“Programming should be interactive, as beautiful as possible, modular, and it should generate assets that are easy to use and learn.” – Michael O. Church
Jig is an application harness providing a beautifully interactive development experience for Clojure projects.
Feedback is at the heart of all agile software development processes. If you can reduce the time between making a change and seeing the result, you can proceed faster, with more confidence and accuracy.
For the majority of developers, the impact of changing code cannot be determined until the entire system has been re-built and re-tested. While there are many advantages to frequent and thorough testing, for developers the wait is long enough for us to lose our concentration and focus.
Unless you have experienced a development environment that offers instant feedback upon change it is difficult to describe the impact it can have on your ability to solve difficult problems, produce reliable code quickly and make programming more enjoyable.
Clojure, in the tradition of dynamic languages, comes very close to providing this kind of experience right out-of-the-box. In LISP, functions are bound to vars, which can be rebound, and when functions are applied, the latest binding of the function is used.
In practice, however, there are some minor quirks that impair the
dependability of the code reloading : adding a new library dependency,
redeclaring a defmulti or Clojure protocol, stale state referenced
in defs and defonces are some examples. One of Jig's aims is
to handle these incidentals for you, letting you concentrate more fully
on your programming.
Jig builds upon Stuart Sierra's excellent reloaded workflow pattern. Therefore it's important that you're familiar with the general idea of this pattern: the developer invokes a 'reset' function at various intervals which causes a minimalist reloading of just the code that has changed since the last reset, and anything else that needs reloading as a result (Due to the intricacies of Clojure and the JVM, this is a non-trivial problem that Stuart has solved). Typically, the reset function is bound to a hotkey, Emacs keybinding (I use "C-c r") or something more exotic. The price of entry is that a developer has to ensure all application state is held in a single map (or record) called the system. Otherwise the pattern doesn't work but in practice this is a good architectural policy to establish regardless.
Jig extends Stuart's work by providing some optional extra features that can help in the development of large Clojure systems:
- modularity through componentisation
- configuration
- support for multiple projects
- a growing set of common re-usable infrastructure components.
Stuart describes the System Constructor which creates the initial
state of a system. Jig provides an implementation of the System
Constructor that delegates the job of creating the system to components,
each component having the same lifecycle interface as Stuart describes:
init, start and stop. The System is created by
threading it through all the components.
A reset stops and restarts all components. Components are initialized and started (in dependency order) and stopped (in reverse dependency order) allowing for a clean shutdown of resources.
There are many good reasons for dividing your System into separate components. One is that it gives you looser coupling between your components, which can make it easier to re-use them (among other benefits). Another is that it allows you flexibility and architectural options at deploy time.
For example, you can deploy all your components in a single JVM for a test environment, while in production you could distribute components across multiple JVMs, for scaleability. If you are forced to deploy lots of small JVMs, in all environments, this can be an inefficient use of precious memory. I prefer to run a smaller number of JVMs, each with more memory. Developing Clojure applications as monolithic systems works well to begin with but can reduce flexibility down the road.
I want the option of deploying early versions of new projects quickly, without the hassle of setting up a new server or incurring the cost of a dedicated JVM (200Mb is not an insignificant overhead when you have dozens of Clojure-based web applications). Jig lets me quickly hook up new web applications and services onto an existing Clojure deployment.
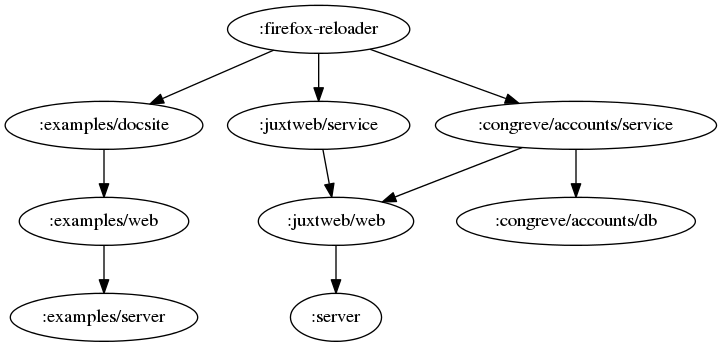
Here's an example of one of my component graphs.
Rather than using a lein template to generate the project and the corresponding dev System, Jig separates these concerns. You can use Jig's workflow to develop on existing projects that don't have a built-in dev workflow.
You can also fork and improve Jig to your own requirements.
One Jig project can be used against many different projects, even simultaneously (see Components)
I wrote Jig because I wanted to create new Clojure projects quickly without having to maintain the development harness for each one. As I make a small improvement to one development harness, I don't want the hassle of going through all my other projects to update them in the same way, but neither do I want dozens of development harnesses that differ from each other. I want one development harness, re-usable 'jig' that I can use against multiple Leiningen-based projects.
Jig lets you specify configuration for your components in a single configuration file. However, components can source their own configuration if desired.
Jig does not have opinions as to how you should build your applications. However, if does provide good support for writing Ring and Pedestal services should you wish to keep using Jig in your deployment. More details can be found below.
Pedestal boasts bidirectional routes, so that URIs can be generated from
route definitions rather than determined some other way. Jig provides a
url-for function in the Pedestal context, and defaults the
app-name and request to make it easy to generate paths that
make sense in the context of the page on which the link is placed.
It can be cost-effective for multiple web applications to share the same
JVM. Jig allows you to host web applications under contextual URI
prefixes. This is a feature made possible by the provision of the
url-for function, since 'portable' web applications can use this
to generate URIs for web links in their content, without resorting to
hard-coding URI paths.
Errors thrown from components that fail during initialization or start-up do not cause the entire system to fail. This reduces the number of times that you have to reboot the JVM. Only components that are successfully initialized are started, and only those that are successfully started are stopped. Any failures are indicated in the REPL, with full details and stack traces written to the log file..
Jig is is not a library and projects don't depend on it. Rather, you clone this repository, configure it to point at an existing (external) project and automatically get Stuart's workflow (plus some optional extras, should you want them).
Stable versions of Jig will be tagged in git, so look for those.
Clone the Jig repository as you would any other Clojure project.
$ git clone https://github.com/juxt/jig
Configure Jig by copying in a config file into the config/config.edn. You can skip this step if you want to see Jig running in its default configuration which includes examples.
If you're using Emacs, load up Jig's project.clj and
M-x nrepl-jack-in
(that's usually bound to 'Control-c, Meta-j')
In the *nrepl* buffer that (eventually) appears, type
user> (go)
Alternatively, on the command line, type
lein repl
and then
user> (go)
Sync the application by calling reset
user> (reset)
Resetting the application will cause namespaces to reload (thanks to
Stuart's work in org.clojure/tools.namespace) such that the
application will be back in sync with the code-base. This is the feature
that makes development fast and interactive, and it's all thanks to
Stuart's hard work.
You should find yourself typing (reset) rather a lot, and soon
even that becomes burdensome. Here's some Emacs code you can paste into
your $HOME/.emacs.d/init.el to provide a shortcut.
(defun nrepl-reset ()
(interactive)
(save-some-buffers)
(set-buffer "*nrepl*")
(goto-char (point-max))
(insert "(user/reset)")
(nrepl-return))
(global-set-key (kbd "C-c r") 'nrepl-reset)After re-evaluating (or restarting Emacs) you'll be able to reset the application using 'Control-c r'.
A configuration specifies the components that you want in your system and the settings they will use. By default, Jig looks for a config/config.edn file, but you can override this by placing a config file in $HOME/.jig/config.edn (where $HOME is your home directory). If a configuration file can't be found, a default will be used.
A configuration is a map which usually contains a :jig/components key listing the
components in a map (each key in the map is the component's label). You can get a good idea of the format by looking at the config/default.edn file.
It's also possible to link to other configuration files, which are merged into a single config :
{
:jig/include ["/home/malcolm/src/octopus/config.clj" "/home/malcolm/src/juxtweb/config.clj"]
}While .edn files are preferred, you can use .clj if you want
to evaluate Clojure expressions, such as calculations.
Important: To avoid injection attacks, never use the .clj suffix
for configuration you don't entirely control, including user submitted
configuration.
A very useful trick is to use Clojure's #= reader macro in the
$HOME/.jig/config.clj (you can't use an .edn file for this
trick). A useful pattern is to load in the default configuration and
make tweaks to it for the environment you're running Jig in. This helps
to prevent a proliferation of diveraging configuration files, which is a
common problem with multiple environments in any configuration
system. Each configuration can inherit from the defaults and use a
Clojure program to derive a modified version. What better language than
Clojure to tweak a map?
Here's an example.
#=(eval
(->
;; Start with the original configuration, stored in the git repo
(clojure.core/read-string (slurp (str (System/getProperty "user.home") "/src/my-proj/config.clj")))
;; Add a 'private' component
(assoc-in [:jig/components :firefox-reloader]
{:jig/component 'jig.web.firefox-reload/Component
:jig/dependencies [:service :cljs-server]
:jig.web.firefox-reload/host "localhost"
:jig.web.firefox-reload/port 32000
})
;; Oh dear, some tricky path munging. We have to change lots of paths!
;; Let's walk the tree.
;; Due to symlinks not working well on Dropbox mounts,
;; replace all instances of relative paths with absolute ones
((partial clojure.walk/postwalk
(fn [x]
(if-let
[path (and (string? x)
(second (re-matches #"\.\./my-proj(.*)" x)))]
(str "/home/malcolm/another-path/src/my-proj" path)
x))))))You can write your own components by defining a type or record. At the
very least it needs to implement the jig.Lifecycle protocol.
(:ns org.example.core
(:import (jig Lifecycle)))
(deftype Component [config]
Lifecycle
(init [_ system] system)
(start [_ system] system)
(stop [_ system] system))
In Stuart's reloaded workflow, the init function is responsible
for creating the System. In Jig's component model, the system map is
threaded through each component's init function, giving it a
chance to add stuff. Likewise for the start and stop
functions. The minimum you need to do is return the original system, for
the next component in the chain.
Once you have declared your component, you need to reference it in the
config file config/config.edn. Jig needs to know which components
you want activated. If this file doesn't already exist, copy over the
contents from config/sample.config.edn. If you need to evaluate
Clojure expressions in your config, use a .clj suffix,
e.g. config/config.clj
For example...
{:jig/components
{:hello-app {:jig/component org.example.core/Component}}}
Components will be instantiated with a single argument: the component's
configuration value as specified in the config file. So if you want to
pass configuration to your component, an easy option is to add it to the
component's entry in the config/config.edn file.
If you want to see the state of the system at any time, it's available from the REPL
user> system
It's nicer if you have pretty printing enabled at the REPL.
M-x cust-var<RET>nrepl-use-pretty-printing
Alternatively, you can be explicit.
user> (pprint system)
Sometimes a component will rely on the existence of
another. Dependencies can be specified in the component configuration
under the :jig/dependencies key, where the value is a vector of
keys to other components in the configuration.
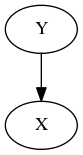
For example, let's suppose component Y is dependent on component X.
{:jig/components
{"X" {:jig/component org.example.core/X}
"Y" {:jig/component org.example.core/Y
:jig/dependencies ["X"]}}}
You can also view the component dependency graph from the REPL :-
user> (graph)
Jig comes with its own components, providing useful functionality and demonstrate how components are written. Each component is configurable. If you need a component which isn't in this list, I am happy to provide it.
Provides a Jetty service that can be used by Ring applications.
Amalgamates Compojure routes contributed by other components into a single handler.
Pulls the latest code from a remote git repository. This can be useful as part of an automatic continuous delivery mechanism.
Provides a reload capability, invokable as a JMX operation.
Clears out the stencil cache to ensure stale Mustache templates do not survive a system reset.
Purges an nginx reverse proxy to ensure cached pages do not survive a system reset.
Provides an nREPL server, useful if the system isn't started with
lein repl but an nREPL service is still desired.
A trigger to get Firefox to reload the current page upon every rest. Requires the Remote Control addon)is installed and enabled (the icon should be green).
Provides a Pedestal service on a Tomcat or Jetty listener, and ensures that the System is made available to each Pedestal handler. This unifies Stuart's approach with the Pedestal framework, allowing you to enjoy Stuart's rapid development workflow while writing Pedestal services.
One of the major benefits of Pedestal over Ring is the support for bi-directionality between routes and handlers. For me, this is a stand-out feature because of the importance of hyperlinks, both in web pages and RESTful web applications.
Asking the library to generate URLs for you, rather than hard-coding
them in your application, reduces the risk of broken links and
maintenance cost. Jig injects a useful function into the Pedestal
context, under the :url-for key, that lets you generate URLs
relative to request you are processing. By default, URLs are generated
to handler within the same application, but you can specify
:app-name to target other applications hosted in the same JVM.
Look at the use of url-for in the example below. See how easy it
is to generate URLs to target other Pedestal handlers. Nice.
(defhandler my-index-page [request]
{:status 200
:headers {"Content-Type" "text/plain"}
:body "Hello World!})
(defbefore my-root-page [{:keys [url-for] :as context}]
(assoc context :response
(ring.util.response/redirect
;; Look, no nasty hard-coded URLs!
(url-for ::my-index-page))))
Provides a web application abstraction on top of
jig.web.server/Component. Other components can add Pedestal routes
to a web application component. These are then combined to form a
complete Pedestal route table.
Applications can share the same jig.web.server/Component, allowing
for 'virtual hosts'. Applications can specify a different host, scheme
or be rooted at a sub-context. This are really useful for hosting
different Clojure-powered websites on the same JVM.
These examples assume a little knowledge about Pedestal, see http://pedestal.io/documentation/service-routing/ for more details.
Jig is self-hosting, so you can reload the code internal to Jig as per Stuart's usual reload procedure.
However, it's more likely that you'll want to use Jig to develop one of
your own projects. You can do this by specifying a :jig/project
entry which declares that the component lives in another project.
:juxtweb/service {:jig/component pro.juxt.website.core/Component
:jig/dependencies [:juxtweb/web]
:jig.web/app-name :juxtweb/web
:jig/project "../juxtweb/project.clj"
}
One advantage with using external projects is that you can change the project.clj file(s) of your project(s) without requiring a JVM restart.
A further advantage is that you don't have to modify Jig's
project.clj file to include dependencies you need in the projects
it references, you only need to edit the main config file itself (which
is filtered by .gitignore so that it doesn't get checked in).
An external project's classes are loaded in a separate classloader, one per project.
However, this classloader will only load classes that are not on Jig's classpath. It will not load a different version of Clojure, nor does it provide any isolation between components and isn't intended for multi-tenanting of applications. Jig is not an application server, it merely provides this feature to allow the separation of the development of components into different Leiningen projects. You should consider the amalgamation of components in Jig as a single composite Clojure application.
The Clojure runtime does not distinguish between namespaces that are loaded from different classloaders, and all namespaces will appear as usual in calls to ns-map, etc.. There is only one Clojure runtime in any given Jig instance.
Unless a project's classloader is explicity pinned, a fresh classloader will be created if the project's project.clj file is modified, and then all the classes will be reloaded. See below for more details about pinning classloaders.
I don't see any reason why others couldn't create their own 'jigs' (a jig is a separate Leiningen project after all). Although this project is named eponymously, there can be others customized for specialist contexts (either new projects, or forks of this one).
If that happens and there's a need to share components between jigs (for
reasons of component portability) then it will make sense to promote the
Lifecycle protocol (and maybe others) to a common library that
different jigs can use.
Jig's support for external projects is very useful. However, there are some caveats to be aware of due to the introduction of multiple classloaders. Most if not all of these caveats will be ironed out over time.
The :jig/project mechanism loads external project namespaces in a
separate classloader. When component lifecycle functions are called,
this classloader is set as the thread's context classloader, so calls to
io/resource and others will work as expected. However, any code
that executes outside of component lifecycle functions may not be able
to reference resources.
Normally, you shouldn't ever notice any difference between an application running standalone and one run within the Jig harness, but it's important to note the possibility and report any problems.
Built-in plugins are specially coded to determine the correct classloader to set on the thread before calling into your code. For example, the web component wraps request threads in middleware which sets the project classloader on the thread.
If an external project depends on a third-party jar which isn't on Jig's
own classpath, then it will not have been visible to Clojure when
clojure.core is first loaded. This means that any data readers declared
in /data_readers.clj will not work. If you use the
edn/read-string in these projects you cannot assume the
*data-readers* dynamic var will contain the data readers declared
in the third-party jar. The workaround is to use the 2-arg form of
edn/read edn/read-string and supply the readers explicitly in the option
map.
For example, when loading Datomic data from a file, you would use the following form :
(edn/read-string
{:readers {'db/id datomic.db/id-literal
'db/fn datomic.function/construct
'base64 datomic.codec/base-64-literal}}
"my-data.edn)
Some components will not be able to shutdown cleanly and the classloader may persist. Examples are components that spawn threads, create agents, bind thread-local vars, and so on.
Datomic is a specific example due to the way it caches
connections. Disable the project reloading by adding a
:jig/projects section in the config and setting the
:jig/classloader-pinned? to true. This will pin the
project's classloader to the project so that the project will not get a
new classloader upon restart (projects are usually restarted if their
project.clj file changes, or if the Jig configuration changes).
{
:jig/projects
[{
:jig/project "../juxtweb/project.clj"
:jig/classloader-pinned? false
}
{
:jig/project "../accounting/project.clj"
:jig/classloader-pinned? true
;; eg. extra classpath, source dirs, etc. here
}
]
}
It is expected that Clojure 1.6 will fix this issue (CLJ-1125). Until then, if you have problems with components such as class linkage errors, protocol dispatch failures, .isInstance checks, then it recommended you disable Jig's project reloading capability. You will still be able to reload the code in external projects as before, but will lose the ability to make changes to a project, such as the project's library dependencies, without having to restart the JVM.
More information can be found in these resources:
- http://immutant.org/news/2012/05/18/runtime-isolation/
- http://wiki.apache.org/tomcat/MemoryLeakProtection
If an external project has a /user.clj file in one of its source
directories, then it will be loaded on a reset and override Jig's user
namespace. Jig will then stop working. The current workaround is to
ensure such a file isn't visible to Jig, either by renaming it or by
removing the source directory containing it in the project's
project.clj file. It is hoped that future versions of Jig will
avoid this issue by disabling the loading of such files by tools.namespace.
Certain evaluations (e.g. nrepl-jump in nrepl.el) from nREPL clients
load resources to determine the code defining symbols. When they use the
usual form of clojure.java.io/resource, the default (Jig)
classloader is used. Unsurprisingly, symbols declared in external
projects are defined in namespaces that are not reachable from Jig's own
classloader, but via the project classloaders it creates each external
project.
The solution to this issue has 3 parts. Firstly, a proxy classloader is
created that delegates to each of the project classloaders, providing a
union across the set of resources in the system. The classloader is
parented by the default Jig classloader, so all Jig symbols are part of
this union. (This part is already implemented on the master branch in
system.clj, commit 99c27).
Secondly, Jig inserts some custom nREPL middleware that sets the proxy
classloader into the :context-classloader slot in the nREPL
message. This is already implemented.
Finally, the nREPL interruptible-eval middleware which evaluates the code sent
by nREPL clients is modified to check for the existence of a value in
this :context-classloader slot and set it as the context
classloader on the evaluating thread. This has been implemented in a
custom version of tools.nrepl available at
[malcolmsparks/tools.nrepl "0.2.3"]. In order to use this you need
apply the following patch to Leiningen 2.3.3 and rebuild it (or apply a
similar fix to later versions of Leiningen). In the meantime, I am
raising a pull request on tools.nrepl to get this work into the master
branch so future versions of Leiningen will work without modification.
diff --git a/leiningen-core/src/leiningen/core/project.clj b/leiningen-core/src
index 7bbca62..ac814f3 100755
--- a/leiningen-core/src/leiningen/core/project.clj
+++ b/leiningen-core/src/leiningen/core/project.clj
@@ -366,7 +366,7 @@
{:displace true})
:test-selectors {:default (with-meta '(constantly true)
{:displace true})}
- :dependencies '[[org.clojure/tools.nrepl "0.2.3"
+ :dependencies '[[malcolmsparks/tools.nrepl "0.2.3"
:exclusions [org.clojure/clojure]]
[clojure-complete "0.2.3"
:exclusions [org.clojure/clojure]]]
Clojure already does code reloading! Why do I need all this stuff?
Clojure, being a LISP, allows you to reload functions at will. But Stuart's pattern (which Jig builds on) extends this to state, compile-time macros, protocols/types/records and multi-methods. Experienced Clojure developers know when to reload some namespaces and when to restart the JVM. It seems better to raise the abstraction so you don't have to think about these technicalities all the time, just 'reset' each time you want consistency while you develop.
See this comment for a better explanation: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=5819912
Jig is trying to provide you with a better development experience, while nudging you towards a modular architecture that will help you when your system grows to a certain size.
Where can I find an example of a real project using Jig?
JUXT Accounting is a full application that is developed with Jig. Find more details here: https://github.com/juxt/juxt-accounting
JUXT's website also uses Jig, for both development and deployment. https://github.com/juxt/juxtweb
What's the relationship between Jig and Up?
Up is deprecated, Jig replaces it (and has stolen all the worthy bits).
The main difference between Up and Jig is that Up added config to the Leiningen project and the dependency relation between projects and infrastructure has been reversed. In due course Jig will add a protocol that components can extend to communicate with other components over a System bus (core.async channel), and will then provide a superset of Up's functionality. Jig is better.
Don't forget the system is available in the REPL, as user/system. That's useful for testing what functions are returning.
You can check what's in the system by outputting it to the
console. (keys user/system) is often useful if the system gets
very large and you need to navigate it.
By default, Jig configures logback and logs are written to
$HOME/.jig/logs. Events such as component init, startup and
shutdown, and exceptions that occur during these phases, are written to
here. When the REPL tells you to check the log files, this is where you
should look.
You should return the system value, modified if necessary, from each component function. If you don't return any value, Jig will detect this and throw an error.
Make sure that you do modify the system, but then return using the symbol representing the unmodified system. That's a common mistake. Jig won't detect that you have returned the same system it gave you, because that's normal behaviour.
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: No implementation of method: :init of protocol: #'jig/Lifecycle found for class
Ensure you require jig before importing the jig/Lifecycle protocol.
By default, a console is provided at http://localhost:8001. This will be
improved to allow you to browse auto-generated
Marginalia and
codox documentation, view your
embedded TODOs and FIXMEs, enable tracing on vars and run
tests from the browser, as well as incorporating webhooks for triggering
a reload remotely.
Many people have asked for a demonstration of how to configure a simple
Ring application. This is provided as a Sudoku example in the
examples/ directory. It is incorporated in the default
configuration and the website is accessible at http://localhost:8091/sudoku.html
Copyright © 2013 JUXT. All rights reserved.
The use and distribution terms for this software are covered by the Eclipse Public License 1.0 which can be found in the file epl-v10.html at the root of this distribution. By using this software in any fashion, you are agreeing to be bound by the terms of this license. You must not remove this notice, or any other, from this software.