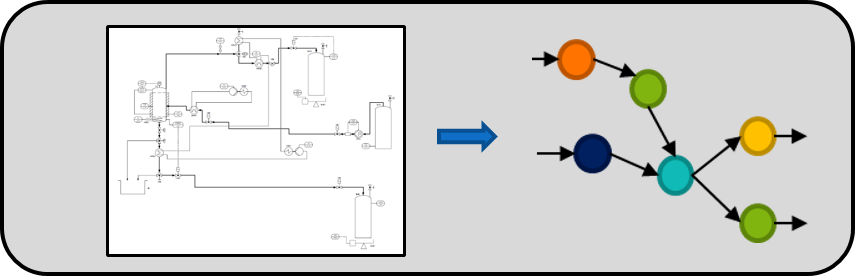
Tool to convert DEXPI-P&ID-Flowsheets into GraphML-graphs, which can be processed in ML/DL-applications via python (e.g. pytorch, keras etc.)
- DEXPI (specification [1]) provides machine-readable plant topology data
- Availability for application in artificial intelligence
- Conversion via a graphical user interface
The skript was tested with P&ID-flowsheets (DEXPI-xml) created with the software PlantEngineer developed by X-Visual Technologies. It is important, that the connection of all MS Visio shapes are correctly connected by the user. Otherwise the tool will not achieve the desired output because of mission topology information of the DEXPI files.
The converter is available as an application well as for Python. A application for Windows 10 will be available soon.
- Install Python (anaconda) from https://www.anaconda.com/products/individual
- Load the following python libraries
- NetworkX (vers. 2.4) [2]
- Matplotlib (vers. 3.2.2) [3]
- Pandas (vers. 1.0.5) [4]
- NLTK (vers. 3.5) [5]
- Pillow (vers. 7.2.0) [6]
- PySimpleGUI (vers. 4.56.0) [7]
- lxml (vers. 4.5.2) [8]
- Download the folder dexpi2graph_python.
- Running the script dexpi2graphML.py starts the converter.
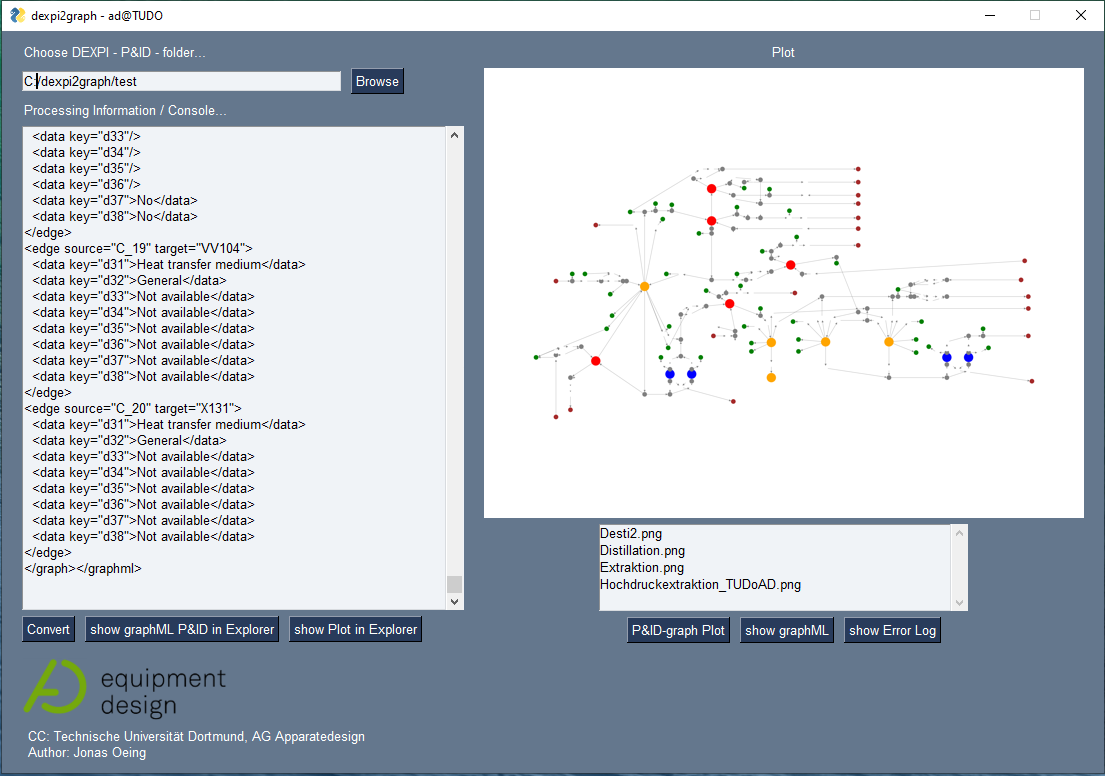
The DEXPI2graphML converter consists a graphical user interface (GUI) shown in Figure 2. On the upper left side you find a bar to browse the input folder, which containts the DEXPI-P&IDs you want to convert. On the left handside a console shows the output as well as the error log of the conversion process. On the left handside you will find a plot window which shows the converted plots.
Figure 2. GUI of the DEXPI2graphML converter.The folder DEXPI_examples containts two different DEXPI P&IDs:
- A laboratory distillation plant P&ID_distillation_laboratory [9]
- Textbooks example distillation plant P&ID_distillation [10]
[1] DEXPI Initiative, DEXPI specification 1.3, https://dexpi.org/specifications/, accessed on 25.08.2021
[2] NetworkX developers, online documentation, https://networkx.org/, accessed on 09.03.2022
[3] Matplotlib development team, online documentation, https://matplotlib.org/, accessed on 09.03.2022
[4] Pandas development team, online documentation, https://pandas.pydata.org/, accessed on 09.03.2022
[5] NLTK project, online documentation, https://www.nltk.org/, accessed on 09.03.2022
[6] Alex Clark and contributors, online documentation, https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/, accessed on 09.03.2022
[7] PySimpleGUI, online documentation, https://pysimplegui.readthedocs.io/en/latest/, accessed on 09.03.2022
[8] lxml development team, online documentation, https://lxml.de/, accessed on 09.03.2022
[9] Oeing, J., Neuendorf, L.M., Bittorf, L., Krieger, W. and Kockmann, N. (2021), Flooding Prevention in Distillation and Extraction Columns with Aid of Machine Learning Approaches. Chem. Ing. Tech., 93: 1917-1929. https://doi.org/10.1002/cite.202100051
[10] Baerns, M., Behr, A., Brehm, A., Gmehling, J., Hinrichsen, K.-O., Hofmann, H., & Onken, U., Palkovits, R., Renken, A. (2013). Technische Chemie. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.