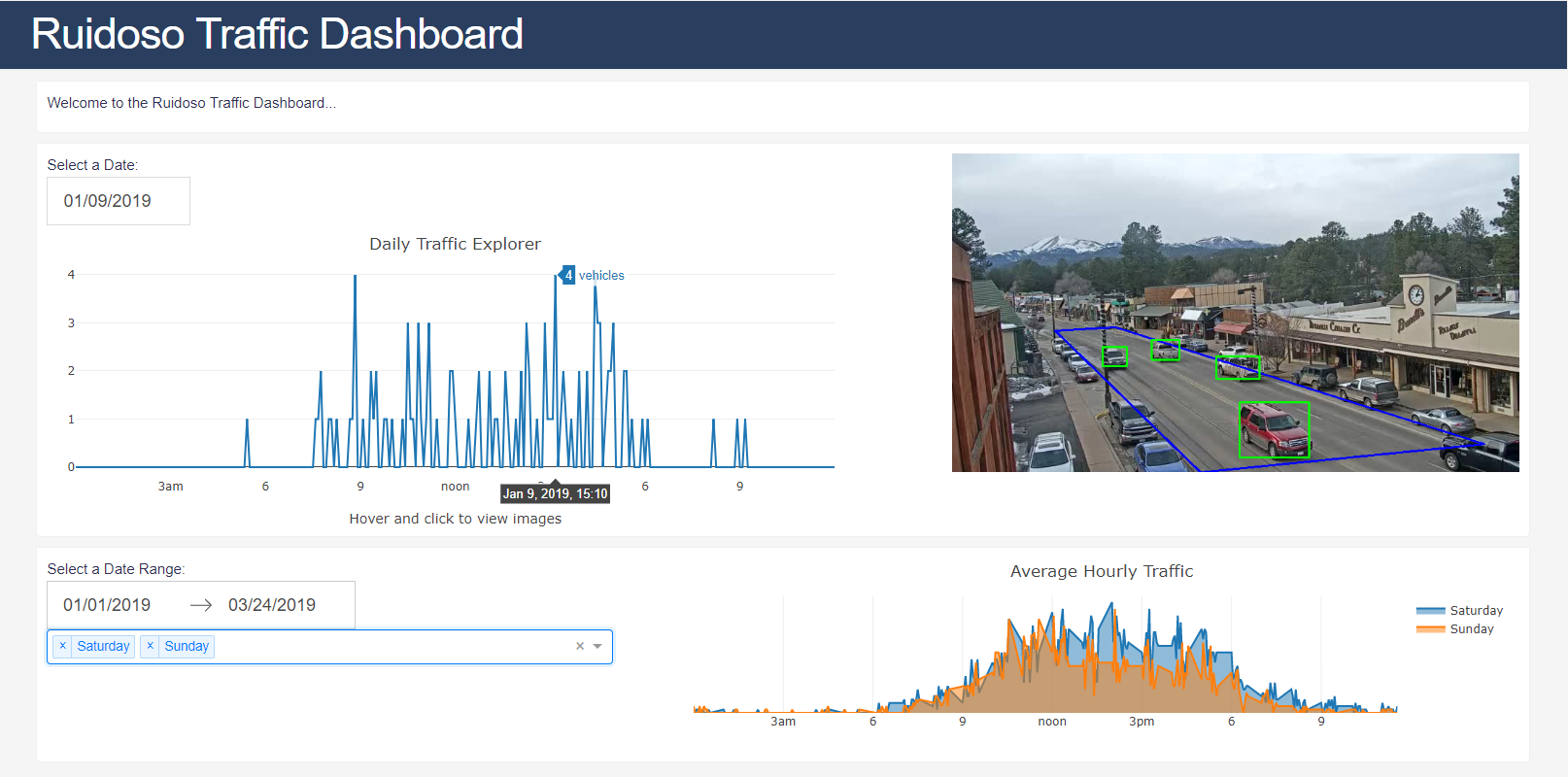
Model training and data acquisition by Laurence Mirabal. Code can be found at https://github.com/lmirabal8689/rgc
Requirements:
- Operating system: Ubuntu 18.04
- User account with sudo privileges
- Python 2 and 3
- Git
Login with a user with sudo privileges and execute the following to install python dependencies:
sudo apt update && sudo apt -y install python python-pip python3 python3-pip
sudo -H pip3 install pipenv --system
The following steps will install Nginx, MariaDB and deploy the code in the app directory.
- In the users home directory, clone this repository and go into the directory.
git clone https://github.com/jonahlyn/dashboard.git
cd dashboard
- Go into the provisioner directory and execute the following to install the provisioner dependencies:
cd provisioner
pipenv install
- Edit the
vars/main.ymlfile and update theserver_namevariable with the fully qualified domain name of the server (or the IP address):
server_name: rgc1
- Create the file
provisioner/vars/.vault_pass.txtand add the vault password to it. (See also "Changing Passwords" in the troubleshooting section below.)
Make sure it has the right permissions.
chmod 600 vars/.vault_pass.txt
- Execute the ansible playbook. When prompted, type in the user's sudo password.
pipenv shell
ansible-playbook provisioner.yml -K
When provisioning is complete, the application will be running on port 80.
Example: http://rgc1
- To allow external connection, open the port on the firewall.
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Start, stop, or check the status of nginx and the gunicorn system services:
sudo systemctl [start|stop|status] nginx
sudo systemctl [start|stop|status] gunicorn
sudo systemctl [start|stop|status] gunicorn.socket
Error messages can also appear here:
sudo journalctl -u gunicorn
Log files are located at:
- access_log:
/var/log/nginx/access.log - error_log:
/var/log/nginx/error.log
Application log files are located in: /var/www/dashapp/logs
A user with sudo privileges can make a connection to the database using the mysql cli. Note: credentials can be found in /root/.my.cnf
- Type
sudo su -and enter the user's password. - Connect to mysql using the cli:
mysql -u root
- Change the vault password in
vars/.vault_pass.txt
For each password in main.yml:
- Execute
ansible-vault encrypt_string. You should prompted with the messageReading plaintext input from stdin. - Enter a new password string followed by
enterand thencontrol+d. - Copy and paste the encrypted string into
provisioner/vars/main.yml.
Note: If you are prompted for the vault password, something is wrong. Please check the following:
- Make sure you are inside the
provisionerdirectory. - Check that the
vars/.vault_pass.txtexists and contains the vault password. - Make sure the
provisionerdirectory and its contents are not world writable. - Make sure the
vars/.vault_pass.txtis not executable.
To install a development environment:
cd app
pipenv install
pipenv shell
Create a configuration file app/config.py with the following contents:
USER = '<username>'
PASSWORD = '<userpassword>'
HOST = 'localhost'
PORT = '3306'
DB = '<databasename>'
DATABASE_URI = 'mysql+mysqlconnector://{}:{}@{}:{}/{}'.format(USER, PASSWORD, HOST, PORT, DB)
To run the dashboard in a temporary development server, run:
APPLICATION_CONFIG=config.py python app.py
Or, run the app manually with gunicorn:
APPLICATION_CONFIG=config.py gunicorn app:server