing a
go.modfile, you must have thegobinary in your IDE'sPATHenvironment. - For Python projects, analyzing a
requirements.txtfile, you must have thepython3andpip3binaries in your IDE'sPATHenvironment. - For base images, analyzing a
Dockerfile, you must have thesyftandskopeobinaries in your IDE'sPATHenvironment.
Procedure
- Install IntelliJ IDEA on your workstation.
- After the installation finishes, open the IntelliJ IDEA application.
- From the menu, click Settings , and click Plugins.
- Search the Marketplace for Red Hat Dependency Analytics.
- Click the INSTALL button to install the plugin.
- To start scanning your application for security vulnerabilities, and view the vulnerability report, you can do one of
the following:
- Open a manifest file, hover over a dependency marked by the inline Component Analysis, indicated by the wavy-red line under a dependency, and click Detailed Vulnerability Report.
- Right click on a manifest file in the Project window, and click Dependency Analytics Report.
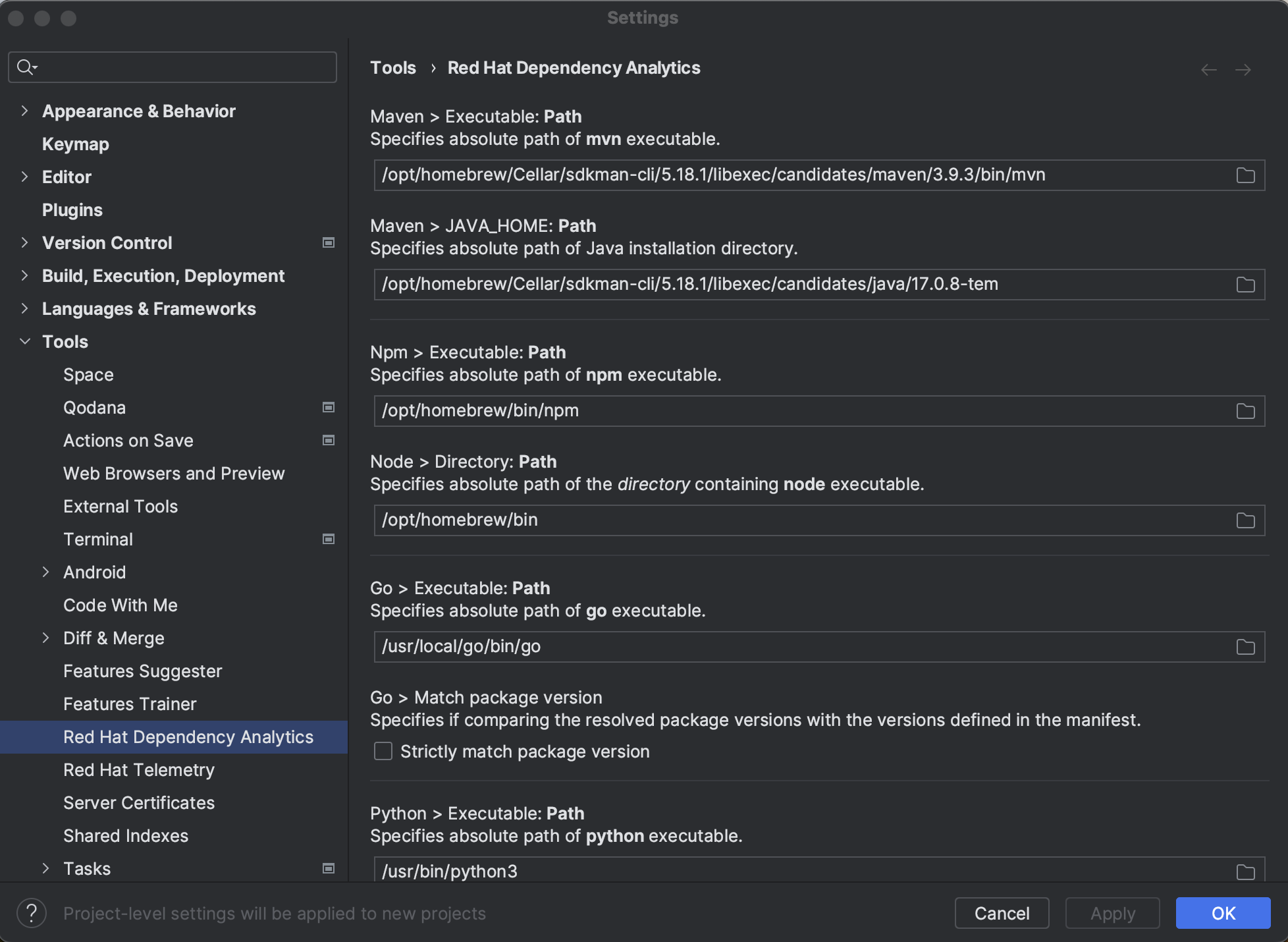
The Red Hat Dependency Analytics plugin has some configurable parameters that allows you to customize its behavior according to your preferences.
Procedure
-
Open the IntelliJ IDEA application.
-
From the menu, click Settings , and click Tools.
-
Click Red Hat Dependency Analytics.
Configurable parameters
-
Maven :
Set the full path of the Maven executable, which allows Exhort to locate and execute themvncommand to resolve dependencies for Maven projects.
Path of theJAVA_HOMEdirectory is required by themvnexecutable.
If the paths are not provided, your IDE'sPATHandJAVA_HONEenvironments will be used to locate the executables. -
Node :
Set the full path of the Node executable, which allows Exhort to locate and execute thenpmcommand to resolve dependencies for Node projects.
Path of the directory containing thenodeexecutable is required by thenpmexecutable.
If the paths are not provided, your IDE'sPATHenvironment will be used to locate the executables. -
Golang :
Set the full path of the Go executable, which allows Exhort to locate and execute thegocommand to resolve dependencies for Go projects.
If the path is not provided, your IDE'sPATHenvironment will be used to locate the executable.
When optionStrictly match package versionis selected, the resolved dependency versions will be compared to the versions specified in the manifest file, and users will be alerted if any mismatch is detected. -
Python :
Set the full paths of the Python and the package installer for Python executables, which allows Exhort to locate and execute thepip3commands to resolve dependencies for Python projects.
Python 2 executablespythonandpipcan be used instead, if theUse python 2.xoption is selected.
If the paths are not provided, your IDE'sPATHenvironment will be used to locate the executables.
When optionStrictly match package versionis selected, the resolved dependency versions will be compared to the versions specified in the manifest file, and users will be alerted if any mismatch is detected.
Python virtual environment can be applied, when selecting theUse python virtual environmentoption.
If selecting optionAllow alternate package versionwhile using virtual environment, the dependency versions specified in the manifest file will be ignored, and dependency versions will be resolved dynamically instead (this feature cannot be enabled whenStrictly match package versionis selected). -
Gradle :
Set the full path of the Gradle executable, which allows Exhort to locate and execute thegradlecommand to resolve dependencies for Gradle projects.
By not setting a path to the gradle binary, IntelliJ IDEA uses its default path environment to locate the file. -
Image :
Set the full path of the Syft executable, which allows Exhort to locate and execute thesyftcommand to generate Software Bill of Materials for the base images.
Optionally, set the full path of the Docker or Podman executable. Syft will attempt to find the images in the Docker or Podman daemon with the executable. Otherwise, Syft will try direct remote registry access.
Set the full path of the Skopeo executable, which allows Exhort to locate and execute theskopeocommand to determine the image digests.
If the paths are not provided, your IDE'sPATHenvironment will be used to locate the executables.
If a Syft configuration file is used and not at the default paths, set the full path to the configuration file in configuration.
If an authentication file is applied forskopeo inspect, set the full path to the file in configuration.
If platform is not specified in theDockerfilefor multi-platform images and a default platform should be applied, set the default platform in the configuration. Otherwise, set the full path of the Docker or Podman executable, then Exhort will use the executable to determine the image platform based on the OS and architecture of the container runtime. -
Inline Vulnerability Severity Alerts :
You can set the vulnerability severity alert level toErrororWarningfor inline notifications of detected vulnerabilities.
-
Component analysis
Upon opening a manifest file, such as apom.xml,package.json,go.modorrequirements.txtfile, a scan starts the analysis process. The scan provides immediate inline feedback on detected security vulnerabilities for your application's dependencies. Such dependencies are appropriately underlined in red, and hovering over it gives you a short summary of the security concern. The summary has the full package name, version number, the amount of known security vulnerabilities, and the highest severity status of said vulnerabilities. -
Dockerfile scanning
Upon opening a Dockerfile, a vulnerability scan starts analyzing the images within the Dockerfile. After the analysis finishes, you can view any recommendations and remediation by clicking the More actions... menu from the highlighted image name. Any recommendations for an alternative image does not replace the current image. By clicking Switch to..., you go to Red Hat's Ecosystem Catalog for the recommended image.
You must have thesyftandskopeobinaries installed on your workstation to use the Dockerfile scanning feature. You can specify a specific path to these binaries, and others by settings the following parameters as environment variables or system properties:EXHORT_SYFT_PATH: Specify the absolute path ofsyftexecutable.EXHORT_SYFT_CONFIG_PATH: Specify the absolute path to the Syft configuration file.EXHORT_SKOPEO_PATH: Specify the absolute path ofskopeoexecutable.EXHORT_SKOPEO_CONFIG_PATH: Specify the absolute path to the authentication file used by theskopeo inspectcommand.EXHORT_DOCKER_PATH: Specify the absolute path ofdockerexecutable.EXHORT_PODMAN_PATH: Specify the absolute path ofpodmanexecutable.EXHORT_IMAGE_PLATFORM: Specify the platform used for multi-arch images.
-
Excluding dependencies with
exhortignore
You can exclude a package from analysis by marking the package for exclusion. If you want to ignore vulnerabilities for a dependency in apom.xmlfile, you must addexhortignoreas a comment against the dependency, group id, artifact id, or version scopes of that particular dependency in the manifest file. For example:<dependency> <!--exhortignore--> <groupId>...</groupId> <artifactId>...</artifactId> <version>...</version> </dependency>
If you want to ignore vulnerabilities for a dependency in a
package.jsonfile, you must addexhortignoreas a attribute-value pair. For example:{ "name": "sample", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "", "main": "index.js", "keywords": [], "author": "", "license": "ISC", "dependencies": { "dotenv": "^8.2.0", "express": "^4.17.1", "jsonwebtoken": "^8.5.1", "mongoose": "^5.9.18" }, "exhortignore": [ "jsonwebtoken" ] }If you want to ignore vulnerabilities for a dependency in a
go.modfile, you must addexhortignoreas a comment against the dependency in the manifest file. For example:require ( golang.org/x/sys v1.6.7 // exhortignore )If you want to ignore vulnerabilities for a dependency in a
requirements.txtfile, you must addexhortignoreas a comment against the dependency in the manifest file. For example:requests==2.28.1 # exhortignoreIf you want to ignore vulnerabilities for a dependency in a
build.gradlefile, you must addexhortignoreas a comment against the dependency in the manifest file. For example:implementation "log4j:log4j:1.2.17" // exhortignore implementation group: 'log4j', name: 'log4j', version: '1.2.17' // exhortignore -
Excluding developmental or test dependencies
Red Hat Dependency Analytics does not analyze dependencies marked asdevortest, these dependencies are ignored. For example, settingtestin thescopetag within apom.xmlfile:<dependency> <groupId>...</groupId> <artifactId>...</artifactId> <version>...</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
For example, setting
devDependenciesattributte in thepackage.jsonfile:{ "name": "sample", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "", "main": "index.js", "keywords": [], "author": "", "license": "ISC", "dependencies": { "dotenv": "^8.2.0", "express": "^4.17.1", "jsonwebtoken": "^8.5.1", "mongoose": "^5.9.18" }, "devDependencies": { "axios": "^0.19.0" } }For example, setting
excludeattribute in thego.modfile:exclude golang.org/x/sys v1.6.7 exclude ( golang.org/x/sys v1.6.7 )You can create an alternative file to
requirements.txt, for example, arequirements-dev.txtor arequirements-test.txtfile where you can add the development or test dependencies there. -
Red Hat Dependency Analytics report
The Red Hat Dependency Analytics report is a temporary HTML file that exist if the Red Hat Dependency Analytics Report tab remains open. Closing the tab removes the temporary HTML file.
The goal of this project is to significantly enhance a developer's experience by providing helpful vulnerability insights for their applications.
The Red Hat Dependency Analytics plugin for IntellJ IDEA collects anonymous usage data and sends it to
Red Hat servers to help improve our products and services.
Read our privacy statement to learn more.
This plugin respects the settings of the Telemetry by Red Hat plugin, which you can learn more
about here.
The Red Hat Dependency Analytics plugin for IntelliJ IDEA in current version, supports the following IntelliJ IDEA versions:
- 2022.1
- 2022.2
- 2022.3
- 2023.1
- 2023.2
- 2023.3
There are two ways you can contact us:
- You can reach out to us at
rhda-support@redhat.comwith any questions, feedback, and general support. - You can also file a GitHub Issue.
EPL 2.0, See LICENSE for more information.