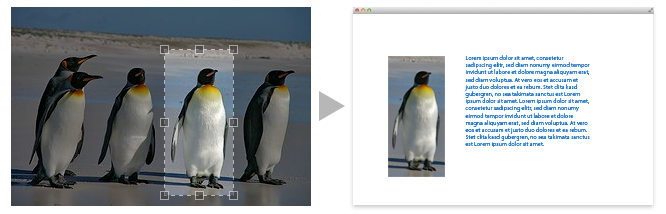
django-image-cropping is an app for cropping uploaded images via Django's admin backend using Jcrop.
Screenshot:
django-image-cropping is perfect when you need images with a specific size for your templates but want your users or editors to upload images of any dimension. It presents a selection with a fixed aspect ratio so your users can't break the layout with oddly-sized images.
The original images are kept intact and only get cropped when they are displayed. Large images are presented in a small format, so even very big images can easily be cropped.
The necessary fields, widgets and a template tag for displaying the cropped image in your templates are provided.
Also works with FeinCMS content types!
Install django-image-cropping using
pip:pip install django-image-cropping
By default django-image-cropping ships with an easy-thumbnails-backend which requires easy-thumbnails to also be installed
and added to the INSTALLED_APPS.
The easy-thumbnails backend requires that you adjust the thumbnail processors in your settings:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'easy_thumbnails',
'image_cropping',
]
from easy_thumbnails.conf import Settings as thumbnail_settings
THUMBNAIL_PROCESSORS = (
'image_cropping.thumbnail_processors.crop_corners',
) + thumbnail_settings.THUMBNAIL_PROCESSORS
Add an ImageRatioField to the model that contains the ImageField for the images you want to crop.
The ImageRatioField simply stores the boundaries of the cropped image.
It expects the name of the associated ImageField and the desired size of the cropped image as arguments.
The size is passed in as a string and defines the aspect ratio of the selection as well as the minimum size for the final image:
from django.db import models
from image_cropping import ImageRatioField
class MyModel(models.Model):
image = models.ImageField(blank=True, upload_to='uploaded_images')
# size is "width x height"
cropping = ImageRatioField('image', '430x360')
You can configure a size warning if users try to crop a selection smaller than the defined minimum.
Add the ImageCroppingMixin to your ModelAdmin:
from django.contrib import admin
from image_cropping import ImageCroppingMixin
class MyModelAdmin(ImageCroppingMixin, admin.ModelAdmin):
pass
admin.site.register(MyModel, MyModelAdmin)
If your setup is correct you should now see the enhanced image widget that provides a selection area.
django-image-cropping delegates the cropped image generation to a backend.
A backend based on easy-thumbnails is provided, but it's possible to use a custom backend.
The IMAGE_CROPPING_BACKEND setting expects a dotted path to a class that implements the required methods.
You can omit this setting if you want to use the default backend.
In case you use a custom backend you can provide an optional dict that will be used to populate the backend's constructor params.
Default settings:
IMAGE_CROPPING_BACKEND = 'image_cropping.backends.easy_thumbs.EasyThumbnailsBackend'
IMAGE_CROPPING_BACKEND_PARAMS = {}
django-image-cropping provides a templatetag for displaying a cropped thumbnail.
Any other processor parameter (like bw=True or upscale=True) will be forwarded to the backend:
{% cropped_thumbnail yourmodelinstance "ratiofieldname" [scale=INT|width=INT|height=INT|max_size="INTxINT"] %}
Example usage:
{% load cropping %}
<img src="{% cropped_thumbnail yourmodel "cropping" scale=0.5 %}">
Or generate the URL from Python code in your view:
from image_cropping.utils import get_backend
thumbnail_url = get_backend().get_thumbnail_url(
yourmodel.image,
{
'size': (430, 360),
'box': yourmodel.cropping,
'crop': True,
'detail': True,
}
)
You can also use the standard easy-thumbnails templatetag with the box parameter:
{% load thumbnail %}
{% thumbnail yourmodel.image 430x360 box=yourmodel.cropping crop detail %}
Or generate the URL from Python code in your view:
from easy_thumbnails.files import get_thumbnailer
thumbnail_url = get_thumbnailer(yourmodel.image).get_thumbnail({
'size': (430, 360),
'box': yourmodel.cropping,
'crop': True,
'detail': True,
}).url
If you want to use the cropping widget outside the admin, you'll need to define the ImageField as
an ImageCropField:
from django.db import models
from image_cropping import ImageCropField, ImageRatioField
class MyModel(models.Model):
image = ImageCropField(blank=True, upload_to='uploaded_images')
# size is "width x height"
cropping = ImageRatioField('image', '430x360')
Alternatively, override the widget in your ModelForm (you just need to do one of these two, not both!):
from django import forms
from image_cropping import ImageCropWidget
class MyModelForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
widgets = {
'image': ImageCropWidget,
}
Remember to include the form media in the <head> of your HTML:
<html>
<head>
{{ form.media }}
</head>
<body>
{{ form }}
</body>
</html>
The cropping itself happens in the ImageRatioField, the ImageCropField will still behave like a regular ImageField.
If you're selectively including or excluding fields from the ModelForm, remember to include the ImageRatioField.
If you need the same image in multiple formats, simply specify another ImageRatioField.
This will allow the image to be cropped twice:
from image_cropping import ImageRatioField, ImageCropField
image = ImageCropField(blank=True, upload_to='uploaded_images')
# size is "width x height"
list_page_cropping = ImageRatioField('image', '200x100')
detail_page_cropping = ImageRatioField('image', '430x360')
In your templates, use the corresponding ratio field:
{% load cropping %}
{% cropped_thumbnail yourmodel "list_page_cropping" %}
If you need to crop an image contained within another model, referenced by a ForeignKey, the ImageRatioField is
composed of the ForeignKey name, a double underscore, and the ImageField name:
from django.db import models
from image_cropping.fields import ImageRatioField
class Image(models.Model):
image_field = models.ImageField(upload_to='image/')
class NewsItem(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=255)
image = models.ForeignKey(Image)
cropping = ImageRatioField('image__image_field', '120x100')
Cropping foreign keys only works in the admin for now, as it reuses the raw_id widget.
If you do not need a fixed ratio, you can disable this constraint by setting free_crop to True.
In this case the size parameter is the desired minimum and is also used for the size-warning:
from image_cropping import ImageRatioField, ImageCropField
image = ImageCropField(blank=True, upload_to='uploaded_images')
# size is "width x height" so a minimum size of 200px x 100px would look like this:
min_free_cropping = ImageRatioField('image', '200x100', free_crop=True)
Use the max_size parameter of the templatetag if you want to limit the display size of a thumbnail:
<img src="{% cropped_thumbnail image "cropping_free" max_size="200x200" %}" />
If you want cropping to be optional, use allow_fullsize=True as an additional keyword argument for your ImageRatioField.
Editors can now switch off cropping by unchecking a checkbox next to the image cropping widget:
image_with_optional_cropping = ImageRatioField('image', '200x100', allow_fullsize=True)
You can define the maximum size of the admin preview thumbnail in your settings:
# size is "width x height" IMAGE_CROPPING_THUMB_SIZE = (300, 300)
You can warn users about crop selections that are smaller than the size defined in the ImageRatioField.
When users try to do a smaller selection, a red border appears around the image.
To use this functionality for a single image add the size_warning parameter to the ImageRatioField:
cropping = ImageRatioField('image', '430x360', size_warning=True)
You can enable this functionality project-wide by adding the following line to your settings:
IMAGE_CROPPING_SIZE_WARNING = True
By default the image cropping widget uses the jQuery version vendored with the Django admin.
You can point to another version using the IMAGE_CROPPING_JQUERY_URL setting, though compatibility
issues may arise if your jQuery version differs from the one that is tested against.
You can also set IMAGE_CROPPING_JQUERY_URL to None to disable inclusion of jQuery by the widget.
You are now responsible for including jQuery yourself, both in the frontend and in the admin interface.
You can define a custom backend:
IMAGE_CROPPING_BACKEND = 'image_cropping.backends.easy_thumbs.EasyThumbnailsBackend'
You can provide an optional dict that will be used to populate the backend's constructor:
IMAGE_CROPPING_BACKEND_PARAMS = {'version_suffix': 'thumb'}
See the built-in backends on Backends.
- Setup a virtualenv with one of the supported versions of Python
- Install the example project:
pip install -r example/requirements.txt - Run
pytest - In case you want to test against multiple Python versions install and run
tox
- The cropping widget is not displayed when using a
ForeignKey. - Make sure you do not add the corresponding image field to
raw_id_fields.
- Use the jQuery bundled with Django as the default jQuery for image cropping
- Add default setting for jquery url to app conf
- Add support for Django 3.2
- Add support for Python 3.9
- Drop support for Python 3.5 (although it should still work)
- Add support for Django 3.1
- Minified JS and reduce potential for incompatibility with other django libraries (See #148)
- Fix formfield_for_dbfield signature (#134)
- Fix CSS property word separator (#131)
- Enforce isort in tests
- Removed more old code
- Move testing and packaging to GitHub Actions
- Add support for Django 3.0
- Drop support for Python < 3.5
- Drop support for Django < 2.2
- Add support for Django 2.1
- Make django-image-cropping compatible with Django 1.11
- Move and encapsulate the logic for creating cropped thumbnails to a swappable backend. (@fgmacedo in #92)
"If your software is being used in production, it should probably already be 1.0.0." (http://semver.org)
This release addresses mainly the test coverage and internal stuff.
Noteable (breaking) changes and things to be considered when upgrading from an older version:
- django-appconf is now used for handling defaults and settings.
- Breaking Change: JQUERY_URL changed to IMAGE_CROPPING_JQUERY_URL as part of this transition.
- The
cropped_thumbnailtag is now based on Django'ssimple tag.- Breaking Change: Arguments for the the tag now need to be put in quotes.
- If you are still using Django 1.4 remember that you can't easily use
TrueorFalseas template tag arguments.
- Any processor parameter (like bw=True or upscale=True) can be used in the
cropped_thumbnailtag. - Moved inline css to a dedicated
image_cropping.cssstyle sheet
- Minimum requirements changed to Django 1.4 and easy-thumbnails 1.4
- Added Python 3 compatibility. Python 2.6 is now the minimum required Python version.
- Added a free cropping option, so cropping is no longer restricted to fixed ratios.
- Removed the deprecated
CropForeignKeyfield.
- Made the widget for the
ImageCropFieldoverwritable to allow custom widgets. (Remember to use theImageCroppingMixinin the admin as the image cropping widgets are no longer implicitly set.) - Updated
JcropandjQuerydependencies. - Moved docs to Read the Docs: https://django-image-cropping.readthedocs.org