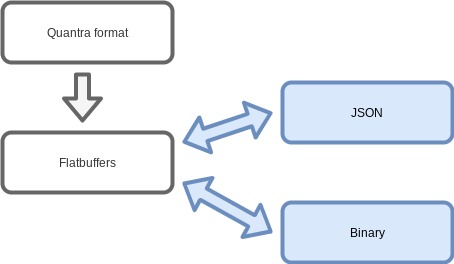
Quantra is a pricing engine based on QuantLib. It allows distributed compuations and serializing quantra objects to JSON and Flatbuffers binary format.
QuantLib is a quantitative finance library implemented in C++ and a standard in the industry. Although it provides a complete set of tools for quantitative finance it can also be seen as a "low level" library that brings some drawbacks in terms of usability such as:
- Written in C++
- Not easy to be executed in multithreading fashion to parallelize computations because of its design (see this)
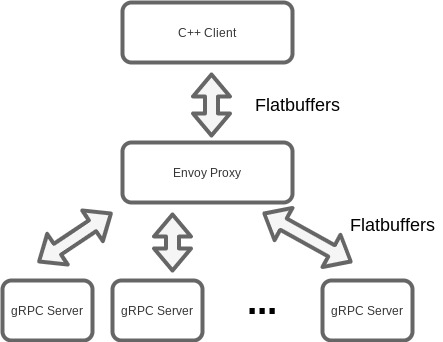
Quantra tries to solve these problems with the implementation of a high level API and allowing multiple process to be executed in parallel. The latter is done running different instances of QuantLib in separate processes that are executed as gRPC servers and communicate with the clients with Flatbuffers.
Quantra allows to execute different processes serving gRPC requests sent by the clients and serialized with Flatbuffers format.
These requests are being processed by an Envoy proxy that forwards them to each of the processes running in the background.
The main format of quantra is Flatbuffers which is used to communicate with the server. As the serialization to Flatbuffers can be tedious part of the client implementation translates from quantra defined C++ structs to Flatbuffers.
https://github.com/joseprupi/quantragrpc/blob/master/examples/data/fixed_rate_bond_request_quantra.h contains a complete example on how to build a request to price a fixed rate bond using the client structs.
Once the data has been serialized it can be stored in binary or JSON format, this is part of Flatbuffers core functionalities.
See https://github.com/joseprupi/quantragrpc/tree/master/examples/data folder that contains examples with the different supported formats, the snippets below show how to create a deposit pillar for a curve in C++ and JSON formats.
auto deposit_zc3m = std::make_shared<structs::DepositHelper>();
deposit_zc3m->rate = 0.0096;
deposit_zc3m->tenor_time_unit = TimeUnit_Months;
deposit_zc3m->tenor_number = 3;
deposit_zc3m->fixing_days = 3;
deposit_zc3m->calendar = Calendar_TARGET;
deposit_zc3m->business_day_convention = BusinessDayConvention_ModifiedFollowing;
deposit_zc3m->day_counter = DayCounter_Actual365Fixed;
auto deposit_zc3m_point = std::make_shared<structs::Point>();
deposit_zc3m_point->point_type = Deposit;
deposit_zc3m_point->deposit_helper = deposit_zc3m;{
"point_wrapper_type": "DepositHelper",
"point_wrapper": {
"rate": 0.0096,
"tenor_time_unit": "Months",
"tenor_number": 3,
"fixing_days": 3,
"calendar": "TARGET",
"business_day_convention": "ModifiedFollowing",
"day_counter": "Actual365Fixed"
}
}The example below first loads a request to price a fixed rate bond from Quantra structs and creates a vector with 1000 of these requests that will be sent to the server.
With this example the client will send 1000 times the same request, meaning the same curve will be bootstrapped 1000 times. This is not realistic as you would probably want to create as many requests as curves to be boostrapped, each of the backend processes will boostrap each of the curves of the request once and it will be reused for each of the bonds that use the same curve.
There is a lot of work to do with the client logic and also provide more (any :) ) documentation to clarify this.
#include <vector>
#include "quantra_client.h"
#include "data/fixed_rate_bond_request_quantra.h"
int main()
{
int n = 1000;
QuantraClient client("localhost:50051");
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<structs::PriceFixedRateBondRequest>> requests;
auto bond_pricing_request = request_bond();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
requests.push_back(bond_pricing_request);
client.PriceFixedRateBondRequest(requests);
return 0;
}These tests have been run executing all processes (client, proxy and background gRPC services) using a single machine with AMD Ryzen 9 3900X 12-Core CPU.
The test measures the time it takes to price n bonds. The code for the test can be found here https://github.com/joseprupi/quantragrpc/blob/master/tests/test.cpp.
The test accepts three parameters:
- Number of bonds per request
- Number of requests
- A flag that is 0 or 1 if just one curve should be bootstrapped and reused to price all the bonds. This is for both Quantra and Quantlib, Quantra will boostrap one curve per process.
It will repeatedly boostrap the same curve an price the same bond with it using both Quantra and QuantLib, this is just for testing purposes. Quantlib will price the total number of bonds (number of bonds per request x number of requests)
| Number of requests (parallel processes in Quantra) | Number of bonds per request (for Quantra) | Total bonds | Quantra time in ms | Quantlib time in ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 1 |
| 1 | 10 | 10 | 21 | 10 |
| 1 | 100 | 100 | 106 | 62 |
| 1 | 1000 | 1000 | 941 | 556 |
| 1 | 10000 | 10000 | 9739 | 5832 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 1 |
| 2 | 10 | 20 | 24 | 16 |
| 2 | 100 | 200 | 109 | 115 |
| 2 | 1000 | 2000 | 993 | 1147 |
| 2 | 10000 | 20000 | 9749 | 11627 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 3 |
| 5 | 10 | 50 | 26 | 36 |
| 5 | 100 | 500 | 137 | 294 |
| 5 | 1000 | 5000 | 1017 | 2759 |
| 5 | 10000 | 50000 | 10167 | 29240 |
| 10 | 1 | 10 | 12 | 8 |
| 10 | 10 | 100 | 27 | 63 |
| 10 | 100 | 1000 | 130 | 554 |
| 10 | 1000 | 10000 | 1057 | 5578 |
| 10 | 10000 | 100000 | 10544 | 56324 |
| Number of requests (parallel processes in Quantra) | Number of bonds per request (for Quantra) | Total bonds | Quantra time in ms | Quantlib time in ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1 | 10 | 12 | 1 |
| 10 | 10 | 100 | 16 | 3 |
| 10 | 100 | 1000 | 37 | 21 |
| 10 | 1000 | 10000 | 213 | 176 |
| 10 | 10000 | 100000 | 1618 | 1675 |
Although the performance is not impressive is not bad when things start to take some time. To parallelize computations it would probably make more sense for more costly operations such as more complex derivatives and for some risk tasks such as simulations and a shared cache storing the scenarios.
I think it still shows it is possible to have a pricing engine for other systems based on a trusted and open source library like QuantLib with decent performance.
This has just been tested with:
- Debian
- gcc 8.3
- QuantLib 1.21
- gRPC 1.35.0
- Flatbuffers 1.11.0
- gRPC and Flatbuffers. Follow the instructions from Flatbuffers at https://github.com/google/flatbuffers/tree/master/grpc.
- Build gRPC with -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON for shared libraries.
- When writing this Flatbuffers does not support gRPC. It used to but at some point gRPC broke its compatibility, hopefully it will be solved soon. Apply this manually to solve it google/flatbuffers#6338
- QuantLib. See https://www.quantlib.org/install.shtml
- C++ build tools and CMake
After cloning the repository set the variables inside config_vars.sh.
git clone https://github.com/joseprupi/quantragrpc
cd quantragrpc
. ./scripts/config_vars.sh
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make -jOnce installed execute start.sh providing the number of processes you want for the backend. Execute below in separate terminals to price 1000 bonds using 10 different processes.
./scripts/start.sh 10./build/examples/bond_request 1000Flatbuffers is the format used by Quantra to communicate with the server and using it provides some extra advantages as the project supports translating to and from JSON and binary formats.
Flabuffers provides and API and also commmand line tools to do so. This should probably be added to the Quantra client libraries but for now take a look to Flatbuffers documentation and the example at https://github.com/joseprupi/quantragrpc/blob/master/examples/bond_request_to_json.cpp to generate a json file from a request to price a bond.