Cite: Haghish, E. F. (2019). Seamless interactive language interfacing between R and Stata. The Stata Journal, 19(1), 61-82.
WARNING
rcall 3.0.0 BETA is under development. If you like to help testing the new development, install the development vesion
github install haghish/rcallOtherwise, install the latest stable release
github install haghish/rcall, stablercall : seamless R in Stata
rcall runs R commands in Stata, allowing the two software automatically communicate variables,
matrices, and data. This is done based on a new interfacing paradigm that attempts to synchronize data between two distinct computer languages, particularly when coding is carried out interactively. For more information read the help file or
visit rcall homepage.
rcall simulates the R language inside Stata and returns rclass scalars, macros, and matrices from R to Stata, anytime an R command is executed.
Similarly, it allows passing macro, matrix, scalar, and data frame from Stata to R. As a result, Stata users can open an R window in the middle of a data analysis, execute the R commands, and continue the rest of the analysis with Stata, given the results of the R analysis already made available to Stata in the form of scalar, macro, matrix, or data frame.
rcall makes it so easy to run R within Stata interactively, pass data or a matrix to R,
and access the results (numeric, matrix, character, lists) automatically within Stata which simply brings the power of R as well as all other programming languages that can be used interactively in R (e.g. C++ using Rcpp or JavaScript using V8) in Stata.
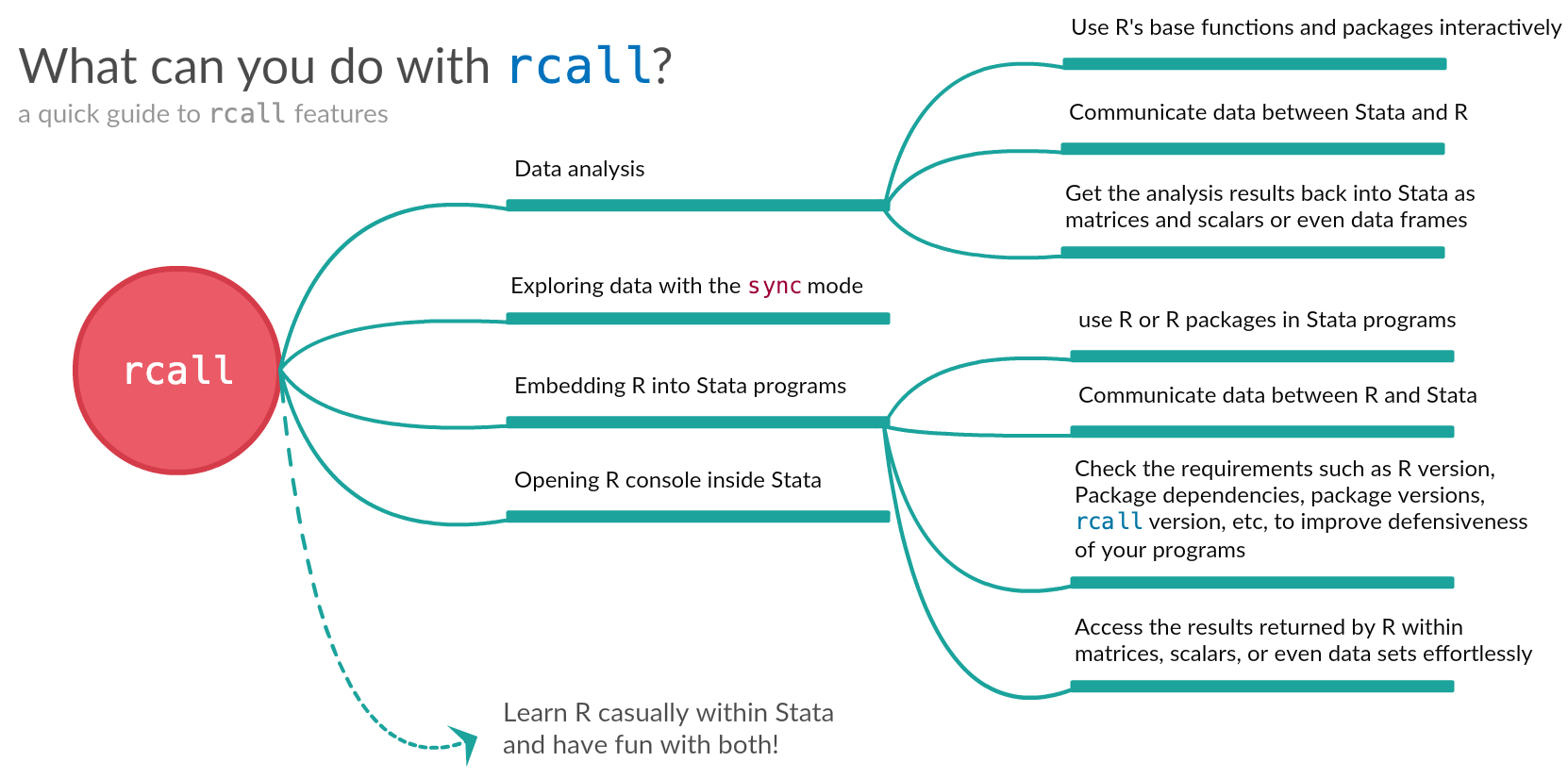
The rcall package is much more than calling R within Stata! It implements a veriety of procedures for quality check and making sure that the R code can proprly gets executed within Stata and it also provides functions to allow Stata programmers evaluate the satisfactory versions of R and R packages in their programs. Moreover, it automatically returns the results of the analysis from R into Stata, in an accessible formats such as matrices, scalars, data sets, etc. Here is a quick and dirty diagram, showing the huge potential of rcall to enhance your Stata:
1. Installation
The github package is the only recommended way for installing rcall. Once github is installed, type:
github install haghish/rcall, stable2. rcall modes of data communication
Language interfacing is done for a veriety of purposes. For example, you may call R within Stata to:
- perform a particular analysis on your data
- develop a Stata program that relies on some functionalities provided in R or its add-on packages
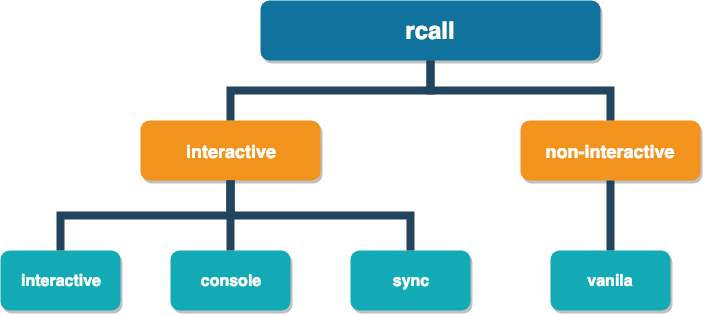
Both require data communication back and forth between Stata and R and this is where rcall stands out. rcall excells in a few modes to facilitates data communication based on your needs. These modes are summarized in the graph below:
In general, it offers 2 modes of data communication which are
-
interactive, often used for data analysis when the user might call R frequently and interactively. This general mode includes a memory that preserves the history of your R session. This mode itself can be used in three ways:
- interactive, where the R session can be continued command by command. this mode allows you call R interactively within Stata do-files
- console, where Stata console is converted to R console. this mode allows you to work with R interactively within Stata, but cannot be called from do-files. However, it provides a much more fun experience, namely to have R console within Stata console!
sync, which is an experimental mode, where all objects (except data frames because they might be heavy) are synced between Stata and R and changing any object in any of the environment (Stata or R) will alter the other one. In other words, when you are using thesyncmode, whatever you do in R will automatically get pushed back into Stata!
-
non-interactive, which is the recommended mode for integrating R into Stata programs. This mode does not have a memory and every call will begin a fresh R session
3. Examples
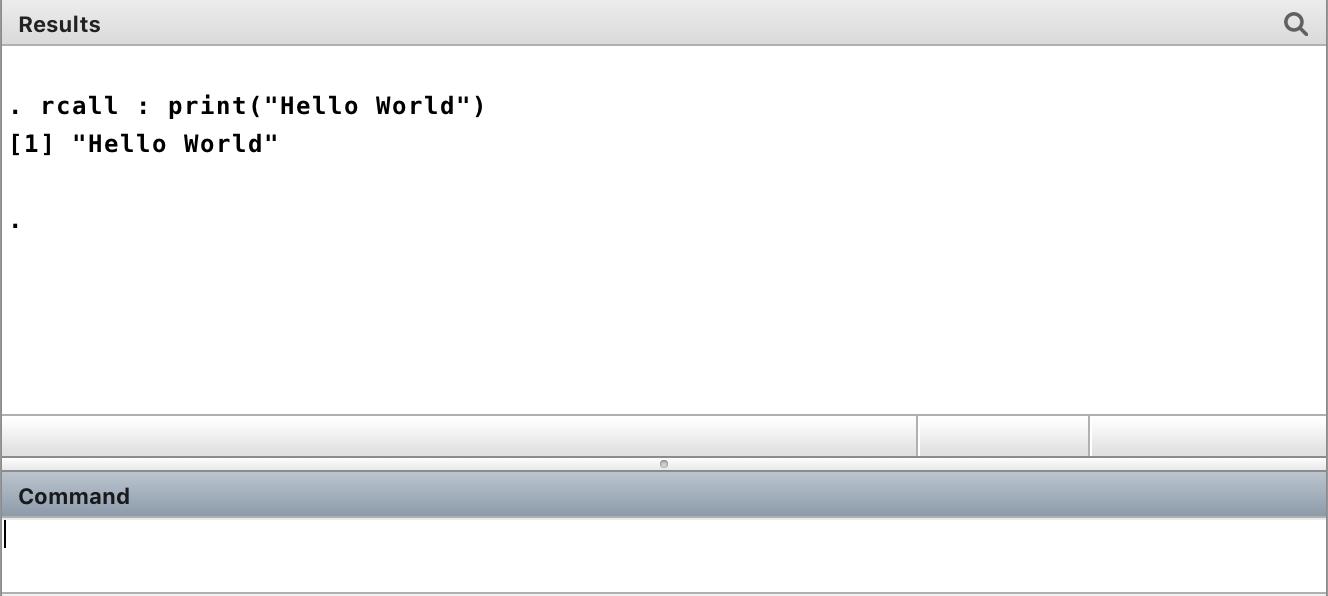
rcall is very powerful, yeat very easy to work with. In the following examples, I simply use R to define a scalar or print a text, just to show you how easy it is to use rcall and to get data back into Stata. But to stand by the traditions, I start with a Hello World example with interactive mode
interactive mode: calling R to print a text
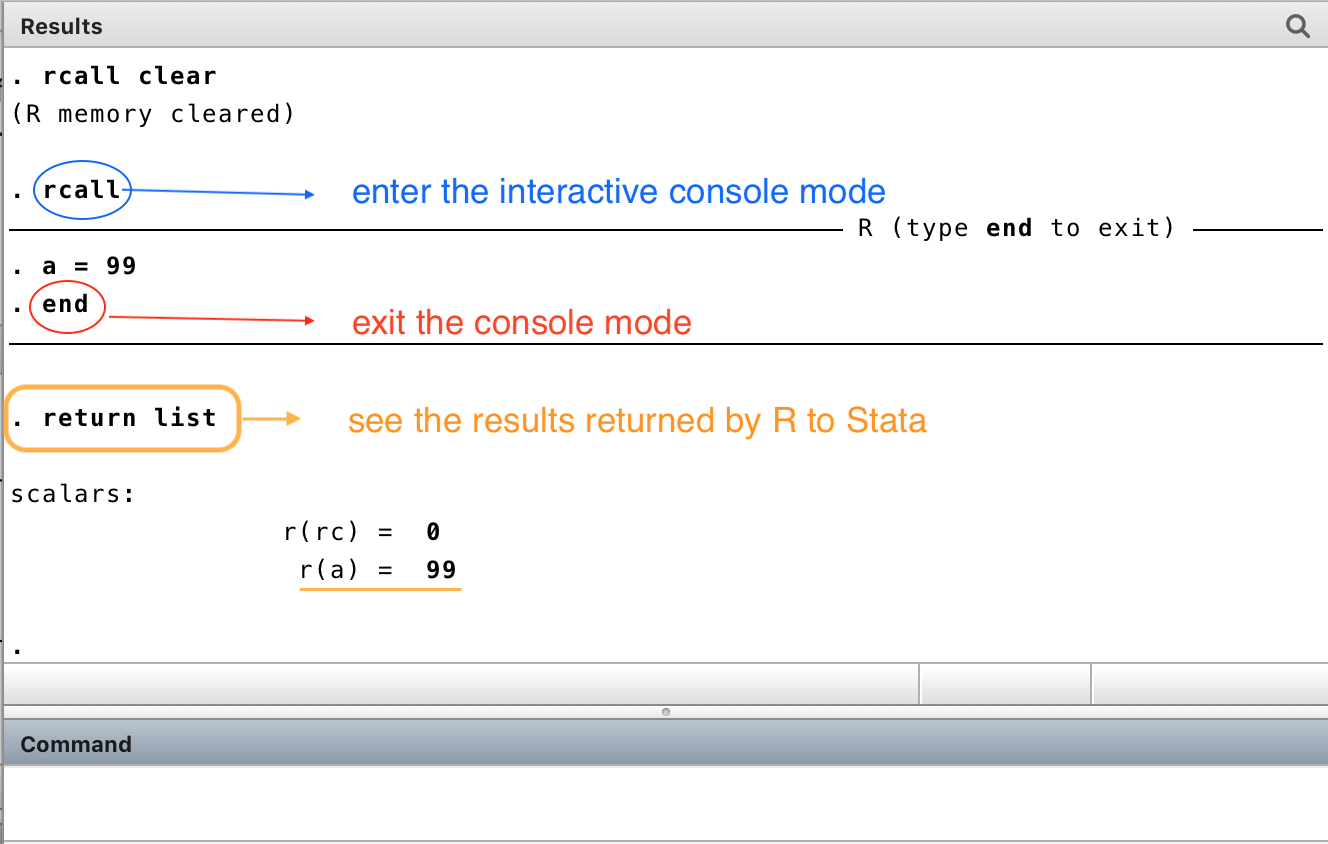
We can also open the R console within Stata to have fun with R without exiting Stata! You notice that working with R interactively in the console mode is even easier than working with MATA within Stata because rcall automatically returns the data from R to Stata.
interactive console mode: defining object a = 99 in R and getting it back in Stata
Type return list to see what objects have ben transfered from R to Stata. This is one of the biggest advantages of rcall, namely, the objects you define in R can be automatically accessed within Stata! Of course, you can control what objects to return (especially if you are programming a Stata ado-program that embeds R). Read the manuscript published by Stata Journal for details.
interactive sync mode: object a is automatically transported into R and you do not need to define it
Resources
 Need help? Ask your questions on statalist.org
Need help? Ask your questions on statalist.org
Author
E. F. Haghish
Center for Medical Biometry and Medical Informatics
University of Freiburg, Germany
haghish@imbi.uni-freiburg.de
http://www.haghish.com/packages/Rcall.php
@Haghish


 Examples
Examples Release notes
Release notes